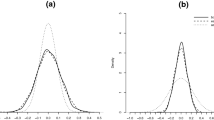
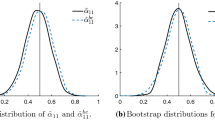
Summary
In recent years, the bootstrap method has been extended to time series analysis where the observations are serially correlated. Contributions have focused on the autoregressive model producing alternative resampling procedures. In contrast, apart from some empirical applications, very little attention has been paid to the possibility of extending the use of the bootstrap method to pure moving average (MA) or mixed ARMA models. In this paper, we present a new bootstrap procedure which can be applied to assess the distributional properties of the moving average parameters estimates obtained by a least square approach. We discuss the methodology and the limits of its usage. Finally, the performance of the bootstrap approach is compared with that of the competing alternative given by the Monte Carlo simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burg J. (1975), Maximal entropy spectral analysis,Ph.D. dissert., Stanford University, Dept. of Geophysics.
Chatterjee S. (1986), Bootstrapping ARMA models: some simulations,IEEE Transactions on System, Man & Cybernetics, 16, 294–299.
Corduas, M. (1990), Approcci alternativi per il ricampionamento nei modelli Autoregressivi,Atti della XXXV Riunione Scientifica SIS, Padova, 2, 61–68.
Durbin J. (1960), The fitting of time series models,Rev. Int. Stat. Inst., 28, 233–244.
Efron B. (1979), Bootstrap methods: another look at jackknife.Annals of Statistics, 7, 1–26.
Efron B. (1982), The jackknife, the bootstrap and other resampling plans,SIAMCBMS Monograph 38, Philadelphia.
Efron B., Tibshirani R. (1986), Bootstrap methods for standard error confidence intervals and other measures of statistical accuracy.Statistical Science, 1, 54–77.
Freedman D. (1984). On bootstrapping two-stage least squares estimates in stationary linear models,Annals of Statistics, 12, 827–842.
Hannan E. J., Rissanen J. (1982), Recursive estimation of mixed autoregressive moving average order,Biometrika, 69, 81–94.
Hannan E. J., Kavalieris L. (1984), A method for autoregressive moving-average estimation.Biometrika, 72, 273–280.
Koreisha S., Pukkila T. (1990), A generalized least-squares approach for estimation of autoregressive moving-average models,Journal of Time Series Analysis, 2, 139–151.
Künsch H. R. (1989), The jackknife and the bootstrap for general stationary observations,Annals of Statistics, 17, 1217–1241.
Liu R. Y., Singh K. (1988), Moving blocks jackknife and bootstrap capture weak dependence,Technical Report, Dept. of Statistics, Rutgers University.
Tjostheim D., Paulsen J. (1983), Bias of some commonly used time series estimates,Biometrika, 48, 197–199.
White H. (1984),Asymptotic theory for econometricians, Academic Press, Orlando (CA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research partially supported by CNR and MURST.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corduas, M. Bootstrapping moving average models. J. It. Statist. Soc. 1, 227–234 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02589032
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02589032