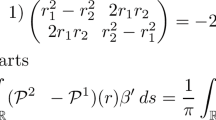Abstract
The development of the Stokes layer in a liquid subjected to a constant shear force at the liquid surface with mass erosion is studied in this paper. It is shown that the velocity in the Stokes layer is weakened by surface receding and the relative decrease of the maximal liquid velocity due to surface recession is a unique function of the time normalized by the recession/diffusion balance time scale, defined as the ratio between the kinematic viscosity and the square of the receding velocity. At a time much larger than the diffusion/recession balance time scale, the role of the surface receding is rather important: instead of being pushed into the liquid at the receding velocity, the development of the Stokes layer is effectively prohibited by surface receding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanury MA. Introduction to Combustion Phenomena. New York: Gordon & Breach Sci Publ, 1977
Lin SP, Reitz RD. Drop and spray formation from a liquid jet.Annu Rev Fluid Mech, 1998, 30: 85–105
Reitz RD, Bracco FV. Mechanism of atomization of a liquid jet.Phys Fluids, 1982, 25: 1730–1742
Schlichtling H. Boundary-layer theory. Chapter 14, New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1979
Bennett CO, Myers JE. Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer, Chapter 32 and Chatper 36. New York: International Student Edition, 1982
Clark CJ, Dombrowski N. Aerodynamic instability and disintegration of inviscid liquid sheets.Proc Roy Soc Lond, 1972, A329: 467–478
Taylor GI. Generation of ripples by wind blowing over a viscous fluid. In: The Scientific Papers of G I Taylor, Vol 3, Cambridge University Press, 1963. 244–254
Wu ZN. Most unstable waves of a stagnant planar liquid film blown by a high speed viscous gas with a Blasius velocity profile.Acta Mechanica, 2001, 149(1): 69–83
Dumouchel C, Ledoux M. Atomization of flat and annular liquid sheets: practical use of linear theories. ICLASS-91, MD, USA, paper 12, 1991. 157-164
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10025210) and the China NKBRSF project (2001CB409600)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziniu, W. Velocity in a liquid subjected to a shear force at the liquid surface with a receding velocity. Acta Mech Sinica 19, 213–219 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02484482
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02484482