Abstract
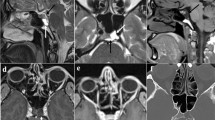
Hearing loss and otitis media are commonly associated with Down syndrome. Hypoplasia of the mastoids is seen in many affected children and sclerosis of mastoid bones is not uncommon in Down syndrome. Awareness and early recognition of mastoid abnormality may lead to appropriate and timely therapy, thereby preserving the child’s hearing or compensating for hearing loss; factors which are important for learning and maximum development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balkany TJ, Mischke RE, Downs MP, Jafek BW (1979) Ossicular abnormalities in Down’s syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 87: 372
Schwartz DM, Schwartz RH (1978) Acoustic impedance and otoscopic findings in young children with Down’s syndrome. Arch Otolaryngol 104: 652
Fitz CR, Harwood-Nash DCF (1974) Radiology of the ear in children. Radiol Clin North Am 12: 553
Resnick D, Niwayama G (1981) Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. Saunders, Philadelphia, Pa.
Miller JDR, Capusten BM Lampard R (1986) Changes at the base of skull and cervical spine in Down syndrome. J Can Assoc Radiol 37: 85
Harada T, Sando I (1981) Temporal bone histopathologic findings in Down’s syndrome. Arch Otolaryngol 107: 96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glass, R.B.J., Yousefzadeh, D.K. & Roizen, N.J. Mastoid abnormalities in down syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 19, 311–312 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02467300
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02467300