Abstract
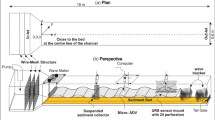
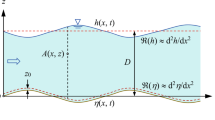
In the flow on a mobile bed in an open channel, sand ripple often appears after the sediment begins to move. Different scholars have different views on the formation of sand ripples. This paper holds that as the ripple in general is very small, its formation is due to the instability of the laminar flow or the evolution of the small-scale coherent structures in the sublayer adjacent to the wall of the open channel. When the shear stresses caused by the disturbing waves or the coherent structure near the bed surface boundary and the water flow itself are greater than the shields stresses, responses on the bed surface appear and the sand ripple forms. If the frequency of the shear stress caused by the disturbance is close to the natural frequency of the sand grains that produced resonance, such a phenomenon is called the “detection property” of the sediment. It is at this point that the maximum resonance appears and the sand ripple develops rapidly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
QIAN Ning, WAN Zhao-hui.Sediment Motion Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985. (in Chinese).
Yalin M S.Mechanics of Sediment Transport[M]. Oxford, Great Britain: Pergamon Press, 1972.
Klebanove P S, Tidstrom K D, Sargent L M. Three dimensional nature of boundary layer instability[J].J Fluid Mech, 1962,12(1):1–34.
Saric W S, Kozlov V V, Levchenko V Y. Forced and unforced subharmonic resonance in boundary layer transition[A]. In:AIAA 22nd Aerospace Science Meeting[C]. New York, 1984, 9–12.
ZHENG Zhao-zhen, WANG Shang-yi. Calculation of sand ripple formation[J].Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1985, (1):39–43. (in Chinese)
BAI Yu-chuan. Research onC-type instability of the laminar flow boundary layer[J].Journal of Aerodynamics, 1985,13(1):92–98. (in Chinese)
ZHOU Heng, YOU Xue-yi. On problems in the weakly nonlinear theory of hydrodynamic stability and its improvement[J].Acta Mechanica Sinica, 1993,25(5):517–528. (in Chinese)
ZHOU Heng, Fujimura K. Improvement of weakly nonlinear theory of hydrodynamic stability[J].Sciences in China A, 1998,41(1):84–92.
BAI Yu-chuan, JIANG Chang-bo, ZENG Qian. Numerical model and dynamic visualization on the large-scale eddy structure in oscillatory bottom layer over sand ripple[A]. In: LI Jia-chun Ed.The 6th National Conference of Fluid Mechanics—Nature, Industry and Flow[C]. Beijing: Meteorological Press, 2001, 341–346. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by ZHOU Heng
Foundation item: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (59809006; 59890200); the science Foundations of Tianjin Municipality (983702011) and the state key Laboratory of Estuarine & Coastal Research (98001)
Biography: BAI Yu-chuan (1967-)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu-chuan, B., Ji-shen, L. The loss of stability of laminar flow in open channel and the mechanism of sand ripple formation. Appl Math Mech 23, 276–293 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438335
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438335