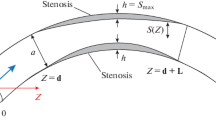
Abstract
A numerical analysis of Newtonian and non-Newtonian flow in an axi-symmetric tube with a local constriction simulating a stenosed artery under steady and pulsatile flow conditions was carried out. Based on these results, the concentration fields of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and Albumin were discussed. According to the results, in great details the macromolecule transport influences of wall shear stress, non-Newtonian fluid character and the scale of the molecule etc are given. The results of Newtonian fluid flow and non-Newtonian fluid flow, steady flow and pulsatile flow are compared. These investigations can provide much valuable information about the correlation between the flow properties, the macromolecule transport and the development of atherosclerosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ojha M, Cobbold R S C, Johnston K W, et al. Detailed visualization of pulsatile flow fields produced by modeled arterial stenoses[J].J Biomedical Engr, 1990,12(4):463–469.
Tutty O R. Pulsatile flow in a constricted channel[J].J Biomech Engr, 1992,114(1):50–54.
Cavalcanti Silvio. Hemodynamics of an artery with mild stenoses[J].J Biomechanics, 199528 (4):387–399.
He X Y, Ku D N. Pulsatile flow in the human left coronary artery bifurcation: average conditions [J].J Biomech Engr, 1996,118(1):74–82.
Perktold K, Resch M. Numerical flow studies in human carotid artery bifurcations: basic discussion of the geometric factor in atherogenesis[J].J Biomedical Engr, 1990,112(2):111–123.
Dutta A, Tarbell J M. Influnce of non-Newtonian behavior of blood on flow in an elastic artery model[J].J Biomech Engr, 1996,118(1):111–119.
Nakamura Masahide, Sawada Tadashi. Numerical study on the flow of a non-Newtonian fluid through an axisymmetric stenosis[J].J Biomedical Engr, 1988,110(2):137–143.
CHENG Tu, Deville Michel. Pulsatile flow of non-Newtonian fluid through arterial stenoses[J].J Biomechanics, 1996,29(7):899–908.
Back L H, Liem T K, Kwack E Y, et al. Flow measurements in a highly curved atherosclerotic coronary artery cast of man[J].J Biomech Engr, 1992,114(2):232–240.
Rappitisch G, Perktold K. Pulsatile Albumin transport in large arteries: a numerical simulation study[J].J Biomech Engr, 1996,118(4):511–519.
Karino T, Deng X Y, Naiki T. Flow-dependent concentration polarization of lipoproteins at the blood-endothelium boundary BED-V29[A]. In: R M Hochmuth, N A Langrana, M S Hefzy Eds.1995 Bioengineering Conference, ASME[C]. New York: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1995.
Fry D L. Certain histological and chemical responses of the vascular interface of acutely induced mechanical stress in the aorta of the dog[J].Circ Res, 1969,24(1):93–109.
Rappitsch G, Pektold K. Computer simulation of convective diffusion processes in large arteries [J].J Biomechanics, 1996,29(2):207–215.
Langeler E G, Ineke Snelting-Havinga, Victor W M, et al. Passage of law density lipoproteins through monolayers of human arterial endothelial cells-effects of vasoactive substance in an in vitro [J].Arteriosclerosis, 1989,9(4):550–559.
ANSYS/Theory Reference 5.3[CP]. ANSYS Inc, 1996.
SHEN Chong-tang, LIU He-nian.Non-Newtonian Fluid and Application[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1989, 7–23. (in Chinese).
FENG Yuan-zhen.Biomechanics[M]. Chapter 11. Beijing: Science Press, 1983, 275–303. (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Wu Wang-yi
Foundation item: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (19732003)
Biography: Li Xin-yu (1971-), Master
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin-yu, L., Gong-bi, W. & Ding, L. Computer simulation of non-Newtonian flow and mass transport through coronary arterial stenosis. Appl Math Mech 22, 409–424 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438307
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438307