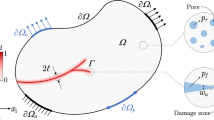
Abstract
Based on the Hamiltonian governing equations of plane elasticity for sectorial domain, the variable separation and eigenfunction expansion techniques were employed to develop a novel analytical finite element for the fictitious crack model in fracture mechanics of concrete. The new analytical element can be implemented into FEM program systems to solve fictitious crack propagation problems for concrete cracked plates with arbitrary shapes and loads. Numerical results indicate that the method is more efficient and accurate than ordinary finite element method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hillerborg A, Modeer M, Petersson P E. Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements[J].Cement and Concrete Research, 1976,6 (6): 773–782.
Bazant Z P, Oh B H. Crack band theory for fracture of concrete[J].RILEM, Materials and Structures, 1983,16(93): 155–177.
Jenq Y S, Shah S P. Two parameters fracture model for concrete[J].Journal of Engineering Mechanics, ASCE, 1985,111(10): 1227–1241.
Karihaloo B L, Nallathambi P. Effective cracks model for the determination of fracture toughness (K Ic s) of concrete[J].Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1990,35(4/5): 637–645.
XU Shi-lang, ZHAO Guo-fan. Double-K fracture criterion for crack propagation of concrete structures[J].China Civil Engineering Journal, 1992,25(2): 32–38. (in Chinese)
XU Shi-lang, Reinhardt H W. Determination of double-K criterion for crack propagation in quasibrittle fracture—Part III: Compact tension specimens and wedge splitting specimens[J].International Journal of Fracture, 1999,98(2): 179–193.
ZHONG Wan-xie.A New Syetmatic Methodology for Theory of Elasticity[M]. Dailian: Dalian University of Technology Press, 1995. (in Chinese)
ZHONG Wan-xie. Plane elasticity in sectorial domain and the Hamiltonian system[J].Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 1994,15(12): 1113–1123.
ZHONG Wan-xie, ZHANG Hong-wu. Analytical formulas on plane crack element[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 1995,17(3): 1–6. (in Chinese)
XU Shi-liang, ZHAO Guo-fan.Research on the Fracture Mechanics of Concrete[M]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology Press, 1991. (in Chinese)
YUAN Jian-wei. Analysis of fracture of concrete by means of nonlinear finite element and fictitious crack model[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 1988, 85–164. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by ZHONG Wan-xie
Foundation items: the Doctorial Foundation of Education Ministry of China (20010141024); the National Natural Science Foundtion of China (10372019)
Biographies: WANG Cheng-qiang (1975 ∼); ZHENG Chang-liang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng-qiang, W., Chang-liang, Z. Semi-analytical finite element method for fictitious crack model in fracture mechanics of concrete. Appl Math Mech 25, 1265–1270 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438282
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438282