Abstract
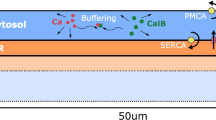
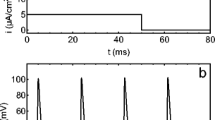
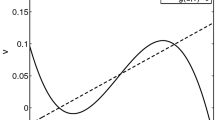
In certain extracellular environments, there would appear a kind of solitary pulse calcium waves in Rana pipiens sympathetic neurons, propagating inwards along the radial direction from the plasma membrane. To gain a deeper insight into the waves, a model describing intracellular calcium waves in frog sympathetic neurons was established. In the piecewise linear approximation, the present model is identical to the Sneyd model. Thus, with Sneyd’s method, analytical expressions for the wave speed and profiles of 1-D solitary pulse wave were obtained. A wave speed of 21.5 μm/s was deduced, which agrees rather well with experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDonough S I, Cseresnyes Zoltan, Schneider M F. Origin site of calcium release and calcium oscillation in Frog sympathetic neurons[J].J Neurosci, 2000,20(11):9059–9070.
Shi Xiaomin. Intracellular spiral and target calcium waves in Xenopus laevis oocyte[J].Journal of Shanghai University, 2003,9(4):365–368. (in Chinese)
Keener J, Snedy J.Mathematical Physiology[M]. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1998,332–353.
Friel D D. [Ca2+] i oscillations in sympathetic neurons: an experimental test of a theoretical model [J].Biophys J, 1995,68(5):1752–1766.
Sneyd J, Girard S, Clapham D. Calcium wave propagation by calcium-induced calcium release: an unusual excitable system[J].Bull Math Biol, 1993,55(2):315–344.
Goldbeter A, Dupont G, Berridge M J. Minimal model for signal-induced calcium oscillations and for their frequency encoding through protein phosphorylation[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1990,87(5):1461–1465.
Chopra O C, Sleeman B D, Brindley J,et al. Velocity and stability of solitary planar traveling wave solutions of intracellular[Ca2+][J].Bull Math Biol, 1999,61(1):273–301.
Shi Xiaomin. The generation, evolution and physiological response of intracellular calcium oscillations and waves[D]. Ph D dissertation. Shanghai University, Shanghai, 2003. (in Chinese)
Murray J D.Mathematical Biology[M]. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 1993,704–705.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contributed by DAI Shi-qiang
Biography: SHI Xiao-min, Doctor, E-mail: xminshi@sohu.com
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Xm., Dai, Sq. Intracellular solitary pulse calcium waves in frog sympathetic neurons. Appl Math Mech 26, 150–159 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438236
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438236