Abstract
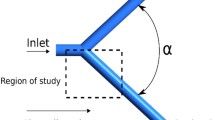
A numerical analysis of the steady and pulsatile, macromolecular (such as low density lipopotein (LDL), Albumin) transport in T-bifurcation was proposed. The influence of Reynolds number and mass flow ratio etc. parameters on the velocity field and mass transport were calculated. The computational results predict that the blood flow factors affect the macromolecular distribution and the transport across the wall, it shows that hemodynamic play an important role in the process of atherosclerosis. The LDL and Albumin concentration on the wall varies most greatly in flow bifurcation area where the wall shear stress varies greatly at the branching vessel and the atherosclerosis often appears there.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Back L H, Liem T K, Kwack E Y,et al. Flow measurements in a highly curved atherosclerotic coronary artery cast on man[J].J Biomechanical Engineering, 1992,114(2):232–240.
Perktold K, Resch M. Numerical flow studies in human carotid artery bifurcations: basic discussion of the geometric factor in atherogenesis[J].J Biomedical Eng, 1990,12(1):111–123.
Fry D L. Certain histological and chemical responses of the vascular interface of acutely induced mechanical stress in the aorta of the dog[J].Circulation Research, 1969,24(1):93–109.
Fry D L, Vaishnav R N. Mass transport in the arterial wall basic hemodynamics and its role[A]. In: Patel D J, Vaishnav R N Eds.Disease Processes[C], University Park Press, 1980, 77–95.
Liepsch D, Moravec S, Rastogi A K,et al. Measurement and calaulations of laminar flow in a ninety degree bifurcation[J].J Biomechanics, 1982,15(7):473–485.
Perktold K, Resch M, Reinfried O P. Three-dimensional numerical analysis of pulsatile flow and wall shear stress in the carotid artery bifurcation[J].J Biomechanics, 1991,24(6):409–420.
Kawaguti M, Hamano A. Numerical study of bifurcating flow of a viscous fluid[J].J Phys Soc (Japan), 1979,46(4):1360–1365.
Kawaguti M, Hamano A. Numerical study of bifurcating flow of a viscous fluid-II: Pulsatile flow [J].J Phys Soc (Japan), 1980,49(2):817–824.
O'Brien V, Ehrlich L W. Simulation of unsteady flow at renal branches[J].J Biomechanics, 1977,10(10):623–631.
Lutz R J, Hsu L, Menawat A. Comparision of steady and pulsatile flow in a double branching arterial model[J].J Biomechanics, 1983,16(9):753–766.
Fernandez R C, DeWitt K J, Botwin M R. Pulsatile flow through a bifurcation with applications to arterial disease[J].J Biomechanics, 1976,9(9):575–580.
Khodadadi J M, Vlachos N S, Liepsch D. LDL measurements and numerical prediction of pulsatile laminar flow in a plane 90-degree bifurcation[j].J Biomechanical Engineering, 1988,110(2):129–136.
Rappitisch G, Perktold K. Pulsatile albumin transport in large arteries: A numerical simulation study[J].J Biomechanicl Engeering, 1996,118(4):511–519.
Barter P J, Rye K. A high density lipoproteins and coronary heart disease[J].Atherosclerosis, 1996,121(1):1–12.
Ojha M. Spatial and temporal variations of wall shear stress within an end-to-side arterial anastomosis model[J].J Biomechanical, 1983,26(12):1377–1388.
He X Y, Ku D N. Pulsatile flow in the human left coronary artery bifurcation: average conditions [J].J Biomechanical Engineering, 1996,118(1):74–82.
Back L H, Liem T K, Kwack E Y,et al.. Flow measurements in a highly curved atherosclerotic coronary artery cast of man[J].J Biomechanical Engineering, 1992,114(2):232–240.
Karino T, Deng X Y, Naiki T. Flow-dependent concentration polarization of lipoproteins at the blood-endothelium boundary[A]. In: Hochmuth R M, Langrana N A, Hefzy M S Eds.Proceedings of the 1995 Bioengineering Conference[C]. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag, 1995.
Jo H, Dull R O, Hollis T M,et al. Endothelial albumin permeability is shear dependent, time dependent and reversible[J].American J Physiology, 1991,260:H1992-H1996.
Friedman M H, Peters O J, Bargeron C B,et al. Shear-dependent thickening of the human arterial intima[J].Atherosclerosis, 1986,60(2):161–170.
Rappitsch G, Pektold K. Computer simulation of convective diffusion processes in large arteries [J].J Biomechanics, 1996,29(2):207–215.
Langeler E G, Ineke S H, Victor W M,et al. Passage of low density lipoproteins through monolayers of human arterial endothelidal cells-effects of vasoactive substance in an in vitro[J].Arteriosclerosis, 1989,9(4):550–559.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Wu Wang-yi
Foundation item: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10002003)
Biographies: Li Ding (1973-) Wen Gong-bi (1935-)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, L., Gong-bi, W. The steady/pulsatile flow and macromolecular transport in T-bifurcation blood vessels. Appl Math Mech 24, 532–544 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02435866
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02435866