Abstract
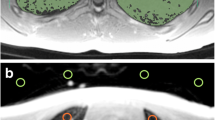
Fourteen children under 3 years of age with possible airway obstruction were evaluated with an ultrafast CT scanner, Imatron C-100. Serial 0.05-second multilevel scans were obtained through the chest at rates of 17 images per second. No patient sedation or contrast medium was used. Time-density curves generated over each lung and specific pulmonary zones were compared to characterize the normal variation of density during inspiration and expiration and to determine abnormal patterns associated with airway obstruction. There was a high, positive correlation value (r>0.79) between time/density curves over those pulmonary regions in which there was no focal bronchial obstruction and a low, negative correlation value (r=< −0.58) with bronchial obstruction. Three studies with reconstruction artifacts were excluded. Furthermore, the results indicate that young children generally have denser lungs, particularly in expiration, than older children or adults. This preliminary study suggests that ultrafast CT offers a promising, unique, rapid and noninvasive approach for diagnosing airway obstruction in childhood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wegener O, Koeppe P, Dester H (1978) Measurement of lung density by computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2: 263
Robinson P, Kreel L (1979) Pulmonary tissue attenuation with computed tomography: comparison of inspiratory and expiratory scans. J Comput Assist Tomogr 3: 740
Lee JY, Shank B, Bonfiglio P, Peid A (1984) CT analysis of lung density changes in patients undergoing total body irradiation prior to bone marrow transplantation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8: 885
Rosenblum L, Manceri R, Wellenstein D, Thomas FD, Bassano DA, Raasch BN, Chamberlain CC, Heitzman ER (1980) Density patterns in the normal lung as determined by computed tomography. Radiology 137: 409
Hedlund LW, Vock P, Effman EL (1983) Computed tomography of the lung. Densitometric studies. Radiol Clin North Am 21: 775
Brasch RC, Gould RG, Gooding CA, Ringertz HG, Lipton MJ (1987) Upper airway obstruction in infants and children: evaluation with ultrafast computed tomography. Radiology 165: 459–466
Van Dyk J, Keane TJ, Rider WD (1982) Lung density as measured by computerized tomography: Implications for radiotherapy. Int J Radiol Oncol Biol Phys 8: 1363
Vock P, Malanowski D; Tschaeppeler H, Kirks DR, Hedlund LW; Effman EL (1987) Computed tomographic lung density in children. Invest Radiol 22: 627
Theander G (1970) Motility of diaphragm in children with bronchial foreign bodies. Acta Radiol [Diagn] (Stockh) 10: 113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ringertz, H.G., Brasch, R.C., Gooding, C.A. et al. Quantitative density-time measurements in the lungs of children with suspected airway obstruction using ultrafast CT. Pediatr Radiol 19, 366–370 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02387628
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02387628