Abstract
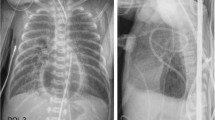
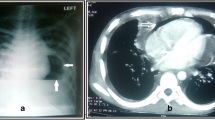
Retrocardiac pneumomediastinum was encountered in two premature infants; one had a tracheal perforation and one an esophageal perforation. Contrast studies showed communication between the sites of perforation and the retrocardiac air. Clinical signs suggestive of such perforation include abnormal course of tubes on plain chest films and bloody aspirates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morrison SC, Fletcher BD (1985) Infra-azygous pneumomediastinum versus pulmonary ligament air collection. CT evaluation. Pediatr Radiol 15: 129
Volberg FM, Everett C, Brill P (1979) Radiologic features of inferior pulmonary ligament air collections in neonates with respiratory distress. Radiology 130: 357
Bowen A'D, Quattromani F (1980) Infraazygous pneumomediastinum in the newborn. Am J Roentgenol 135: 1017
Kassner GE (1985) Iatrogenic disorders of the fetus, infant and child. Springer New York 191
Schild J, Wuilloud A, Konberg H, Bossi E (1976) Tracheal perforation as a complication of nasotracheal intubation in a neonate. Pediatrics 88: 631
Serlin S, Daily W (1975) Tracheal perforation in the neonate. A complication of endotracheal intubation. Pediatrics 86: 596
Purohit D, Lorenzo R, Smith DC, Bradford B (1985) Bronchial laceration in a newborn with persistent posterior pneumomediastinum. J Pediatr Surg 20: 82
Anderson K, Chandra P (1976) Pneumothorax secondary to perforation of sequential bronchi by suction catheters. J Pediatr Surg 11: 687
Wells S, Leonidas J, Conckle D, Holder T, Amoury R, Ashcroft K (1974) Traumatic prevertebral pharyngoesophageal pseudodiverticulum in the newborn infant. J Pediatr Surg 9: 217
Talbert J, Rodgers B, Felmton A, Moazam F (1977) Traumatic perforation of the hypopharynx in infants. J Thoracic CV Surg 74: 152
Lee S, Kuhn J (1976) Esophageal perforation in the neonate. Am J Dis Child 130: 325
Touloukian R, Beardsley G, Ablow R, Effman E (1977) Traumatic perforation of the pharynx in the newborn. Pediatric 59: 1019
Clarke T, Cohen R, Feldman B, Papile L (1980) Esophageal perforations in premature infants and comments on diagnosis. Am J Dis Child 134: 367
Girdany B, Sieber W, Osman M (1969) Traumatic pseudodiverticulosis of the pharynx in newborn infants. NEJM 280: 237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amodio, J.B., Berdon, W.E., Abramson, S.J. et al. Retrocardiac pneumomediastinum in association with tracheal and esophageal perforations. Pediatr Radiol 16, 380–383 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386813
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386813