Abstract
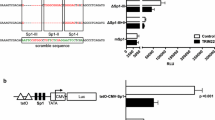
HIV-1 gene expression is regulated by the interplay of transcription factors with multiple binding motifs present within the U3, R and U5 regions of the long terminal repeat (LTR). Here we report novel DNA binding complexes (termed 9a, 9b and 9c) between nuclear proteins from T-lymphoid and non-T-lymphoid cells and a region of the U3 LTR between nucleotides (nts) −320 to −281 in the HIV strain HXB2. Complex 9b bound a motif predicted to bind E-box or c-Myb proteins and a partially overlapping dyad symmetrical motif, and included basic helix-loop-helix proteins (E12, E47 or ITF-1) but surprisingly not c-Myb. Complex 9c, which bound to a pair of GATA sites, included GATA-3 and GATA-4 in Jurkat and MT-2 cells, respectively. We also demonstrate that the c-Myb/E-box and GATA sites form a bipartite motif required for the formation of complex 9a. Transient transfection experiments with T cells revealed that in the context of a minichromosome assembled full-length LTR, mutation of region −320 to −281 increased basal and PMA-stimulated LTR activity. These findings suggest that this region is an important component of the HIV-1 LTR required for response to different cellular transcription factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson KP, Crable SC, Lingrel JB. The GATA-E box-GATA motif in the EKLF promoter is required for in vivo expression. Blood 95:1652–1655;2000.
Barat C, Rassart E. Members of the GATA family of transcription factors bind to the U3 region of Cas-Br-E and Graffi retroviruses and transactivate their expression. J Virol 72:5579–5588;1998.
Bassuk AG, Anandappa RT, Leiden JM. Physical interactions between Ets and NF-κB/NFAT proteins play an important role in their cooperative activation of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells. J Virol 71:3563–3573;1997.
Cannone-Hergaux F, Aunis D, Schaeffer E. Interactions of the transcription factor AP-1 with the long terminal repeat of different human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains in Jurkat, glial and neuronal cells. J Virol 69:6634–6642;1995.
Churchill M, Ramsay R, Rhodes DI, Deacon NJ. c-Myb influences HIV-1 gene expression and virus production. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses (in press); 2001.
Cohen-Kaminsky S, Maouche-Chrétien L, Vitelli L, Vinit M-A, Blanchard I, Yamamoto M, Peschle C, Roméo PH. Chromatin immunoselection defines a TAL-1 target gene. EMBO J 17:5151–5160;1998.
Crossley M, Merika M, Orkin SH. Self-association of the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 mediated by its zinc finger domains. Mol Cell Biol 15:2448–2456;1995.
Dasgupta P, Saikumar P, Reddy D, Reddy EP. Myb protein binds to human immunodeficiency virus 1 long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences and transactivates LTR-mediated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:8090–8094;1990.
Duncan DD, Adlam M, Siu G. Asymmetric redundancy in CD4 silencer function. Immunity 4:301–311;1996.
Elefanty AG, Antoniou M, Custodio N, Carmo-Fonseca M, Grosveld FG. GATA transcription factors associate with a novel class of nuclear bodies in erythroblasts and megakaryocytes. EMBO J 15:319–333;1996.
Galio L, Briquet S, Vaquero C. Real-time study of interactions between a composite DNA regulatory element (HIV-1 LTR NRE) and several transcription factors of nuclear extracts. Biochem Biophys Res Commum 264:6–13;1999.
Gao X, Sedgwick T, Shi YB, Evans T. Distinct functions are implicated for the GATA-4, -5, and -6 transcription factors in the regulation of intestine epithelial cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 18:2901–2911;1998.
Giacca M, Gutierrez MI, Menzo S, Di Fagagna FD, Falaschi A. A human binding site for transcription factor USF/MLTF mimics the negative regulatory element of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Virology 186:133–147;1992.
Grassi G, Pozzato G, Moretti M, Giacca M. Quantitative analysis of hepatitis C virus RNA in liver biopsies by competitive reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction. J Hepatol 23:403–411;1995.
Henderson AJ, Zou X, Calame KL. C/EBP proteins activate transcription from the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat in macrophages/monocytes. J Virol 69:5337–5344;1995.
Hsiang YHH, Goldman JP, Raulet DH. The role of c-Myb or a related factor in regulating the T cell receptor γ gene enhancer. J Immunol 154:5195–5204;1995.
Kuiken C, Foley B, Hahn B, Marx P, McCutcheon F, Mellors J, Mullins J, Wolinsky S, Korber B. Human retroviruses and AIDS: A compilation and analysis of nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Theoretical Biology and Biophysics Group, Los Alamos Laboratory, Los Alamos. 34–199;1999.
Ladias JAA. Convergence of multiple nuclear receptor signaling pathways onto the long terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus-1. J Biol Chem 269:5944–5951;1994.
Li Y, Mak G, Franza Jr BR. In vitro study of functional involvement of Sp1, NF-κB/Rel, and AP1 in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-mediated HIV-1 long terminal repeat activation. J Biol Chem 269:30616–30619;1994.
Molkentin JD. The zinc finger-containing transcription factors GATA-4, -5 and -6. J Biol Chem 275:38949–38952;2000.
Mouthon MA, Bernard O, Mitjavila MT, Romeo PH, Vainchenker W, Mathieu-Mahul D. Expression oftal-1 and GATA-binding proteins during hematopoiesis. Blood 81:647–655;1993.
Murre C, Bain G, van Dijk MA, Engel I, Furnari BA, Massari E, Matthews JR, Quong MW, Rivera RR, Stuiver MH. Structure and function of helix-loop-helix proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1218:129–135;1994.
Nakagoshi H, Nagase T, Kanei-Ishii C, Ueno Y, Ishii S. Binding of the c-myb proto-oncogene product to the simian virus 40 enhancer stimulates transcription. J Biol Chem 265:3479–3483;1990.
Ness SA, Marknell A, Graf T. The v-myb oncogene product binds to and activates the promyelocyte-specificmim-1 gene. Cell 59:1115–1125;1989.
Nielsen AL, Nørby PL, Pedersen FS, Jørgensen P. Various modes of basic helix-loop-helix protein-mediated regulation of murine leukemia virus transcription in lymphoid cell lines. J Virol 70:5893–5901;1996.
Nielsen AL, Pallisgaard N, Pedersen FS, Jørgensen P. Basic helix-loop-helix proteins in murine type C retrovirus transcriptional regulation. J Virol 68:5638–5647;1994.
Orkin SH. GATA-binding transcription factors in hematopoietic cells. Blood 80:575–581;1992.
Ou SHI, García-Martínez LF, Paulssen EJ, Gaynor RB. Role of flanking E-box motifs in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TATA element function. J Virol 68:7188–7199;1994.
Peeters A, Lambert PF, Deacon NJ. A fourth Sp1 site in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat is essential for negative-sense transcription. J Virol 70:6665–6672;1996.
Pereira LA, Bentley KA, Peeters A, Churchill MJ, Deacon NJ. A compilation of cellular transcription interactions with the HIV-1 LTR promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 28:663–668;2000.
Schwartz C, Cannone-Hergaux F, Aunis D, Schaeffer E. Characterisation of nuclear proteins that bind to the regulatory TGATTGGC motif in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Nucleic Acids Res 25:1177–1184;1997.
Sheridan PL, Sheline CT, Cannon K, Voz ML, Pazin MJ, Kadonaga JT, Jones KA. Activation of the HIV-1 enhancer by the LEF-1 HMG protein on nucleosome-assembled DNA in vitro. Genes Dev 9:2090–2104;1995.
Siekevitz M, Josephs SF, Dukovich M, Peffer N, Wong-Staal F, Greene WC. Activation of the HIV-1 LTR by T cell mitogens and the trans-activator protein of HTLV-1. Science 238:1575–1578;1987.
Sieweke MH, Tekotte H, Jarosch U, Graf T. Cooperative interaction of Ets-1 with USF required for HIV-1 enhancer activity in T cells. EMBO J 17:1728–1739;1998.
Thompson MA, Ramsay RG. Myb: an old oncoprotein with new roles. Bioessays 17:341–350;1995.
Towatari M, Kanei Y, Saito H, Hamaguchi M. Hematopoietic transcription factor GATA-2 activates transcription from the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J AIDS 12:253–259;1997.
Visvader J, Adams JM. Megakaryocytic differentiation induced in 416B myeloid cells by GATA-2 and GATA-3 transgenes or 5-azacytidine is tightly coupled to GATA-1 expression. Blood 82:1493–1501;1993.
Vyas P, McDevitt MA, Cantor AB, Katz SG, Fujiwara Y, Orkin SH. Different sequence requirements for expression in erythroid and megakaryocytic cells within a regulatory element upstream of theGATA-1 gene. Development 126:2799–2811;1999.
Wadman IA, Osada H, Grütz GG, Agulnick AD, Westphal H, Forster A, Rabbitts TH. The LIM-only protein Lmo2 is a bridging molecule assembling an erythroid DNA-binding complex which includes the TAL1, E47, GATA-1 and Ldb1/NLI proteins. EMBO J 16:3145–3157;1997.
Yamagata T, Nishida J, Sakai R, Tanaka T, Honda H, Hirano N, Mano H, Yazaki Y, Hirai H. Of the GATA-binding proteins, only GATA-4 selectively regulates the human interleukin-5 gene promoter in interleukin-5-producing cells which express multiple GATA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol 15:3830–3839;1995.
Yamamoto K, Mori S, Okamoto T, Shimotohno K, Kyogoku Y. Identification of transcriptional suppressor proteins that bind to the negative regulatory element of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res 19:6107–6112;1991.
Yamamoto M, Ko LJ, Leonard MW, Beug H, Orkin SH, Engel JD. Activity and tissue-specific expression of the transcription factor NF-E1 multigene family. Genes Dev 4:1650–1662;1990.
Yang HS, Evans T. Homotypic interactions of chicken GATA-1 can mediate transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 15:1353–1363;1995.
Yang Z, Engel JD. Human T cell transcription factor GATA-3 stimulates HIV-1 gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 21:2831–2836;1993.
Zeichner SL, Kim JY, Alwine JC. Linker-scanning mutational analysis of the transcriptional activity of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. J Virol 65:2436–2444;1991.
Zhang Y, Doyle K, Bina M. Interactions of HTF4 with E-box motifs in the long terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol 66:5631–5634;1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, L.A., Churchill, M.J., Elefanty, A.G. et al. Characterization of interactions between transcription factors and a regulatory region spanning nt −320 to −281 of the HIV-1 LTR in T-lymphoid and non-T-lymphoid cells. J Biomed Sci 9, 68–81 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256580
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256580