Abstract
Background
It is wellknown that sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) concentrations in the follicle are relatively low in comparison with the corresponding estradiol (E2) levels, which are extremely high. A direct comparison of these data in stimulated and unstimulated cycles, as well as the relationship of SHBG with testosterone (T) and E2 in serum and follicular fluid (FF), is assessed.
Methods
SHBG was measured in serum and FF in 42 cycles stimulated by GnRH agonists and gonadotropins and in 15 unstimulated cycles. The levels of SHBG were compared to the corresponding total estradiol and total testosterone concentrations. The analyzed FFs of 42 women, 12 of whom conceived, were randomly selected from 90 patients participating in an in vitro fertilization program. Mature oocytes were retrieved from all follicles from which FFs were analyzed.
Results
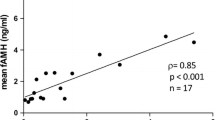
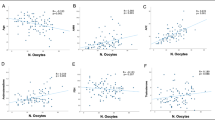
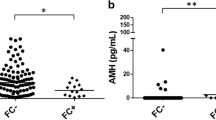
Markedly elevated SHBG was found in both the serum and the FF of stimulated cycles compared to unstimulated cycles. In contrast, serum T and E2 were significantly higher in induced than in unstimulated cycles, while there was no significant difference in FF T or E2 between the two groups of cycles. No correlation was found between serum and FF SHBG in either stimulated or unstimulated cycles. In stimulated cycles, only in FF, SHBG was significantly correlated with both E2 and T. In unstimulated cycles, no correlation was found between SHBG and either one of the corresponding steroids either in serum or in FF.
Conclusions
The fraction of non-SHBG bound, biologically active sex steroids may be lower in the FF of stimulated than that of unstimulated cycles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson DC: Sex-hormone-binding globulin. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1974;3:69–96
Partridge WM: Transport of protein-bound hormones into tissues in vivo. Endocrinol Rev 1981;2:103–125
Dunn JF, Nisula BC, Rodbard D: Transport of steroid hormones. Binding of 21 endogenous steroids to both testosterone-binding globulin and corticosteroid-binding globulin in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1981;53:58–68
Siiteri PK, Murai JT, Hammond GL, Nisker JA, Raymoure WJ, Kuhn RW: The serum transport of steroid hormones. Rec Prog Horm Res 1982;38:457–503.
Schwartz S, Heidemann P, Stecher W: Specific and non specific modulation of various liver proteins, especially hormone-binding globulins, steroids and antimetabolites.In The Endocrines and the Liver. Serono Symposia, Vol 51. M Langer, L Chaindussi, IJ Chopra, L Martine (eds). New York, Academic Press, 1982, pp 387–391
Odling V, Elamsson K, Englund DE, Victor A, Johanson EDB: Effects of oestradiol on sex hormone binding globulin. Acta Endocrinol 1985;101:248–253
Dowsett M, Attree SL, Virdee SS, Jeffcoate SL: Oestrogenrelated changes in sex hormone binding globulin levels during normal and gonadotropin-stimulated cycles. Clin Endocrinol 1985;23:303–312
Ben-Rafael Z, Mastroianni L, Meloni F, Lee MS Flickinger GL: Total estradiol, free estradiol, sex hormone-binding-globulin in human follicular fluid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1986;63:1106–1111
von Schoultz S, Carlstrom K: On the regulation of sex-hormone-binding globulin—A challenge of an old dogma and outlines of an alternative mechanism. J Steroid Biochem 1989;32:327–334
Yding-Andersen C, Byskov AG, Petersen K, Westergaard LG: Steroid-binding proteins in serum and follicular fluid as predictors of IVF-ET outcome. VI World Congress on in Vitro Fertilization and Alternate Assisted Reproduction, Jerusalem 1989, p 31
Yding-Andersen C: Levels of steroid-binding proteins and steroids in human preovulatory follicle and serum as predictors of success in in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1990;71:1375–1381
Veeck L: Atlas of the Human Oocyte and Early Conceptus. Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, 1986, p 7
Yding-Andersen C: Concentrations of free oestradiol and progesterone in human preovulatory follicular fluid. Hum Reprod 1991;6:359–364
Yding-Andersen C, Westergaard LG, Teisner B, Byskov AG, Ziebe S, Helledie L, Petersen K, Westergaard JG: Changes induced in serum protein profiles by ovarian stimulation during in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer treatment: A comparison between conception and nonconception cycles. Hum Reprod 1992;7:585–591
Gustafsson JA, Mode A, Norstedt G, Skett P: Sex steroids induced changes in hepatic enzymes. Annu Rev Physiol 1983;45:51–60
Fleetwood JA, Watson MJ, Wostell HJ, Weddel A: Hormone studies in a case of virilisation due to ovarian tumour. Ann Clin Biochem 1985;22:498–501.
Dewis P, Newman M, Ratcliffe WA, Anderson DC: Does testosterone affect the normal menstrual cycle? Clin Endocrinol 1986;24:515–521
Gustafsson O, Lunell N-O, Nylund L, Pousette A, Akerlof E, Carlstrom K: Sex hormone-binding globulin, oestradiol-17Β, progesterone, and testosterone at stimulation and after embryo transfer. Hum Reprod 1991;6:1039–1042
Peters H, McNatty KP: The Ovary. London, Granada.
Younglai EV, Short RV: Pathways of steroid biosynthesis in the intact Graafian follicle of mares in oestrus. J Endocrinol 1970;47:321–331
Ben-Radael Z, Mastroianni L, Meloni F, Strauss JF III, Flickinger GL: Changes in serum sex hormone-binding globulin, free estradiol and testosterone during gonadotropin treatment. Fertil Steril 1985;46:593–598
Motohashi T, Wu CH, Abdel-Rahman HA, Marymor M, Mikhail G: Estrogen/androgen balance in health and disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1979;135:89–95.
Pymate SR, Moore DE, Cheng CY, Bardin CW, Southworth MB, Levinski MJ: Sex hormone-binding globulin changes during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1985; 61:993–996
Steingold K, James C, Reznikov S, Smetzer J, Matt D: The role of sex hormone binding globulin in follicular fluid. Fertil Steril (Suppl S-115), 44th Annual Meeting of the Americal Fertility Society, Abstr P-218
Phocas I, Mantzavinos Th, Rizos D, Sarandakou A, Dimitriadou F, Zourlas PA: A comparative study of serum and follicular fluid α-immunoreactive inhibin in stimulated and unstimulated patients. Ann NY Acad Sci 1993;687:288–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phocas, I., Mantzavinos, T., Sarandakou, A. et al. Serum and follicular fluid sex hormone-binding globulin in stimulated and unstimulated cycles. J Assist Reprod Genet 12, 348–353 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02215725
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02215725