Abstract
The stability of cisplatin in sodium chloride 0.9% intravenous solutions contained in glass bottles, polyvinyl chloride bags, polyethylene and polypropylene containers was studied over two weeks. The solubility of cisplatin at 4°C was also studied for possible precipitation. The type of container had no effect on cisplatin decomposition. No precipitation at 4°C was observed within the time period studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
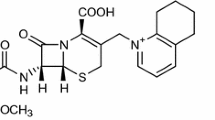
Leh FK, Wolf W. Platinum complexes: a new class of antineoplastic agents. J Pharm Sci 1976;65:315–28.
Speer RJ, Ridgway H, Hall LM. Coordination complexes of platinum as antitumor agents. Cancer Chemother Rep 1975;59:629–41.
Kunin CM. Dosage schedules of antimicrobial agents: a historical review. Rev Infect Dis 1981;144:380–5.
Atilla AH, Long DF, Repta AJ. Cisplatin stability in aqueous parenteral vehicles. J Parenter Drug Assoc 1979;65:315–28.
Repta AJ, Long DF, Atilla AH.cis-Dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) stability in aqueous vehicles. Cancer Treat Rep 1979;62:229–30.
Greene RF, Chatterji DC, Hiranaka PK, Gallelli JF. Stability of cisplatin in aqueous solution. Am J Hosp Pharm 1979;36:38–43.
Cheung Y, Cradock JC, Vishnuvajjala BR, Flora KP. Stability of cisplatin, iproplatin, carboplatin and tetraplatin in commonly used intravenous solutions. Am J Hosp Pharm 1987;44:124–30.
Benerjea D, Basolo F, Pearson RG. Mechanism of substition reactions of complex ions XII. Reactions of some platinum (II) complexes with various reactants. J Am Chem Assoc 1957;79:4055–62.
Reishus JW, Martin DS Jr.cis-Dichlorodiammineplatinum(II). Acid hydrolysis and isotopic exchange of the chloride ligands. J Am Chem Assoc 1961;59:2457–62.
Lee KW, Martin DS Jr.cis-Dichlorodiammineplatinum(II). Aquation equilibria and isotopic exchange of chloride ligands with free chloride and tetrachloroplatinate. Inorg Chim Acta 1976;17:105–10.
Mariani EP, Southard BJ, Woolever JT, Erlich RH, Granatek AP. Physical compatibility and chemical stability of cisplatin in various diluents and in large volume parenteral solutions. In: Prestayko AW, Crooke ST, Carter SK, eds. Cisplatin. Current status and new developments. New York: Academic Press, 1980:305–16.
Girona V, Duran S, Prat J, Cots J, Pujol M, Olivares M, Solé LA. Cálculo de la constante de evaporación de Iíquido en diferentes contenedores plásticos para soluciones intravenosas [Liquid evaporation constants calculated for intravenous solutions stored in different plastic containers]. SEFH 1980, 14:207–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cubells, M.P., Aixela, J.P., Brumos, V.G. et al. Stability of cisplatin in sodium chloride 0.9% intravenous solution related to the container's material. Pharm World Sci 15 (Suppl 1), 34–36 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02116167
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02116167