Abstract
Purpose: In this study we investigated whether metaphase I oocytes collected in an intracytoplasmic sperm injection program could successfully be matured and fertilized by injecting aged (>20-hr) spermatozoa.
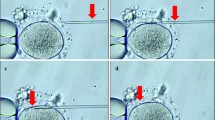
Materials and Methods: Metaphase I oocytes aspirated were preincubated for 20 hr to allow the oocytes to reach meiotic maturity. Only metaphase II oocytes were injected. The original sperm sample processed on the day of aspiration was used in the microinjection process.
Results: One hundred eighty-three oocytes were collected, of which 42 (23%) were metaphase I oocytes. These were incubated for 20 hr and microinjected with the original sperm sample. Thirty-one (74%) of the metaphase I oocytes reached meiotic maturity (extruded polar body); 67.7% showed two pronuclei 18 hr after injection and 61.3% embryo development 40 hr postinjection. No difference in fertilization and embryo development rate was found in metaphase II oocytes injected 6 hr postaspiration versus 20 hr postaspiration. An ongoing pregnancy was also achieved using only embryos obtained from matured metaphase I oocytes.
Conclusions: Metaphase I oocytes can be successfully maturedin vitro and injected using aged (>20-hr) sperm samples. Matured metaphase I oocytes, if successfully injected, produce embryos able to induce pregnancy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asch R, Simerly C, Ord T, Ord VA, Schatten G: The stages at which human fertilization arrests: microtubule and chromosome configurations in inseminated oocytes which failed to complete fertilization and development in humans. Hum Reprod 1995;10:1897–1906
Van der Merwe JP, Kruger TF, Swart Y, Lombard CJ: The role of oocyte maturity in the treatment of infertility because of teratozoospermia and normozoospermia with gamete intrafallopian transfer. Fertil Steril 1992;58:581–586
Van Streirteghem AC, Liu J, Joris H, Nagy Z, Janssenswillen C, Tournaye H, Derde M-P, Van Assche E, Devroey P: Higher success rate by intracytoplasmic sperm injection than by subzonal insemination. Report of a second series of 300 consecutive treatment cycles. Hum Reprod 1993;8:1055–1060
Van Streirteghem AC, Nagy Z, Joris H, Liu J, Staessen C, Smitz J, Wisanto A, Devroey P: High fertilization and implantation rates after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod 1993;8:1061–1066
Singer SL, Lambert H, Overstreet JW, Hanson FW, Yanagimachi R: The kinetics of human sperm binding to human zona pellucida and zona-free hamster oocytesin vitro. Gamete Res 1985;12:29–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coetzee, K., Windt, ML. Fertilization and pregnancy using metaphase I oocytes in an intracytoplasmic sperm injection program. J Assist Reprod Genet 13, 768–771 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066495