Abstract
Purpose: A placenta with a partial hydatidiform mole was studied using DNA polymorphic markers to determine whether it has a triploid cell line.
Method: Parent-mole transmission of alleles at 23 polymorphic loci was traced in cells from a molar region and a normal-looking region of the placenta by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification or Southern blot analysis, both followed by densitometric analysis.
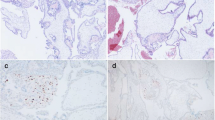
Results: Allele patterns for 8 of the 23 loci were identical between the DNA from the molar and normal regions of the placenta, while those of the remaining 15 loci were uninformative. In the molar region, the band intensity for the paternally derived allele at each informative locus was always greater than that of the maternally derived allele, the average intensity ratio of the former to the latter being 1.5, whereas the ratio in the normal region was even.
Conclusions: The results suggested that the molar region was a mixoploid consisting of diploid and triploid cells and the phenotypically normal region had a mainly diploid constitution. It is most likely that the placenta may have originated from a single diploid or triploid conceptus, followed by postzygotic gain or loss of a paternal haploid set, and that an extra paternal set contributed to hydropic changes of the placenta.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kajii T, Ohama K: Androgenetic origin of hydatidiform mole. Nature 1977;268:633–634
Jacobs PA, Szulman AE, Funkhouser J, Matsuura JS, Wilson CC: Human triploidy: Relationship between parental origin of the additional haploid complement and development of partial hydatidiform mole. Ann Hum Genet 1982;46:223–231
Kajii T: The road to diploid androgenesis. Jpn J Hum Genet 198;31:61–71
Lawler SD, Fisher RA, Dent J: A prospective genetic study of complete and partial hydatidiform moles. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:1270–1272
Sarno AP, Moorman AJ, Kalousek DK: Partial molar pregnancy with fetal survival: An unusual example of confined placental mosaicism. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:716–719
Tharapel AT, Wilroy RS, Martens PR, Holbert JM, Summitt RL: Diploid-triploid mosaicism: delineation of the syndrome. Ann Genet (Paris) 1983;26:229–233
Pettenati MJ, Mirkin LD, Goldstein DJ: Diploid-triploid mosaicism: Report of necropsy findings. Am J Med Genet 1986;24:23–28
Woods CG, Bankier A, Curry J, Sheffield LJ, Slaney SF, Smith K, Voullaire L, Wellesley D: Asymmetry and skin pigmentary anomalies in chromosome mosaicism. J Med Genet 1994;31:694–701
Kalousek DK: Current topic: Confined placental mosaicism and intrauterine fetal development. Placenta 1994;15:219–230
Polymeropoulos MH, Xiao H, Rath DS, Merril CR: Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human CTLA4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 1991;19:4018
Spirio L, Joslyn G, Nelson L, Leppert M, White R: A CA repeat 30–70Kb downstream from the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. Nucleic Acids Res 1991;19:6348
Browne DL, Gault J, Thompson MB, Hange XY, Evans GA, Litt M: Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D11S527 locus. Nucleic Acids Res 1991;19:4790
Warnich L, Groenewald I, Theart L, Retief AE: High informative dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D11S29 locus on chromosome 11q23. Hum Genet 1992;89:357–359
Watkins HC, MacRae CA, Thierfelder L, McKenna WJ, Seidman CE, Seidman JG: A dinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the human LAMB2 gene on chromosome 1q. Hum Mol Genet 1993;2:1084
Zhang Y, Tycko B: Monoallelic expression of the human H19 gene. Nature Genet 1992;1:40–44
Fey MF, Peter HJ, Hinds HL, Zimmermann A, Gallati SL, Gerber H, Studer H, Tobler A: Clonal analysis of human tumors with M27β, a highly informative polymorphic X chromosomal probe. J Clin Invest 1992;89:1438–1444
Hamabe J, Niikawa N:Sty1 polymorphism at the D15S11 locus. Nucleic Acids Res 1992;18:5579
Procter SE, Gray ES, Watt JL: Triploidy, partial mole and dispermy. An investigation of 12 cases. Clin Genet 1984;26:46–51
Niebuhr E: Triploidy in man: Cytogenetical and clinical aspects. Humangenetik 1974;21:103–125
Surani MAH, Barton SC, Norris ML: Development of reconstituted mouse eggs suggests imprinting of the genome during gametogenesis. Nature 1984;308:548–550
Cattanach BM, Kirk M: Different activity of maternally and paternally derived chromosome regions in mice. Nature 1985;316:496–498
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, Y., Jinno, Y., Masuzaki, H. et al. A partial hydatidiform mole with 2N/3N mosaicism identified by molecular analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet 13, 739–744 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066430
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066430