Abstract
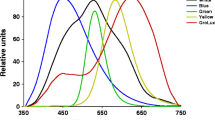
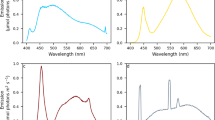
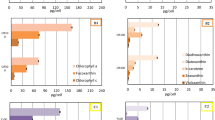
The effect of light quality on growth, photosynthesis and carbon metabolism in two species of marine algae,Cyclotella nana (Hustedt) andDunaliella tertiolecta (Butcher), was examined. Relative growth constants forC. nana were 0.37, 0.29 and 0.25 in blue, white and green light, respectively. Corresponding constants were 0.41, 0.31 and 0.29 forD. tertiolecta. Photosynthetic rates in both species were higher in blue light and lower in green light compared with white light of the same intensity. More than 60% of14C assimilated byC. nana orD. tertiolecta grown in blue or green light was incorporated into the ethanol-insoluble fraction, compared with 10 to 30% in this fraction in white light. The relative importance of the various components within this fraction was independent of light quality. Although less14C was assimilated into the ethanol-soluble fraction in blue or green light, there was a relative increase in some amino acids and organic acids in this fraction and a decrease in sugars and sugar phosphates relative to white light of the same intensity. These differences were independent of light intensity, photosynthetic rate and cell density in the cultures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Baatz, I.: Die Bedeutung der Lichtqualität für Wachstum und Stoffproduktion planktonischer Meeresdiatomeen. Planta31, 726–766 (1941).
Baldry, C. W., C. Bucke andJ. Coombs: Light/phosphoenolpyruvate dependent carbon dioxide fixation by isolated sugar cane chloroplasts. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.37, 828–832 (1969).
Beattie, A., E. L. Hibst andE. Percival: Studies on the metabolism of the Chrysophyceae. Comparative structural investigations on leucosin (chrysolaminarin) separated from diatoms and laminarin from the brown algae. Biochem. J.79, 531–537 (1961).
Champigny, M. L.: L'incorporation de14CO2 dans les aminoacides des feuilles deBryophyllum diagremontianum. C. r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris243, 83–85 (1956).
Craigie, J. S., J. McLaohlan W. Majak, R. G. Ackman andC. S. Tocher: Photosynthesis in algae. II. Green algae with special reference toDunaliella spp. andTetraselmis spp. Can. J. Bot.44, 1247–1254 (1966).
Emerson, R. andC. M. Lewis: The dependence of the quantum yield ofChlorella photosynthesis on wave length of light. Am. J. Bot.30, 165–178 (1943).
Hatch, M. D. andC. R. Slack: Photosynthesis by sugarcane leaves. A new carboxylation reaction and the pathway of sugar formation. Biochem. J.101, 103–111 (1966).
Hauschild, A. H. W.: The interconversion of glycine and serine inZea mays Can. J. Biochem. Physiol.37, 887–894 (1959).
—,C. D. Nelson andG. Kbotkov: The effect of light quality on the products of photosynthesis inChlorella vulgaris. Can. J. Bot.40, 179–189 (1962a).
—, — and —: The effect of light quality on the products of photosynthesis in green and blue-green algae, and in photosynthetic bacteria. Can. J. Bot.40, 1619–1630 (1962b).
Hess, J. L. andN. E. Tolbert: Glycolate pathway in algae. Pl. Physiol., Lancaster42, 371–379 (1967).
Hofstra, G.: An approach to the study of the physiological control of translocation in higher plants, 111 pp. Ph. D. Thesis, Department of Biological Sciences, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, B. C. 1967.
Humphrey, G. F. andD. V. Subba Rao: Photosynthetic rate of the marine diatomCylindrotheca closterium. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat Res.18, 123–127 (1967).
Jerlov, N. G.: Optical studies of ocean waters. Rep. Swed. deep Sea Exped.3, 1–59 (1951).
Jones, R. F., H. L. Speer andW. Kury: Studies on the growth of the red algaPorphyridium cruentum. Physiologia Pl.16, 636–643 (1963).
Kowallik, W.: Die Zellteilung vonChlorella im Verlaufe einer Farblichtkultur. Planta60, 100–108 (1963).
—: Action spectrum for an enhancement of endogenous respiration by light inChlorella. Pl. Physiol., Lancaster42, 672–676 (1967).
Krotkov, G.: The influence of the wavelength of incident light on the path of carbon in photosynthesis. Trans. R. Soc. Can.2, 205–215 (1964).
Majak, W., J. S. Craigie andJ. McLachlan: Photosynthesis in algae. I. Accumulation products in the Rhodophyceae. Can. J. Bot.44, 541–549 (1966).
Mohr, H. undG. Z. Holl: Die Regulation der Zellaktivität bei Farnvorkeimen durch Licht. Z. Bot.52, 209–221 (1964).
Nihei, T., T. Sasa, S. Niyachi, K. Suzuki, andH. Tamiya: Change of photosynthetic activity ofChlorella cells during the course of their normal life cycle. Arch. Mikrobiol.21, 155–164 (1954).
Ouellet, C.: The path of carbon in photosynthesis. XII. Some temperature effects. J. exp. Bot.11, 316–320 (1951).
— andA. A. Benson: The path of carbon in photosynthesis. XIII. pH effects in14CO2 fixation byScenedesmus. J. exp. Bot.3, 237–245 (1952).
Peng, C. T.: Quenching correction in liquid scintillation counting.In: Advances in tracer methodology, Vol. 3, pp 81–94. Ed. byS. Rothchild. New York: Plenum Press 1966.
Rabinowitch, E.: Photosynthesis and related processes. Vol. 2, 1208 pp. New York: Interscience 1951.
Steemann Nielsen, E. andV. K. Hansen: Measurements with the carbon-14 technique of the respiration rates in natural populations of phytoplankton. Deep Sea Res.5, 222–233 (1959).
— and —: Influence of surface illumination on phytoplankton photosynthesis in Danish waters (56° N) throughout the year. Physiologia Plant.14, 593–613 (1961).
— andE. G. Jørgensen: The adaptation of plankton algae. I. General part. Physiologia Plant.21, 401–413 (1968).
Striokland, J. D. H.: Measuring the production of marine phytoplankton. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can.122, 1–172 (1960).
Talling, J. F.: Photosynthetic characteristics of some freshwater plankton diatoms in relation to underwater radiation. New Phytol.56, 1–50 (1957).
Tanada, T.: The photosynthetic efficiency of carotenoid pigments inNavicula minima. Am. J. Bot.38, 276–283 (1951).
Voskresenskaya, N. P.: Synthesis of organic and amino acids during photosynthesis under various conditions of illumination. Fiziologiya Rast.3, 49–57 (1956).
Walker, D. A.: Pyruvate carboxylation and plant metabolism. Biol. Rev.37, 215–256 (1962).
Yentsch, C. S. andR. W. Lee: A study of photosynthetic light reactions, and a new interpretation of sun and shade phytoplankton. J. mar. Res.42, 319–337 (1966).
Zak, E. G.: Influence of molecular oxygen on the formation of amino acids during photosynthesis inChlorella under various conditions of illumination. Fiziologiya Rast.12, 263–269 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated byT. R. Pabsons, Nanaimo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallen, D.G., Geen, G.H. Light quality in relation to growth, photosynthetic rates and carbon metabolism in two species of marine plankton algae. Mar. Biol. 10, 34–43 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02026764
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02026764