Abstract
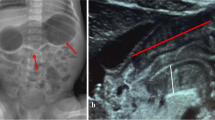
Prostaglandin infusion is used to maintain patency of the ductus arteriosus in infants with cyanotic congenital heart disease. Recently, gastric outlet obstruction as a result of prostaglandin infusion has been described. In our case, an upper gastrointestinal contrast study seemed to depict the typical appearance of pyloric stenosis in an infant who had received an infusion of prostaglandin for a prolonged period. Serial ultrasonograms, however, disclosed progressive elongation of the antropyloric channelwithout wall thickening. This report is the second to illustrate prostaglandin-induced gastric outlet obstruction in a vomiting infant with a gastrointestinal series diagnosis of pyloric stenosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forman HP, Leonidas JC, Kronfeld GD (1990) A rational approach to the diagnosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: do the results match the claims? J Pediatr Surg 25: 262–266
Breaux CW, Georgeson KE, Royal SA, Curnow AJ (1988) Changing patterns in the diagnosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Pediatrics 81: 213–217.
Mollitt DL, Gollady ES, Williamson S, Seibert JJ, Sutterfield SL (1987) Ultrasonography in the diagnosis of pyloric stenosis. South Med J 80: 47–50
Haller JO, Cohen HL (1986) Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: diagnosis using US. Radiology 161: 335–339
Blumhagen JD, Maclin L, Krauter D, Rosenbaum DM, Weinberger E (1988) Sonographic diagnosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. AJR 150: 1367–1370
Tunell WP, Wilson DA (1984) Pyloric stenosis: diagnosis by real time sonography, the pyloric muscle length method. J Pediatr Surg 19: 795–799
O'Keeffe FN, Stansberry SD, Swischuk LE, Hayden CK (1991) Antropyloric muscle thickness at US in infants: what is normal? Radiology 178: 827–830
Kofoed P-EL, Host A, Elle B, Larsen C (1988) Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: determination of muscle dimensions by ultrasound. Br J Radiol 61: 19–20
Cohen HL, Schechter S, Mestel AL, Eaton DH, Haller JO (1987) Ultrasonic “double track” sign in hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Ultrasound Med 6: 139–143
Peled N, Dagan O, Babyn P, Silver MM, et al (1992) Gastric-outlet obstruction induced by prostaglandin therapy in neonates. NEJM 327: 505–510
Tytgat GNJ, Offerhaus GJA, Van Minnen AJ, Everts V, Hensen-Logmans SC, Samson G (1986) Influence of oral 15(R)-15methyl prostaglandin E2 on human gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 90: 1111–1120
McAlister WH, Katz ME, Perlman JM, Tack ED (1988) Sonography of focal foveolar hyperplasia causing gastric obstruction in an infant. Pediatr Radiol 18: 79–81
Katz ME, Blocker SH, McAlister WH (1985) Focal foveolar hyperplasia presenting as an antral-pyloric mass in a young infant. Pediatr Radiol 15: 136–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercado-Deane, M.G., Burton, E.M., Brawley, A.V. et al. Prostaglandin-induced foveolar hyperplasia simulating pyloric stenosis in an infant with cyanotic heart disease. Pediatr Radiol 24, 45–46 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02017660
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02017660