Abstract
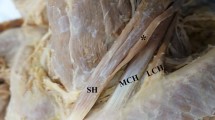
The sonographic appearance of the sternocleidomastoid muscles of 36 children with congenital muscular torticollis was studied. Sternocleidomastoid tumour was detected in all of them and the images were more complex than described in the literature. A patchy echotexture was as frequent as a homogeneous echo-texture, and was more common in the younger child. The echogenicity of the mass could be hyperechoic, isoechoic or hypoechoic relative to normal muscle. A hypoechoic rim surrounding the mass was frequently present. Change of the proportion of the mass relative to the entire musclemass complex in different ages matching clinical observations was also noted. These sonographic findings would be important in establishing a sonographic diagnosis. The higher sensitivity of ultrasound in detection of sternocleidomastoid tumour over clinical methods, and the importance of the sonographic findings in the management of congenital muscular torticollis were also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coventry MB, Harris LE (1959) Congenital muscular toricollis. Some observations regarding treatment. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 41: 815–822
Ling CM, Low YS (1972) Sternomastoid tumor and muscular torticollis. Clin Orthop 86: 144–150
Crawford SC, Harnsberger HR, Johnson L, Aoki R, Giley J (1988) Fibromatosis colli of infancy: CT and sonographic findings. AJR 151; 1183–1184
Mcqueen WJ, Johnson JT, Edwards PA (1980) Fibromatosis colli: a case report. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 88: 49–51
Gruhn J, Hurwitt E (1951) Fibrous sternomastoid tumor of infancy. Paediatrics 8: 522–526
Sherman NH, Rosenberg HK, Heyman S, Templeton J (1985) Ultrasound evaluation of neck masses in children. J Ultrasound Med 4: 127–134
Friedman AP, Haller JO, Goodman JD, Nagar H (1983) Sonographic evaluation of non-inflammatory neck masses in children. Radiology 147: 693–697
Kraus R, Han BK, Babcock DS, Oestreich AE (1985) Sonography of neck masses in children. AJR 146: 609–613
Glasier CM, Seibert JJ, Williamson SL, Corbitt SL, Rodgers AB, Lange TA (1987) High resolution ultrasound characterization of soft tissue masses in children. Pediatr Radiol 17: 233–237
Morrissy RT (1990) Lovell and Winter's paediatric orthopaedics. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 728–730
Middleton DS (1930) The pathology of congenital torticollis. Br J Surg 18: 188–204
Thawley SE, Panje WR, Batsakis JG, Lindberg RD (1987) Comprehensive management of head and neck tumours. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 1249
Chandler FA (1948) Muscular torticollis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 38: 566–570
MacDonald D (1969) Sternomastoid tumour and muscular torticollis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 51: 432–443
Lidge RT, Bechtol RC, Lambert CN (1957) Congenital muscular torticollis. Etiology and pathology. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 39: 1165–1182
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, Y.L., Cheng, J.C.Y. & Metreweli, C. Ultrasonography of congenital muscular torticollis. Pediatr Radiol 22, 356–360 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02016256
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02016256