Abstract
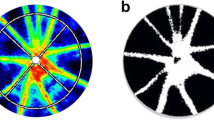
We have studied the antiangiogenetic effects of hydrocortisone and protamine given intra-arterially. The cornea of male, Sprague-Dawley rats were cauterized with silver nitrate. The following treatments were given :30 μg hydrocortisone topical (t.p.), b.i.d., 50 mg/kg/day intraperitoneally (i.p.) or intra-arterially (i.a.), 10 mg/ kg/day protamine i.p. or i.a. Saline was administered to the control groups. In separate experiments we also evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of hydrocortisone, i.p., on the cauterized corneas.
Five days after cauterization, the animals were killed, exsanguinated and India ink was injected to show the network of neovessels. The percentage area of the cornea covered by neovessels was measured morphometrically and evaluated statistically. Hydrocortisone t.p. (−84%), i.a. (−60%) and protamine i.a. (−44%) significantly inhibited angiogenesis in the cauterized cornea. Either drugs, i.p., had any antiangiogenetic effects, but hydrocortisone significantly reduced cell infiltration of the corneas. The results suggest that locoregional administration of antiangiogenetic drugs might be clinically useful.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Folkman,Angiogenesis. InThrombosis and haemostasis. (Eds. M. Verstraete J. Vermylen, H. R. Lijnen and J. Arnout) pp. 583–596. Leuven University Press, Leuven 1987).
R. Crum, S. Szabo and J. Folkman,A new class of steroids inhibits angiogenesis in the presence of heparin or a heparin fragment. Science230, 1375–1378 (1985).
J. Folkman and D. E. Ingber,Angiostatic steroids. Ann. Surg.243, 374–383 (1987).
J. Folkman, R. Langer, R. Linhardt, C. Handenschild and S. Taylor,Angiogenesis inhibition and tumor regression caused by heparin or a heparin fragment in the presence of cortisone. Science221, 719–725 (1983).
J. Folkman, P. B. Weisz, M. M. Jouilliè, W. W. Li and W. R. Ewing,Control of angiogenesis with synthetic heparin substitutes. Science243, 1490–1493 (1989).
S. Taylor and J. Folkman,Protamine is a inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature297, 307–312 (1982).
T. E. Maione, G. S. Gray, J. Petro, A. J. Hunt, A. L. Dorner, S. I. Bauer, H. F. Carson and R. Sharpe,Inhibition of angiogenesis by recombinant human platelet factor 4 and related peptides. Science247, 77–79 (1990).
D. Ingber and J. Kolkman,Inhibition of angiogenesis through modulation of collagen metabolism. Lab. Invest.59, 44–51 (1988).
E. A. Woltering, R. Barrie, T. O'Dorisio, D. Arce, T. Ure, A. Cramer, D. Holmes, J. Robertson and J. Fassler,Somatostatin analogues inhibit angiogenesis in the chick chorioallantoic membrane. J. Surg Res.50, 245–251 (1991).
J. Folkman,Regulation of angiogenesis: A new function of heparin. Biochem. Pharmacol.34, 905–909 (1985).
T. Matsubara, R. Saura, K. Hirohata and M. Ziff,Inhibition of human endothelial cell proliferation in vitro and neovascularization in vivo by D-penicillamine. J. Clin. Invest.83, 158–167 (1989).
D. Ingber, T. Fujita, S. Kishimoto, K. Sudo, T. Karramuro, D. Brem and J. Folkman,Synthetic analogues of fumagillin that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumor growth. Nature348, 555–557 (1990).
J. T. Beranek,Antiangiogenesis comes out of its shell. Cancer J.2, 87–89 (1988).
H. S. G. Chen and F. Gross,Intra-arterial infusion of anticancer drugs: Theoretic aspects of drug delivery and review of responses. Cancer Treat. Rep.64, 31–40 (1980).
R. G. Azizkhan, J. C. Azizkhan, B. R. Zetter and J. Folkman,Mast cell heparin stimulates migration of capillary endothelial cells in vitro. J. Exp. Med.152, 931–944 (1980).
N. Sakamoto, N. G. Tanaka, A. Tohgo, Y. Osada and H. Ogawa,Inhibitory effects of heparin plus cortisone acetate on endothelial cell growth in cultures and in tumor masses. J. Nat. Cancer Inst.78, 581–585 (1987).
D. E. Ingber, J. A. Madri and J. Folkman,A possible mechanism for inhibition of angiogenesis by angiostatic steroids: Induction of capillary basement membrane dissolution. Endocrinology119, 1768–1775 (1986).
J. B. Robin, L. F. Regis-Pacheco, R. L. Kash and D. J. SchanzlinThe histopathology of corneal neovascularization. Arch. Ophthalmol.103, 284–287 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foschi, D., Castoldi, L., Corsi, F. et al. Inhibition of inflammatory angiogenesis in rats by loco-regional administration of hydrocortisone and protamine. Agents and Actions 42, 40–43 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02014298
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02014298