Abstract
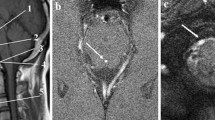
41 comprehensive colour Doppler studies (including spectral analysis) of the ventricular system were performed in 6 infants with CSF-flow (age range: 2 to 27 days). Two premature infants showed no evidence of disease related to the central nervous system (CNS). Overt intraventricular hemorrhage or CNS-infection were present in the other infants. All children were examined several times until CSF-flow was no longer visible. The entire ventricular system, including the fourth ventricular outlet, was investigated for the presence of CSF-flow signals. Dynamic CSF-flow studies consisted of scanning during typical infant activity (crying, sucking, leg movement) and with external manoeuvres (abdominal or fontanellar palpation). CSF-flow was found to be: 1. synchronous with respiration 2. induced by rising intraabdominal (retrograde CSF-pulse) and transfontanellar pressure (orthograde CSF-pulse) 3. predominantly within the cerebral aqueduct, but also found at the foramina of Monro, within the third and fourth ventricles and at the foramen of Magendie. CSF-flow was not detected at the foramina of Luschka or within the lateral ventricles, except adjacent to the foramina of Monro. Dynamic CSF-flow as observed in infants may have important clinical and scientific implications. Examples of this are activity-related ventricular “reflux” of bacteria, erythrocytes, drugs, radionuclides or contrast; the importance of CSF-flow pulses for the development or progression of hydrocephalus; flow dynamics at the fourth ventricular outlet foramina and the study of CSF-pulse wave velocity and regional compliance. These issues are discussed and the new diagnostic approach is compared with other methods of CSF-investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albeck MJ, Børgesen SE, Gjerris F, Schmidt JF, Sørensen PS (1991) Intracranial pressure and cerebrospinal fluid outflow conductance in healthy subjects. J Neurosurg 74:597
Atkinson P, Woodcock JP (1982) Doppler ultrasound and its use in clinical measurement. Academic Press, London, p. 38
Bergstrand G, Bergström M, Nordell B, Ståhlberg F, Ericsson A, Hemmingsson A, Sperber G, Thuomas K-Å, Jung B (1985) Cardiac gated MR imaging of cerebrospinal fluid flow, J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:1003
Bering EA (1955) Choroid plexus and arterial pulsation of cerebrospinal fluid. Demonstration of the choroid plexuses as a cerebrospinal fluid pump. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 73:165
Blomquist HK, Sundin S, Ekstedt J (1986) Cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamic studies in children. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:536
Bradley WG, Whittemore AR, Kortman KE, Watanabe AS, Homyak M, Teresi LM, Davis SJ (1991) Marked cerebrospinal fluid void: indicator of successful shunt in patients with suspected normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Radiology 178:459
Britt RH, Rossi GT (1982) Quantitative analysis of methods for reducing physiological brain pulsations. J Neurosci Methods 6: 219
Cabanes J, Marti J, Orozco M, Beltran A (1983) Bicompartmental analysis of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. Theory and clinical applications. J Neurosurg 59:311
Cardoso ER, Rowan JO, Galbraith S (1983) Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid pulse wave in intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg 59:817
Chattha AS, Delong GR (1975) Sylvian aqueduct syndrome as a sign of acute obstructive hydrocephalus in children. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 38:288
Czosnyka M, Wollk-Laniewski P, Batorski L, Zaworski W (1988) Analysis of intracranial pressure waveform during infusion test. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 93:140
Den Hout van JHW, Bakker CJG, Mali WPTM, Dijk van P, Faber JAJ, Feldberg MAM, Gooskens RHJM, Witkamp TD (1989) Magnetic resonance imaging of the cerebral aqueduct. Signal intensity time curves demonstrated by fast acquisition with multiple excitation (FAME). Invest Radiol 24:855
Di Chiro G, Hammock MK, Bleyer WA (1976) Spinal descent of cerebrospinal fluid in man. Neurology 26:1
Drake JM, Sainte-Rose C, DaSilva M, Hirsch J-F (1991) Cerebrospinal fluid flow dynamics in children with external ventricular drains. Neurosurgery 28:242
Drayer BP, Rosenbaum AE (1978) Studies of the third circulation. Amipaque CT cisternography and ventriculography. J Neurosurg 48:946
du Boulay GH (1966) Pulsatile movements in the CSF pathways. Br J Radiol 39:255
du Boulay G (1972) Specialisation broadens the view. The significance of a CSF pulse. Clin Radiol 23:401
England MA, Wakely J (1991) A colour atlas of the brain and spinal cord. Wolfe, London, p. 77
Enzmann DR, Pelc NJ (1991) Normal flow patterns of intracranial and spinal cerebrospinal fluid defined with phase-contrast cine MR imaging. Radiology 178:467
Feinberg DA, Mark AS (1987) Human brain motion and cerebrospinal fluid circulation demonstrated with MR velocity imaging. Radiology 163:793
Frank E, Buonocore M, Hein L (1990) The use of magnetic resonance imaging to assess slow fluid flow in a model cerebrospinal fluid shunt system. Br J Neurosurg 4:53
Hakim S, Venegas JG, Burton JD (1976) The physics of the cranial cavity, hydrocephalus and normal pressure hydrocephalus: mechanical interpretation and mathematical model. Surg Neurol 5:187
Hatle L, Angelsen B (1985) Blood velocity measurements using the Doppler effect of backscattered ultrasound. In: Doppler ultrasound in cardiology. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, p. 38
Jolesz FA, Patz S, Hawkes RC, Lopez I (1987) Fast imaging of CSF flow/motion patterns using steady-state free precession (SSFP). Invest Radiol 22:761
Kadowaki C, Hara M, Numoto M, Takeuchi K (1987) Factors affecting cerebrospinal fluid flow in a shunt. Br J Neurosurg 1:467
Kaiser AM, Whitelaw AGL (1986) Normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure in the newborn. Neuropediatrics 17:100
Kusske JA, Turner PT, Ojemann GA, Harris AB (1973) Ventriculostomy for the treatment of acute hydrocephalus following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 38:591
Lane B, Kricheff II (1974) Cerebrospinal fluid pulsations at myelography: a videodensitometric study. Radiology 110:579
Levy LM, Di Chiro G (1990) MR phase imaging and cerebrospinal fluid flow in the head and spine. Neuroradiology 32:399
Lorenzo AV, Page LK, Watters GV (1970) Relationship between cerebrospinal fluid formation, absorption and pressure in human hydrocephalus. Brain 93:679
Maki Y, Kokubo Y, Nose T, Yoshii Y (1976) Some characteristic findings of isotope cisternograms in children. J Neurosurg 45:56
Mark AS, Feinberg DA, Brant-Zawadzki MN (1987) Changes in size and magnetic resonance signal intensity of the cerebral CSF spaces during the cardiac cycle as studied by gated, high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 22:290
Mascalchi M, Ciraolo L, Tanfani G, Taverni N, Inzitari D, Siracusa GF, Dal Pozzo GC (1988) Cardiac-gated phase MR imaging of aqueductal CSF flow. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12:923
O'Connell JEA (1970) Cerebrospinal fluid mechanics. Proc R Soc Med 63:507
Quencer RM, Post MJD, Hinks RS (1990) Cine MR in the evaluation of normal and abnormal CSF flow: intracranial and intraspinal studies. Neuroradiology 32:371
Samuels LD, Natelson S, Miller CA (1971) RISA brain scans in children. Movement of radioactive albumin in cerebrospinal fluid aids recognition of disturbances in flow. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 10:109
Shapiro K, Marmarou A, Shulman K (1980) Characterization of clinical CSF dynamics and neural axis compliance using the pressure-volume index: I. The normal pressure-volume index. Ann Neurol 7:508
Shapiro WR, Young DF, Mehta BM (1975) Methotrexate: distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular and lumbar injections. N Engl J Med 293:161
Sherman JL, Citrin CM (1986) Magnetic resonance demonstration of normal CSF flow. AJNR 7:3
Sherman JL, Citrin CM, Gangarosa RE, Bowen BJ (1987) The MR appearance of CSF flow in patients with ventriculomegaly. AJR 148:193
Ståhlberg F, Mogelvang J, Thomsen C, Nordell B, Stubgaard M, Ericsson A, Sperber G, Greitz D, Larsson H, Henriksen O, Persson B (1989) A method for MR quantification of flow velocities in blood and CSF using interleaved gradient-echo pulse sequences. Magn Reson Imaging 7:655
Stehling MK, Firth JL, Worthington BS, Guilfoyle DN, Ordidge RJ, Coxon R, Blamire AM, Gibbs P, Bullock P, Mansfield P (1991) Observation of cerebrospinal fluid flow with echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Radiol 64: 89
Thomsen C, Ståhlberg F, Stubgaard M, Nordell B (1990) Fourier analysis of cerebrospinal fluid flow velocities: MR imaging study. Radiology 177:659
Van Eijndhoven JHM, Avezaat CJJ (1986) Cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and the pulsatile variation in cerebral blood volume: An experimental study in dogs. Neurosurgery 19:507
White DN, Wilson KC, Curry GR, Stevenson RJ (1979) The limitation of pulsatile flow through the aqueduct of Sylvius as a cause of hydrocephalus. J Neurol Sci 42:11
Winkler P, Helmke K (1989) Duplex-scanning of the deep venous drainage in the evaluation of blood flow velocity of the cerebral vascular system in infants. Pediatr Radiol 19:79
Winkler P (1992) Colour-coded echographic flow imaging and spectral analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in meningitis and hemorrhage. Part I. Clinical evidence. Pediatr Radiol 22:24–30
Winkler P, Helmke K (1992) Colour-coded echographic flow imaging and spectral analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Part III. In-vitro study of low flow velocity detection related to decreasing particle concentration (hematocrit) and tube lumen. Pediatr Radiol 22:43–47
Witzleb E (1985) Funktionen des Gefäßsystems. in: Schmidt RF, Thews G (eds) Physiologie des Menschen. Springer, Berlin p 449f
Yamada H, Tajima M, Nagaya M (1975) Effect of respiratory movement on cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in hydrocephalic infants with shunts. J Neurosurg 42:194
Ziegler P (1896) Ueber die Mechanik des normalen und pathologischen Hirndruckes. Arch Klin Chir 53:75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winkler, P. Colour-coded echographic flow imaging and spectral analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in infants. Pediatr Radiol 22, 31–42 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02011606
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02011606