Abstract
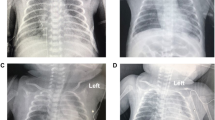
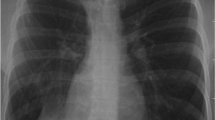
The purpose of this study was to determine whether retention of fetal lung liquid is more prevalent in polyalveolar congenital lobar emphysema than in conventional congenital lobar emphysema. Two patients with congenital lobar emphysema were prospectively identified in a 3-year period. Twenty-five such patients were identified in a retrospective study covering 39 years. Medical records were available for 22 patients who had 23 emphysematous lobes. Both babies from the prospective study and six subjects from the retrospective group had respiratory symptoms and underwent chest X-ray in the first day of life. Six of the eight babies with respiratory symptoms and chest imaging in the first day of life had retention of fetal lung liquid in an emphysematous lobe. All six of these lobes were polyalveolar. The lobe in one child was a polyalveolar lobe but without retained fetal lung liquid, and one child exhibited conventional lobar emphysema also without retained fetal lung liquid. One polyalveolar lobe caused no neonatal symptoms and was not imaged until the child was 3 months old. No baby with conventional lobar emphysema was shown to have retained fetal lung liquid. There seems to be a correlation between polyalveolar lobe and onset of respiratory symptoms in the first day of life. Retention of fetal lung liquid within the affected lobe was documented only in cases of polyalveolar lobe.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tapper D, Schuster S, McBride J, Eraklis A, Wohl ME, Williams A, Reid L (1980) Polyalveolar lobe: anatomic and physiologic parameters and their relationship to congenital lobar emphysema. J Pediatr Surg 15: 931
Hislop A, Reid L (1970) New pathological findings in emphysema of childhood. 1. Polyalveolar lobe with emphysema. Thorax 25: 682
Corbett DP, Washington JE (1971) Respiratory obstruction in the newborn and excess pulmonary fluid. AJR 112: 18
Allen RP, Taylor RL, Reiquam CW (1966) Congenital lobar emphysema with dilated septal lymphatics. Radiology 86: 929
Fraken EA, Buehl I (1966) Infantile lobar emphysema. Report of two cases with unusual roentgenographic manifestation. AJR 98: 354
Fegan CJ, Swischuk LE (1972) The opaque lung in lobar emphysema. AJR 114: 300
Case Records of the Massachusetts General Hospital (1990) N Engl J Med 323: 398
Hedlund GL, Kirks DR (1991) Respiratory system. In: Kirks DR (ed) Practical pediatric imaging: diagnostic radiology of infants and children, 2nd edition. Little, Brown Boston, pp 557–581
Leape LL, Longino LA (1964) Infantile lobar emphysema. Pediatrics 34: 246
Cooney TP, Thurlbeck WM (1982) The radial alveolar count method of Emery and Mithal: a reappraisal. 1. Postnatal lung growth. Thorax 37: 572
Conney TP, Thurlbeck WM (1982) The radial alveolar count method of Emery and Mithal: a reappraisal. 2. Intrauterine and early postnatal lung growth. Thorax 37: 580
Griscom NT, Harris GBC, Wohl MEB, Vawter GF, Eraklis AJ (1969) Fluid-filled lung due to airway obstruction in the newborn. Pediatrics 43: 383
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cleveland, R.H., Weber, B. Retained fetal lung liquid in congenital lobar emphysema: A possible predictor of polyalveolar lobe. Pediatr Radiol 23, 291–295 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02010918
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02010918