Abstract
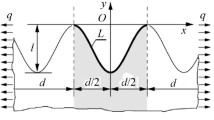
In this paper we consider uniform extension problems for joined two half-planes with different thickness and material behavior and one of which contains an elliptical hole, the other contains a crack. Along the boundary of these half-planes there is a stiffening stringer. Computational formulas are given in power series form by complex variable—pertubation method. Results obtained here give extension to those of “Handbook of stress intensity factors”. Numerical results of special cases in this paper coincide with those of refs. [1], [3].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isida, M., On the determination of stress intensity factors for some common problems,Engng. Fract. Mech.,2 (1973), 61;Methods of Analysis and Solutions of Crack Problems, edited by G. C. Sih, Noordhoff Int. Pub. (1973), 80.
Sih, G. C., P. C. Paris and F. Erdogan, Crack tip stress intensity factors for plane extension and plate bending problems,J. Appl. Mech., Trans. ASME, ser.E, 29 (1962, 306.
Sih, G. C.,Handbook of Stress Intensity Factors, Leheigh Univ., Bethlehem, Pa., U.S.A. (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, O., Shiao-kang, Z. On computations of stress intensity factors for stiffened half planes with imperfections and cracks. Appl Math Mech 6, 119–130 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01874950
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01874950