Summary
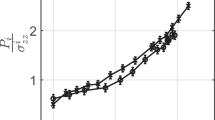
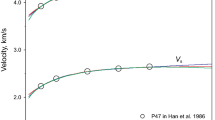
In a series of triaxial experiments we have measuredV p ,V s and volumetric strain simultaneously in dilating dry and saturated rocks. For the first time these data permit quantitative comparison of seismic velocities or their ratio and dilatant volumetric strain. In air-dry samplesV p /V s decreases by a few per cent at strains of 10−3; in saturated materials with high pore pressure,V p /V s increases by a comparable amount. Decreases in seismic velocity ratio are difficult to generate in initially saturated rocks even with low pore pressures and at strain rates of 10−4/sec. A liquid-vapor transition will not produce a significant drop inV p /V s . If dilatancy and fluid flow are responsible for seismic travel time anomalies prior to earthquakes, our results suggest that such anomalies will occur only in regions where pore fluid source to sink dimensions are of the order of 10 km or more, or in regions where the rocks are not saturated to begin with.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. N. Semenov,Variations in the travel time of transverse and longitudinal waves before violent earthquakes, Izv. Phys. Solid Earth3 (1969), 245.
I. L. Nersesov, A. N. Semenov andI. G. Simbireva,Space-time distribution of the travel time ratios of transverse and longitudinal waves in the Garm area, inThe Physical Basis of Foreshocks (Nauka Publ., Moscow 1969).
D. L. Anderson andJ. H. Whitcomb.The dilatancy-diffusion model of earthquake prediction, in Proc. of Conf. on Tectonic Problems of the San Andreas Fault System, edited byR. L. Kovach andA. Nur (Stanford University Press, California 1973), p. 417.
Y. P. Aggarwal, L. Sykes, D. W. Simpson andP. G. Richards,Spatial and temporal variations in t s /t p and in P-wave residuals at Blue Mountain Lake, New York: Application to earthquake prediction (Preprint, 1974).
A. Nur,Dilatancy, pore fluids, and premonitory variations of t s /t p travel times, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer.62 (1972), 1217.
C. H. Scholz, L. R. Sykes andY. P. Aggarwal,Earthquake prediction: A physical basis, Science181 (1973), 803.
B. Bonner,Shear wave birefringence in dilating granite, Geophys. Res. Lett.1 (1974), 217 and pers. comms.
D. Tocher,Anisotropy in rocks under simple compression, AGU Trans.38 (1957), 89.
S. Matsushima,Variation of the elastic wave velocities of rocks in the process of deformation and fracture under high pressure. Dis. Prev. Res. Inst. Bull32 (1960), 2.
R. E. Thill,Acoustic methods for monitoring failure in rock, in Proc. of the 14th Sympos. on Rock Mech. edited byH. R. Hardy,Jr. andR. Stefanko (Am. Soc. Civil. Eng., N. Y., 1973).
I. N. Gupta,Seismic velocities in rock subjected to axial loading up to shear fracture, J. Geophys. Res.78 (1973), 6936.
F. Birch,The velocity of compressional waves in rocks to 10 kilobars, J. Geophys. Res.66 (1961), 2199.
W. F. Brace, J. B. Walsh andW. T. Frangos,Permeability of granite under high pressure, J. Geophys. Res.73 (1968), 2225.
H. S. Carslaw andJ. C. Jaeger,Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd ed. (Oxford Univ. Press 1959), 510 pp.
W. F. Brace, A. S. Orange andT. R. Madden,The effect of pressure on the electrical resistivity of water-saturated crystalline rocks, J. Geophys. Res.70 (1965), 5669.
W. F. Brace andA. S. Orange,Further studies of the effects of pressure on electrical resistivity of rocks, J. Geophys. Res.73 (1968), 5407.
K. Hadley,Laboratory investigation of dilatancy and motion on fault surfaces at low confining pressures, in Proc. of Conf. on Tectonic Problems of the San Andreas Fault System, edited byR. L. Kovach andA. Nur (Stanford University Press, California 1973), p. 427.
W. F. Brace, B. W. Paulding, Jr., andC. Scholz, Dilatancy in the fracture of crystalline rocks, J. Geophys. Res.71 (1966), 3939.
W. F. Brace andR. J. Martin III,A test of the law of effective stress for crystalline rocks of low porosity, Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci.5 (1968), 415.
C. H. Scholz andR. Kranz,Notes on dilatancy recovery, J. Geophys. Res.79 (1974), 2132.
B. T. Brady,Theory of earthquakes, Part I: A scale independent theory of rock failure, Pure and Appl. Geophys., in press.
R. J. O'Connell andB. Budiansky,Seismic velocities in dry and saturated cracked solids, Preprint, 1974.
D. L. Anderson andJ. H. Whitcomb,Time dependent seismology, Preprint, 1974.
E. W. Washburn (editor),International Critical Tables: Vol. V (McGraw-Hill, N.Y. 1929, for the National Research Council).
G. C. Kennedy andW. T. Holster,Pressure-volume-temperature and phase relations of water and carbon dioxide, inHandbook of Physical Constants, Geol. Soc. Amer. Mem.97 (1966).
T. L. de Fazio, K. Aki andJ. Alba,Solid earth tide and observed change in the in situseismic velocity, J. Geophys. Res.78 (1973), 1319.
P. Reasenberg andK. Aki,A precise, continuous measurement of seismic velocity for monitoring in situstress, J. Geophys. Res.79 (1974), 399.
J. B. Walsh,The effect of cracks on the compressibility of rock, J. Geophys. Res.70 (1965), 381.
J. B. Walsh,The effect of cracks on the uniaxial elastic compression of rocks, J. Geophys. Res.70 (1965), 399.
J. B. Walsh,The effect of cracks on Poisson's ratio, J. Geophys. Res.70 (1965), 5249.
T. C. Hanks,Constraints on the dilatancy-diffusion model of the earthquake mechanism, J. Geophys Res.79 (1974), 3023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadley, K. V p /V s anomalies in dilatant rock samples. PAGEOPH 113, 1–23 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01592894
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01592894