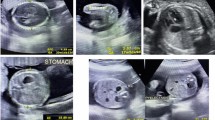
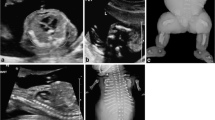
Abstract
Based on the findings in 12 patients with skeletal dysplasia diagnosed antenatally, the authors propose a tailored approach to the evaluation of foetuses with shortened long bones, depending on the time of discovery, the degree of shortening and the associated findings. During the second trimester, a very short femur [2 standard deviations (SD) −5 mm and less] most probably corresponds to a bone dysplasia, although the differential diagnosis is mainly early intra-uterine growth retardation, and the foetal skeleton should be surveyed completely in order to find supplementary features suggestive of dwarfism. Anomalies of long bones in their shape, thickness or contour, or spinal ossification disorders or under-mineralisation (best evaluated at the level of calvarial bones) are most helpful in determining the type of dysplasia. A short femur (between 2 SD and 2 SD −4 mm) may indicate growth retardation, a chromosomal anomaly or dwarfism. Follow-up examinations are mandatory in order to differentiate between them. During the third trimester a very short femur may indicate a bone dysplasia and the work-up should be the same as in the second trimester. A short femur may correspond to dwarfism of late development, a growth-retarded foetus or constitutional shortness. Various ratios, especially that of the femur/foot, are helpful in differentiating between them. In case of previous family history, a short or very short femur usually indicates recurrence of the dwarfism. In all cases of antenatal diagnosis, confirmation of the sonographic findings should be obtained either by foetal or neonatal radiographs. The approach proposed by the authors should provide sufficient information to counsel the family not only for the ongoing pregnancy but also for subsequent ones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurz AB, Needlman L, Wapner RJ, Hilpert PH et al (1990) Usefulness of a short femur in the in utero diagnosis of skeletal dysplasias. Radiology 177: 197–200
Goncalves L, Jeanty P (1994) Fetal biometry of skeletal dysplasias: a multicentric study. J Ultrasound Med 13: 767–775
Driscoll DA (1991) Fetal limbs: normal and abnormal. Semin Roentgenol 26: 12–20
Spirt BA, Oliphant M, Gottlieb RH, Gordon LP (1990) Prenatal sonographic evaluation of short-limbed dwarfism: an algorithmic approach. Radiographics 10: 217–230
Sanders RC, Blakemore K (1989) Lethal fetal anomalies: sonographic demonstration. Radiology 172:1–6
Pretorius DH, Rumack CM, Manco-Johnson ML, Manchester D, Meier P, Bramble J, Cllewell W (1986) Specific skeletal dysplasias in utero: sonographic diagnosis. Radiology 159: 237–242
Romero R, Athanassiadis AP, Jeanty P (1989) Fetal skeletal anomalies. Radiol Clin North Am 28: 75–99
Bronshtein N, Keret D, Deutsch M, Liberson A, Bar Chava I (1993) Transvaginal sonographic detection of skeletal anomalies in the first and early trimesters. Prenat Diagn 13: 597–601
Patarelli P, Pretorius D, Edwards DK (1990) IURG mimicking skeletal dysplasia on antenatal US. J Ultrasound Med 9:737–739
Munoz C, Filly RA, Golbus MS (1990) Osteogenesis imperfecta type II: prenatal sonographic diagnosis. Radiology 174:181–185
Bulas DI, Stern HJ, Rosenbaum KN, Fonda JA, Glass RBJ, Tifft C (1994) Variable prenatal appearance of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Ultrasound Med 13:419–427
Brous JTJ, van der Harten HJ, Wladimoroff JW van Geijn HP, Dijkstra PF, Exalto N, Reuss A et al (1988) Prenatal US diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Obstet Gynecol 159: 176–181
Maroteaux P (1982) Maladies osseuses de l'enfant. Flammarion Médecine Sciences, Paris
Taybi H, Lachman RS (1990) Radiology of syndromes, metabolic disorders and skeletal dysplasia, 3rd edn. Year Book
Mahony BS, Filly RA, Cooperberg PL (1984) Antenatal diagnosis of achondrogenesis. J Ultrasound Med 3: 333–335
Skiptunas SM, Weiner S (1987) Early prenatal diagnosis of asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jenne's syndrome). Value of fetal thoracic measurement. J Ultrasound Med 6: 41–43
Benaceraff BR, Cnann A, Gelman R, Laboda LA, Frigoletto FD (1989) Can sonographers reliably identify anatomic features associated with Down syndrome in fetuses. Radioloy 173: 377–380
Lynch L, Barkowitz GS, Chitkara U Wilkins IA, Mehalek KE, Berkowicz RL (1989) US detection of Down syndrome: is it really possible? Obstet Gynecol 73: 267–270
Zimmer EZ, Divon MY (1992) Sonographic diagnosis of IUGR — macrosomia. Clin Obstet Gynecol 35: 172–184
Campbell J, Henderson RGN, Campbell S (1988) The fetal femur/foot ratio: a new parameter to assess dysplastic limb reduction. Obstet Gynecol 72: 181–184
Winter RM, Sandin BM, Mitchell RA, Price AB (1984) The radiology of stillbirths and neonatal deaths. Br J Obstet Gynecol 91: 762–765
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Jacques Sauvegrain.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avni, E.F., Rypens, F., Zappa, M. et al. Antenatal diagnosis of short-limb dwarfism: Sonographic approach. Pediatr Radiol 26, 171–178 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01405292
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01405292