Abstract
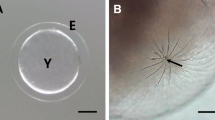
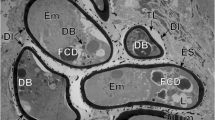
Transmission electron microscope studies on the morphology of subitaneous and diapause eggs in the neustonic copepodPontella mediterranea, collected in coastal waters of the Gulf of Naples from May to December 1986, revealed striking structural differences between the two egg types and the existence of a third egg type that was morphologically similar to a diapause egg but which hatched within 2 to 3 d. In smooth, subitaneous eggs the plasma membrane was surrounded by a thin outer chorion as compared to the thick and highly complex four-layer structure enveloping subitaneous eggs with short spines, and diapause eggs. This coat may be assembled just prior to or after deposition since the morphology of developing oocytes was similar in females laying either subitaneous or diapause eggs. The only other major structural difference between the two egg types was the presence of numerous, disc-like bodies in the ooplasm of diapause eggs. Development was arrested for at least 3 mo, prior to the initiation of the first cleavage, suggesting that these eggs were kept dormant by some endogenous and, possibly, structural mechanism preceeding the termination of diapause.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Arnaud, J., Brunet, M., Mazza, J. (1978). Studies on the midgut ofCentropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida). I. Structural and ultrastructural data. Cell Tissue Res. 187: 333–353
Birge, E. A., Juday, C. (1908). A summer resting stage in the development ofCyclops bicuspidatus Claus. Trans. Wis. Acad. Sci., Arts Lett. 23: 1–9
Blades-Eckelbarger, P. I. (1986). Aspects of internal anatomy and reproduction in the copepoda. Proc. 2nd int Conf. Copepoda, Ottawa. Syllogeus (Nat. Mus. Can.) 58: 26–50
Brewer, R. H. (1964). The phenology ofDiaptomus stagnalis (Copepoda: Calanoida): the development and the hatching of the egg stage. Physiol. Zoöl. 37: 1–20
Bunner, H. C., Halcrow, K. (1977). Experimental induction of ephippia byDaphnia magna Straus (Cladocera). Crustaceana 32: 77–86
Champalbert, G. (1969). L'hyponeuston dans le Golfe de Marseille. Téthys 1: 585–666
Cheung, T. S. (1966). The development of egg membranes and egg attachment in the shore crab,Carcinus maenas, and some related decapods. J. mar. biol. Ass. U. K. 46: 373–400
Drinkwater, L. E. Crowe, J. H. (1987). Regulation of embryonic diapause inArtemia: environmental and physiological signals. J. exp. Zool. 241: 297–307
Grice, G. D., Gibson, V. R. (1981). Hatching of eggs ofPontella mediterranea Claus (Copepoda: Calanoida). Vie Milieu 31: 49–51
Grice, G. D., Lawson, T. J. (1976). Resting eggs in the marine calanoid copepod,Labidocera aestiva Wheeler. Crustaceana 30: 9–12
Grice, G. D., Marcus, N. H. (1981). Dormant eggs of marine copepods. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 19: 125–140
Kasahara, S., Uye, S., Onbé, T. (1974). Calanoid copepod eggs in sea-bottom muds. Mar. Biol. 26: 167–171
Marcus, N. H. (1979). On the population biology and nature of diapause ofLabidocera aestiva (Copepoda: Calanoida). Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 157: 297–305
Marcus, N. H. (1980) Photoperiodic control of diapause in the marine calanoid copepodLabidocera aestiva. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 159: 311–318
Marcus, N. H. (1982a) The reversibility of subitaneous and diapause egg production by individual females ofLabidocera aestiva (Copepoda: Calanoida). Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 162: 39–44
Marcus, N. H. (1982b) Photoperiodic and temperature regulation of diapause ofLabidocera aestiva (Copepoda: Calanoida). Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 162: 45–52
Marcus, N. H. (1984a) Variation in the diapause response ofLabidocera aestiva (Copepoda: Calanoida) from different latitudes and its importance in the evolutionary process. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 166: 127–139
Marcus, N. H. (1984b) Recruitment of copepod nauplii into the plankton: importance of diapause eggs and benthic processes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 15: 47–54
Reynolds, E. S. (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as electronopaque stain in electron-microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17: 208–212
Sars, G. O. (1908) Freshwater Copepoda from Victoria, Southern Australia. Arch. math. Naturv. 29: 1–24
Sazhina, L. I. (1968) On hibernating eggs of marine calanoida. Zool. Zh. 47: 1554–1556 [in Russ.]
Stross, R. G., Hill, J. C. (1968) Photoperiod control of winter diapause in the fresh-water crustacean,Daphnia. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 134: 176–198
Uye, S. (1980) Development of neritic copepodsAcartia clausi andA. steueri. I. Some environmental factors affecting egg development and the nature of resting eggs. Bull. Plankton Soc. Japan 27: 1–9
Uye, S. (1985) Resting egg production as a life history strategy of marine planktonic copepods. Bull. mar. Sci. 37: 440–449
Uye, S., Kasahara, S., Onbe, T. (1979) Calanoid copepod eggs in sea-bottom muds. IV. Effects of some environmental factors on the hatching of resting eggs. Mar. Biol. 51: 151–156
Watson, N. H. F., Smallman, B. N. (1971) The role of photoperiod and temperature in the induction and termination of an arrested development in two species of freshwater cyclopid copepods. Can. J. Zool. 49: 855–862
Zillioux, E. J., Gonzalez, J. G. (1972) Egg dormancy in the neritic calanoid copepod and its implications to overwintering in boreal waters. Archo. Oceanogr. Limnol. (Eur. Mar. Biol. Symp.) 5: 217–230
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Sará, Genova
Dedicated to B. Scotto di Carlo, teacher and friend, who died tragically at sea during the course of a cruise on December 15, 1988
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santella, L., Ianora, A. Subitaneous and diapause eggs in Mediterranean populations ofPontella mediterranea (Copepoda: Calanoida): A morphological study. Mar. Biol. 105, 83–90 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01344273
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01344273