Abstract
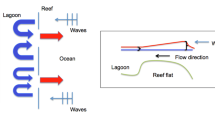
The slicks of tidally induced fronts and Langmuir circulations were studied near Bowden Reef, Great Barrier Reef, in December 1987. There were two components to the study: (1) a description of physical oceanography adjacent to the reef; (2) sampling for planktonic organisms, designs being stratified according to hydrology. Tidal fronts extended 1 to 2 km from the reef outside the lagoon. Fish of a variety of developmental forms and zooplankton were most abundant in slicks of fronts. Sixteen to 81% of fish that were captured were presettlement reef-fishes. There was an unclear relationship between the presence of slicks of Langmuir circulations and abundance of fish in the lagoon. This relationship was largely because well developed atherinids and recently hatched pomacentrids showed no predictable relationship with the presence of windrows. Jellyfish,Aurelia aurita, were found in extremely high concentrations in the slicks of Langmuir circulations; small carangids were associated with jellyfish. Movements of fronts were influenced by the tide and wind. In some conditions we observed fronts to change position as the tide reversed direction. Fronts that were orientated offshore (1 to 2 km), were observed to rotate and align with the reef. Because of a “halo” of oceanographic features such as tidal fronts, the reef may be a larger target for presettlement fishes than its topography would suggest. It is argued that some organisms are advected into slicks, while others respond to high concentrations of zooplanktonic food and remain in slicks. Localised oceanographic features may also affect the settlement patterns of fishes on reefs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Alldredge, A. L., Hamner, W. M. (1980). Recurring aggregation of zooplankton by a tidal current. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 10: 31–37
Barstow, S. F. (1983). The ecology of Langmuir circulation: a review. Mar. envirl Res. 9: 211–236
Church, J. A., Andrews, J. C., Boland, F. M. (1985). Tidal currents in the central Great Barrier Reef. Contin. Shelf Res. 4: 515–531
Deleersnijder, E., Wolanski, E., Norro, A. (1989). Numerical simulation of the three-dimensional tidal circulation in an island wake. In: G. M. Carlomago, Brebbia, C. A. (eds.) Computer and experiments in fluid flow. Springer-Verlag, New York, p. 355–381
Dight, I. J., James, M. K., Bode, L. (1989). Models of larval dispersal within the central Great Barrier Reef: patterns of connectivity and their implications for management. Proc. 6th int. coral Reef Symp. 3: 217–244. [Choat, J. H. et al. (eds.) Sixth International Coral Reef Symposium Committee, Townsville]
Doherty, P. J. (1983). Diel, lunar and seasonal rhythms in the reproduction of two tropical damselfishes:Pomacentrus flavicauda andP. wardi. Mar. Biol. 75: 215–224
Doherty, P. J. (1987) Light-traps: selective but useful devices for quantifying the distributions and abundance of larval fishes. Bull. mar. Sci. 41: 423–431
Doherty, P. J., Williams, D. McB. (1988). The replenishment of coral reef fish populations. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 26: 487–551
Faller, A. J., Auer, S. J. (1988). The roles of Langmuir circulations in the dispersion of surface tracers. J. phys. Oceanogr. 18: 1108–1123
Faller, A. J., Woodcock, A. H. (1964). The spacing of windrows ofSargassum in the ocean. J. mar. Res. 22: 22–29
Hamner, W. M., Schneider, D. (1986). Regularly spaced rows of medusae in the Bering Sea: role of Langmuir circulation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31: 171–177
Kingsford, M. J. (1988). The early life history of fish in coastal waters of northern New Zealand: a review. N.Z. Jl mar. Freshwat. Res. 22: 463–479
Kingsford, M. J. (1990). Linear oceanographic features: a focus for research on recruitment processes. Aust. J. Ecol. 15: 10–20
Kingsford, M. J., Choat, J. H. (1985). The fauna associated with drift algae captured with a plankton-mesh purse seine net. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30: 618–630
Kingsford, M. J., Choat, J. H. (1986). Influence of surface slicks on the distribution and movements of small fish. Mar. Biol. 91: 161–171
Kingsford, M. J., Choat, J. H. (1989). Horizontal distribution patterns of presettlement reef fish: are they influenced by the proximity of reefs? Mar. Biol. 101: 285–297
Kingsford, M. J., MacDiarmid, A. B. (1988). Interrelationships between planktivorous reef fish and zooplankton in temperate waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 48: 103–117
Le Fèvre, J. (1986). Aspects of the biology of frontal systems. Adv. mar. Biol. 23: 163–299
Leis, J. M. (1981). Distribution of fish larvae around Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef: coral reef lagoon as a refuge? Proc. 4th int. coral Reef Symp. 2: 471–477
Leis, J. M. (1986). Vertical and horizontal distribution of fish larvae near coral reefs at Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Biol. 90: 505–516
Leis, J. M. (in press). The pelagic stage of reef fishes: the larval biology of coral reef fishes. In: Sale P. F. (ed.) Ecology of coral reef fish. Academic Press, New York
Leis, J. M., Goldman, B. (1984). A preliminary distributional study of fish larvae near a ribbon coral reef in the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 2: 197–203
Leis, J. M., Goldman, B. (1987). Composition and distribution of larval fish assemblages in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon, near Lizard Island, Australia. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 38: 211–223
Leis, J. M., Rennis, D. S. (1983). The larvae of Indo-Pacific coral reef fishes. New South Wales University Press, Sydney
Milward, N. E., Hartwick, R. F. (1986). Temporal and spatial distribution of fish larvae across the continental shelf lagoon of the central Great Barrier Reef. In: Uyeno, T., Arai, R., Tanaiuchi, T., Matsura, K. (eds.) Indo-Pacific fish biology: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Indo-Pacific Fishes. Ichthyological Society of Japan, Tokyo, p. 748–758
Möller, H. (1980). Scyphomedusae as predators and food competitors of larvae fish. Meeresforsch. Rep. mar. Res. 28: 90–100 (Ber. dt. wiss. Kommn Meeresforsch.)
Oliver, J. K., Willis, B. L. (1987). Coral-spawn slicks in the Great Barrier Reef: preliminary observations. Mar. Biol. 94: 521–529
Owen, R. W. (1981). Fronts and eddies in the sea: mechanisms, interactions and biological effects. In: A. R. Longhurst (ed.) Analysis of marine ecosystems. Academic Press, London, p. 197–233
Provis, D.G., Lennon, G. W. (1983). Eddy viscosity and tidal cycles in a shallow sea. Estuar., cstl Shelf Sci. 16: 351–361
Sakamoto, W., Tanaka, Y. (1986). Water temperature patterns and distributions of fish eggs and larvae in the vicinity of shallow sea front. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 52: 767–776
Sale, P. F. (1980). The ecology of fishes on coral reefs. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 18: 367–421
Schmitt, P. D. (1986). Feeding by larvae ofHypoatherina tropicalis (Pisces: Atherinidae) and its relation to prey availability in One Tree Lagoon, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Envir. Biol. Fish. 16: 79–94
Shanks, A. L. (1983). Surface slicks associated with tidally forced internal waves may transport pelagic larvae of benthic invertebrates and fishes shoreward. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 13: 311–315
Shanks, A. L. (1986). Vertical migration and cross-shelf dispersal of larvalCancer spp. andRandallia ornata (Crustacea: Brachyura) off the coast of southern California. Mar. Biol. 92: 189–199
Turner, J. T., Tester, P. A., Hettler, W. F. (1985). Zooplankton feeding ecology: a laboratory study of predation on fish eggs and larvae by the copepodsAnomalocera ornata andCentropages typicus. Mar. Biol. 90: 1–8
Underwood, A. J. (1981). Techniques of analysis of variance in experimental marine biology and ecology. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 19: 513–605
Van der Veer, H. W., Oorthuysen, W. (1985). Abundance, growth and food demand of the scyphomedusaAurelia aurita in the western Wadden Sea. Neth. J. Sea Res. 19: 38–44
Williams, D. McB., Dixon, P., English, S. (1988). Cross-shelf distribution of copepods and fish larvae across the central Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Biol. 99: 577–589
Williams, D. McB., Wolanski, E., Andrews, J. C. (1984). Transport mechanisms and the potential movement of planktonic larvae in the central region of the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 3: 229–236
Wolanski, E. (1986). Island wakes and internal tides in stratified shelf waters. Annls Geophysicae 4: 425–440
Wolanski, E., Burrage, D., King, B. (1989). Trapping and dispersion of coral eggs around Bowden Reef, Great Barrier Reef, following a mass coral spawning. Contin. Shelf Res. 9: 479–496
Wolanski, E., Drew, E., Abel, K. M., O'Brien, J. (1988). Tidal jets, nutrient upwelling and their influence on the productivity of the algaHalimeda in the ribbon reefs, Great Barrier Reef. Estuar. cstl Shelf Sci. 26: 169–201
Wolanski, E., Hamner, W. M. (1988). Topographically controlled fronts in the ocean and their biological influence. Science, N. Y. 241: 177–181
Wolanski, E., Imberger, J., Heron, M. L. (1984). Island wakes in shallow coastal waters. J. geophys. Res. 89: 553–569
Wolanski, E., Thompson, R. E. (1984). Wind-driven circulation on the northern Great Barrier Reef continental shelf in summer. Estuar., cstl Shelf Sci. 18: 271–289
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G.F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kingsford, M.J., Wolanski, E. & Choat, J.H. Influence of tidally induced fronts and Langmuir circulations on distribution and movements of presettlement fishes around a coral reef. Mar. Biol. 109, 167–180 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01320244
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01320244