Summary
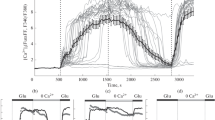
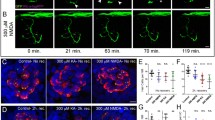
Exposure of cultured cerebellar neurons to the histamine H1 receptor antagonist terfenadine resulted in neuronal degeneration and death. Terfenadine neurotoxicity was dependent upon concentration and time of exposure. After 2h exposure, 20µM terfenadine reduced the number of surviving neurons by 75%, and as low as 10nM terfenadine induced significant neurotoxicity after 5 days of exposure. Neuronal sensitivity to terfenadine changed with age in culture, and at 25 days in culture neurons appeared to be much less sensitive than at 5 or 9–17 days in culture. Neurotoxicity by terfenadine could not be prevented by high concentrations of histamine (5 mM), but it was significantly delayed by blocking NMDA or non-NMDA glutamate receptors with MK-801 or CNQX respectively, suggesting the involvement of excitatory transmission mediated by glutamate in the neurotoxicity induced by terfenadine in these neurons. We also found that the presence of terfenadine (5,µM) unveiled the potential excitotoxicity of the non-NMDA receptor agonist AMPA (100µM), and reduced the concentration of glutamate necessary to induce excitotoxicity, compared to untreated cultures. These results suggest a role for terfenadine in the modulation of the excitotoxic response mediated in cerebellar neurons through ionotropic glutamate receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekkers JM (1993) Enhancement by histamine of NMDA-mediated synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Science 261: 104–106
Brown RE, Reymann KG (1996) Histamine H3 receptor-mediated depression of synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus of the rat in vitro. J Physiol 496: 175–184
Didier M, Bursztajn S, Adamec E, Passani L, Nixon RA, Coyle JT, Wei JY, Berman SA (1996) DNA strand breaks induced by sustained glutamate excitotoxicity in primary neuronal cultures. J Neurosci 16: 2238–2250
Dillon-Carter O, Chuang D-M (1989) Homologous desensitization of muscarinic cholinergic, histaminergic, adrenergic, and serotonergic receptors coupled to phospholipase C in cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem 52: 598–603
Hack NJ, Sluiter AA, Baläzs R (1995) AMPA receptors in cerebellar granule cells during development in culture. Dev Brain Res 87: 55–61
Hollmann M, Heinemann S (1994) Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 17: 31–108
Hösli E, Hösli L (1984) Autoradiographic localization of binding sites for [3H] histamine and H1- and H2 antagonists on cultured neurons and glial cells. Neuroscience 13: 863–870
Inoue I, Yanai K, Kitamura D, Taniuchi I, Kobayashi T, Niimura K, Watanabe T, Watanabe T (1996) Impaired locomotor activity and exploratory behavior in mice lacking histamine H1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 13316–13320
Langlais PJ, Zhang SX, Weilersbacher G, Hough LB, Barke KE (1994) Histaminemediated neuronal death in a rat model of Wernicke's encephalopathy. J Neurosci Res 38: 565–574
McTavish D, Goa KL, Ferrill M (1990) Terfenadine: an updated review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 39: 552–574
Nicoletti F, Wroblewski JT, Novelli A, Alho H, Guidotti A, Costa E (1986) The activation of inositol phospholipid metabolism as a signal-transducing system for excitatory amino acids in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci 6: 1905–1911
Novelli A, Reilly JA, Lysko PG, Henneberry RC (1988) Glutamate becomes neurotoxic via the N-Methyl-D-Aspartate receptor when intracellular energy levels are reduced. Brain Res 451: 205–212
Palacios JM, Wamsley JK, Kuhar MJ (1981) The distribution of histamine H1 receptors in the rat brain: an autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 6: 15–37
Panula P, Takagi H, Inagaki N, Yamatodani A, Tohyama M, Wada H, Kotilainen E (1993) Histamine-containing nerve fibers innervate human cerebellum. Neurosci Lett 160: 53–56
Pollard H, Schwartz JC (1987) Histamine neuronal pathways and their function. Trends Neurosci 10: 86–89
Prell GD, Green JP (1986) Histamine as neuroregulator. Annu Rev Neurosci 9: 209–254
Rodríguez FJ, Iluch M, Dot J, Blanco I, Rodríguez-Álvarez J (1997) Histamine modulation of glutamate release from hippocampal synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol 323: 283–286
Schwartz JC, Arrang J-M, Garbarg M, Pollard H, Ruat M (1991)Histaminergic transmission in the mammalian brain. Physiol Rev 71:1–51
Schwartz JC, Arrang J-M, Garbarg M, Traiffort E (1995) Histamine. In: BloomFE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 397–405
Sharma HS, Nyberg F, Cervos-Navarro J, Dey PK (1992) Histamine modulates heat stress-induced changes in blood brain barrier permeability, cerebral blood flow, brain edema and serotonin levels: an experimental study in conscious young rats. Neuroscience 50: 445–454
Thomas JW, Novelli A, Tao-Cheng JH, Henneberry RC, Smith HH, Banner C (1989) Developmental induction of glutaminase in primary cultures of cerebella granule cells. Mot Brain Res 6: 47–54
Vorobjev VS, Sharonova IN, Walsh IB, Haas HL (1993) Histamine potentiates NMethyl-D-Aspartate responses in acutely isolated hippocampal neurons. Neuron 11: 837–844
Xu J, Chuang D-M (1987) Serotonergic adrenergic and histaminergic receptors coupled to phospholipase C in cultured granule cells of rats. J Neurochem 36: 2353–2358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz-Trelles, R., Solana-López, A., Fernández-González, J.R. et al. Terfenadine induces toxicity in cultured cerebellar neurons: A role for glutamate receptors. Amino Acids 16, 59–70 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01318885
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01318885