Abstract
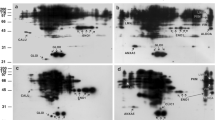
The treatment of mouse eggs with phorbol esters and diacylglycerol inhibits sperm peretration and results in biochemical modification of the zona pellucida. In this report, we have demonstrated the presence of protein kinase C (PKC) activity in mouse eggs as determined by 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate (TPA) dependent in vivo and in vitro protein phosphorylation in mouse eggs. When mouse eggs were radiolabeled with [32P]phosphate and treated with TPA, two specific proteins, 70 and 20 kDa, were phosphorylated. The 70-kDa protein was also phosphorylated in vitro by endogenous PKC. In addition, we have shown that exogenous PKC induced the in vitro phosphorylation of 70-, 55-, and 20-kDa proteins in egg extract. The 70-kDa protein was also phosphorylated in vitro after treatment of the cytosol fraction of mouse eggs with TPA, suggesting that this protein might be a specific substrate for PKC and that it is located in the cytosol. These results demonstrate that mouse eggs contain PKC activity and suggest that PKC-catalyzed protein phosphorylation of specific proteins might be involved in the regulation of egg-induced modification of the zona pellucida.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros C, Yanagimachi R: Polyspermy-preventing mechanisms in the golden hamster egg. J Exp Zool 1972;180:251–266
Inoue M, Wolf DP: Sperm binding characteristics of the murine zone pellucida. Biol Reprod 1975;13:340–346
Bleil JD, Wassarman PM: Mammalian sperm-egg interaction: Identification of a glycoprotein in mouse egg zonae pellucidae possessing receptor activity for sperm. Cell 1980; 20:873–882
Bleil JD, Wassarman PM: Sperm-egg interactions in the mouse: Sequence of events and induction of the acrosome reaction by a zona pellucida glycoprotein. Dev Biol 1983; 95:317–324
Vacquier VD: The isolation of intact cortical granules from sea urchin eggs: Calcium ions trigger granule discharge. Dev Biol 1975;43:62–73
Epel D: Mechanism of activation of sperm and egg during fertilization of sea urchin gametes. Curr Top Dev Biol 1978; 12:185–246
Jaffe LF: The role of calcium explosions, waves, and pulses in activating eggs.In Biology of Fertilization, Vol. 1, CB Metz, A. Monroy (eds). New York, Academic Press, 1985, pp 127–165
Turner PR, Sheetz MP, Jaffe LA: Fertilization increases the polyphosphoinositide content of sea urchin eggs. Nature (London) 1984;310:414–415
Whitaker M, Irvine RF: Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate microinjection activates sea urchin eggs. Nature (London) 1984;312: 636–639
Turner PR, Jaffe LA, Fein A: Regulation of cortical vesicle exocytosis in sea urchin eggs by inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and GTP-binding protein. J Cell Biol 1986;102:70–76
Kurasawa S, Schultz RM, Kopf GS: Egg-induced modifications of the zona pellucida of the mouse eggs: Effects of microinjected inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate. Dev Biol 1989; 133:295–304
Creutz CE, Dowling LG, Sando JJ, Villar-Palasi C, Whipple JH, Zaks WJ: Characterization of the chromobindins: Soluble proteins that binds to the chromaffin granule membrane in the presence of Ca2+. J Biol Chem 1983;258:14664–14674
Summers TA, Creutz CE: Phosphorylation of a chromaffin granule-binding protein by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 1985;260:2437–2443
Takai Y, Kikkawa U, Kaibuchi K, Nishizuka Y: Membrane phospholipid metabolism and signal transduction for protein phosphorylation. Adv Cyclic Nucl Prot Phos Res 1984;18: 119–154
Cuthbertson KSR, Cobbold PH: Phorbol esters and sperm activate mouse oocytes by inducing sustained oscillations in cell Ca2+. Nature (London) 1985;316:541–542
Endo Y, Schultz RM, Kopf GS: Effects of phorbol esters and a diacylglycerol on mouse eggs: Inhibition of fertilization and modification of the zona pellucida. Dev Biol 1987; 119:199–209
Endo Y, Mattei P, Kopf GS, Schultz RM: Effects of phorbol ester on mouse eggs: Dissociation of sperm receptor activity from acrosome reaction-inducing activity of the mouse zona pellucida protein, ZP3. Dev Biol 1987;123:574–577
Yamamura H, Ota N, Yamamoto H, Umeda Y, Oosugi H, Takagishi Y, Hidaka H: Immunocytochemical demonstration of protein kinase C isozymes in mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Presented at the 30th annual meeting of Japanese Society of Teratology, Miyazaki, Japan, 1990
Bornslaeger EA, Poueymirou WT, Mattei P, Schultz RM: Effects of protein kinase C activators on germinal vesicle breakdown and polar body emission of mouse oocytes. Exp Cell Res 1986;165:507–517
Endo Y, Kopf, GS, Schultz RM: Stage-specific changes in protein phosphorylation accompanying meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes and fertilization of mouse eggs. J Exp Zool 1986;239:401–409
Toyoda Y, Chang MC: Fertilization of rat eggs in vitro by epididymal spermatozoa and the development of eggs following transfer. J Reprod Fertil 1974;36:9–22
O'Farrell PH: High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem 1975;250:4007–4021
Hirai M, Shimizu N: Stimulation of a Mr 80,000 protein phosphorylation by EGF in EGF receptor-hyperproducing human tumor cells. J Cell Physiol 1989;139:9–17
Hirai M, Gamou S, Kobayashi M, Shimizu N: Lung cancer cells often express high levels of protein kinase C activity. Jpn J Cancer Res (Gann) 1989;80:204–208
Blackshear PJ, Wen L, Glynn BP, Witters LA: Protein kinase C-stimulated phosphorylation in vitro of a Mr 80,000 protein phosphorylated in response to phorbol esters and growth factors in intact fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 1986;261: 1459–1469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Endo, Y., Komatsu, S., Hirai, M. et al. Protein kinase C activity and protein phosphorylation in mouse eggs. J Assist Reprod Genet 8, 160–166 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01131708
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01131708