Abstract
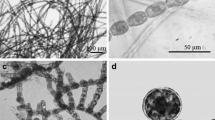
The effects of cold-dark conditions on excystment ofAlexandriuin pseudogonyaulax (Biecheler) Horiguchi ex Yuki et Fukuyo (Gonyaulacales: Dinophyceae) resting cysts were studied for different lengths of time (0 to 120 d). Cyst populations of the same age were obtained by incubating a culture in a diluted growth medium. Cysts that were not exposed to cold-dark conditions showed a long dormancy period and low germination success. A high percentage of excystment, together with a rather synchronous germination, were observed for cysts exposed to cold-dark conditions for 40 to 100 d. Shorter (20 d) and longer (120 d) periods of storage in the cold-dark incubator lowered excystment success and germination synchrony. These results indicate that low temperatures and absence of light during the dormancy period are strongly effective, not only in enhancing germination success, but also in modulating and timing the whole excystment process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM (1980) Effects of temperature conditioning on development and germination ofGonyanlax tamarensis (Dinophyceae) hypnozygotes. J Phycol 16: 166–172
Anderson DM, Coats DW, Tyler MA (1985) Encystment of the dinoflagellateGyrodinium uncatenum: temperature and nutrient effects. J Phycol 21: 200–206
Anderson DM, Coats DW, Tyler MA, Armbrust EV (1987) The effects of darkness and anaerobiosis on dinoflagellate cyst germination. Limnol Oceanogr 32: 340–351
Anderson DM, Keafer BA (1987) An endogenous annual clock in the toxic marine dinoflagellateGonyaulax tamarensis. Nature, Lond 325: 616–617
Anderson DM, Kulis DM, Binder BJ (1984) Sexuality and cyst formation in the dinoflagellateGonyaulax tamarensis. I. Cyst yield in batch cultures. J Phycol 20: 418–425
Anderson DM, Lindquist NL (1985) Time-course measurements of phosphorons depletion and cyst formation in the dinoflagellateGonyaulax tamarensis Lebour. J exp mar Biol Ecol 86: 1–13
Anderson DM, Morel FMM (1979) The seeding of two red tide blooms by the germination of benthicGonyaulax tamarensis hypnocysts. Estuar cstl mar Sci 8: 279–293
Anderson DM, Wall D (1978) Potential importance of benthic cysts ofGonyanlax tamarensis andG. excavata in initiating toxic dinoflagellate blooms. J Phycol 14: 224–234
Biecheler B (1952) Recherches sur les Péridiniens. Bull biol Fr Belg 36 (Suppl): 1–149
Binder BJ, Anderson DM (1986) Green light-mediated photomorphogenesis in a dinoflagellate resting cyst. Nature, Lond 322: 659–661
Binder BJ, Anderson DM (1987) Physiological and environmental control of germination inScrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae) resting cysts. J Phycol 23: 99–107
Binder BJ, Anderson DM (1990) Biochemical composition and metabolic activity ofScrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae) resting cysts. J Phycol 26: 289–298
Blanco J (1995) Cyst production in four species of neritic dinoflagellates. J Plankton Res 17: 165–182
Bolch CJ, Blackburn SI, Cannon JA, Hallegraeff GM (1991) Cyst of the red-tide dinoflagellateAlexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae). Phycologia 30: 215–219
Bravo I, Anderson DM (1994) The effects of temperature, growth medium and darkness on excystment and growth of the toxic dinoflagellateGymnodinium catenatum from northwest Spain. J Plankton Res 16: 513–525
Cabrini M, Cataletto B, Ganis P, Pecchiar I, Fonda Umani S (1995) Relationships between toxic phytoplankton and environmental factors in the Gulf of Trieste: multifactorial analysis. In: Lassus P, Arzul G, Ehrard-Le Denn E, Gentien P, Marcaillou-Le Baut C (eds) Harmful marine algal blooms. Lavoisier Publ., Paris, pp 139–150
Carrada GC, Sacchi CF, Troncone Rigillo M (1965) Ricerche sulla valenza ecologica dei Briozoi salmastri. I. Significato delle variazioni ritmiche dei fatiori ambientali. Boll Pesca Piscic Idrobiol 20: 1–58
Dale B (1983) Dinoflagellate resting cysts: “benthic plankton”. In: Fryxell GA (ed) Survivals trategies of the algae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 69–136
Honsell G, Boni L, Cabrini M, Pompei M (1992) Toxic or potentially toxic dinoflagellates from the northern Adriatic Sea. Sci total Envir 1992 (Suppl): 107–114
Huber G, Nipkow F (1923) Experimentelle Untersuchungen über die Entwicklung und Formbildung vonCeratium hirundinella O.F. Müller. Flora, Jena 116: 114–215
Keller MD, Selvin RC, Clans W, Guillard RRL (1987) Media for the culture of oceanic ultraphytoplankton. J Phycol 23: 633–638
Lirdwitayaprasit T, Okaichi T, Montani S, Ochi T, Anderson DM (1990) Changes in cell chemical composition during the life cycle ofScrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 26: 299–306
Matsuoka K, Fukuyo Y, Anderson DM (1989) Methods for dinoflagellate cyst studies. In: Okaichi T, Anderson DM, Nemoto T (eds) Red tides: biology, environmental science, and toxicology. Elsevier, New York, pp 461–479
Montresor M (1995) The life history ofAlexandrium pseudogonyaulax (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). Phycologia 34: 444–448
Montresor M, Zingone A, Marino D (1992) Cisti di dinoflagellati nei sedimenti marini della Campania. Oebalia 17 (Suppl): 375–376
Montresor M, Zingone A, Marino D (1993) The paratabulate resting cyst ofAlexandrium pseudogonyaulax (Dinophyceae). In: Smayda TJ, Schimizu Y (eds) Toxic phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Elsevier Scientific Publications, Amsterdam, pp 159–164
Nichetto P, Honsell G, Bressan G (1995) First survey of dinoflagellate cysts in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). In: Lassus P, Arzul G, Ehrard-Le Denn E, Gentien P, Marcaillou-Le Baut C (eds) Harmful marine algal blooms. Lavoisier Publ., Paris, pp 205–211
Pfiester LA (1977) Sexual reproduction ofPeridinium gatunense (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 13: 92–95
Pfiester LA, Anderson DM (1987) Dinoflagellate reproduction. In: Taylor FJR (ed) The biology of dinoflagellates. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 611–648
Sarno D, Zingone A, Saggiomo V, Carrada GC (1993) Phytoplankton biomass and species composition in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Hydrobiologia 271: 27–40
Vleeshouwers LM, Bouwmeester HI, Karssen CM (1995) Redefining seed dormancy: an attempt to integrate physiology and ecology. J Ecol 83: 1031–1037
von Stosch HA (1973) Observations on vegetative reproduction and sexual life cycles of two freshwater dinoflagellates,Gymnodinium pseudopalustre Schiller andWoloszynskia apiculata sp. nov. Br Phycol J 8: 105–134
Wall D, Dale B (1969) The “hystrichosphaerid” resting spore of the dinoflagellatePyrodinium bahamense, Plate, 1906. J Phycol 5: 140–149
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Sarà, Genova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montresor, M., Marino, D. Modulating effect of cold-dark storage on excystment inAlexandrium pseudogonyaulax (Dinophyceae). Mar. Biol. 127, 55–60 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00993643
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00993643