Abstract
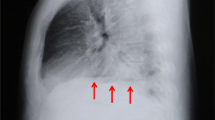
Pneumatic rupture of the esophagus occurs when gas under pressure is accidentally delivered into the oral cavity. To the 4 cases previously described we add 2 pediatric patients and in both the source of the offending gas was a bottle of carbonated drink. The mild initial symptoms were followed in both by physical and radiographic findings suggesting pharyngoesophageal perforation. Early radiologic findings included free subcutaneous and mediastinal air, followed later by hydropneumothorax and mediastinal widening as well as leak of contrast material on gastrografin swallow. CT findings contributed to patient evaluation and management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerr HH, Sloun H, O'Brien CE, Mich AA (1953) Rupture of the esophagus by pressed air. Surgery 33: 447
Randolph H, Melnick DW, Grant AR (1967) Perforation of the oesophagus from external trauma or blast injury. Dis Chest 5: 121
Bountain WL, Lynn (1972) Traumatic pneumatic disruption of the oesophagus. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 63: 553
McQuillian RF, Blake NS, Courtney D (1982) Pneumatic rupture of the oesophagus. Injury 14: 270
Dubos JP, Bouchez MC, Kacet N, Liesse A, Lequein P, Remy J (1986) Spontaneous rupture of the esophagus in the newborn. Pediatr Radiol 16: 317
Larsen H, Jensen BS, Axelsen I (1983) Perforation and rupture of the oesophagus. Scand J Cardiovasc Surg 17: 311
Shepherd RL, Raffens PL, Raffens GL, Raffens JG, Goldstein R (1977) Pediatric esophageal perforation. J Int Cardiovasc Surg 74: 261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyerovitch, J., Ben Ami, T., Rozenman, J. et al. Pneumatic rupture of the esophagus caused by carbonated drinks. Pediatr Radiol 18, 468–470 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00974081
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00974081