Abstract
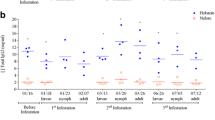
Mice were pluriinfested with nymphs and rabbits, with adultIxodes ricinus. As determined by immunoblotting, >50% of sera from these animals reacted against a tick antigen with a molecular weight of 25 kDa, which was detected in total extracts of partially fedI. ricinus females and in tick integumental extract. It was also found in engorged nymphs but was absent from larvae. Sera ofI. ricinus-infested rabbits and mice or of rabbits infested withRhipicephalus appendiculatus adults reacted with a 20-kDa antigen in total extracts of partially fedR. appendiculatus females and the integument of this species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowessidjaou J, Brossard M, Aeschlimann A (1977) Effects and duration of resistance acquired by rabbits on feeding and egg laying inIxodes ricinus L. Experientia 33:528–530
Brossard M (1977) Rabbits infested with the adults ofIxodes ricinus L.: passive transfer of resistance with immune serum. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 70:289–294
Brossard M (1982) Rabbits infested with adultIxodes ricinus L.: effects of mepyramine on acquired resistance. Experientia 38:702–704
Brossard M, Girardin P (1979) Passive transfer of resistance in rabbits infested with adultIxodes ricinus L.: humoral factors influence feeding and egg laying. Experientia 35:1395–1396
Brossard M, Rais O (1984) Passage of hemolysins through the midgut epithelium of femaleIxodes ricinus L. fed on rabbits infested or reinfested with ticks. Experientia 40:561–563
Brossard M, Monneron JP, Papatheodorou V (1982) Progressive sensitization of circulating basophils againstIxodes ricinus L. antigens during repeated infestations of rabbits. Parasite Immunol 4:355–361
Brown SJ (1985) Immunology of acquired resistance to ticks. Parasitol Today 1:166–171
Brown SJ, Shapiro SZ, Askenase PW (1984) Characterization of tick antigens inducing host immune resistance: I. Immunization of guinea pigs withAmblyomma americanum-derived salivary gland extracts and identification of an important salivary gland protein antigen with guinea pig anti-tick antibodies. J Immunol 133:3319–3325
Burnette N (1981) “Western blotting” electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem 112:195–203
Gill HS, Boid R, Ross CA (1986) Isolation and characterization of salivary antigens fromHyalomma anatolicum anatolicum. Parasite Immunol 8:11–25
Girardin P (1986) Immunité du lapin contre la tiqueIxodes ricinus L.: mécanismes effecteurs et leurs effets sur la biologie de l'ectoparasite. PhD Thesis, University of Neuchâtel, Switzerland
Girardin P, Brossard M (1985) Développement d'une hypersensibilité retardée chez des lapins infestés par les femelles d'Ixodes ricinus L. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 60:299–309
Graf JF (1978) Copulation, nutrition et ponte chezIxodes ricinus L. (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae)-1ere partie. Bull Soc Entomol Suisse 51:89–97
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Reich CI, Zorzopulos J (1980)Boophilus microplus: cattle antienzymes to larval phosphomonoesterases. Exp Parasitol 50:272–277
Shapiro SZ, Voigt WP, Fujisaki K (1986) Tick antigens recognized by serum from a guinea pig resistant to infestation with the tickRhipicephalus appendiculatus. J Parasitol 72:454–463
Tsang VCM, Peralta JM, Simons AR (1983) Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol 92:377–391
Whelen AC, Richardson LK, Wikel SK (1984) Ixodid tick antigens recognized by the infested host: immunoblotting studies. IRCS Med Sci 12:910–911
Wikel SK (1982) Immune responses to arthropods and their products. Ann Rev Entomol 27:21–48
Wikel SK, Whelen AC (1986) Ixodid-host immune interaction. Identification and characterization of relevant antigens and tick-induced host immunosuppression. Vet Parasitol 20:149–174
Willadsen P (1980) Immunity to ticks. Adv Parasitol 18:293–313
Willadsen P, Riding GA (1979) Characterization of a proteolytic enzyme inhibitor with allergenic activity. Multiple functions of a parasite-derived protein. Biochem J 177:41–47
Willadsen P, Williams PG (1976) Isolation and partial characterization of an antigen from the cattle tick,Boophilus microplus. Immunochemistry 13:591–597
Willadsen P, Williams PG, Roberts JA, Kerr JD (1978) Responses of cattle to allergens fromBoophilus microplus. Int J Parasitol 8:89–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rutti, B., Brossard, M. Repetitive detection by immunoblotting of an integumental 25-kDa antigen inIxodes ricinus and a corresponding 20-kDa antigen inRhipicephalus appendiculatus with sera of pluriinfested mice and rabbits. Parasitol Res 75, 325–329 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00931818
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00931818