Abstract
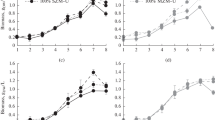
The effect of ammonium on growth ofCandida apicola and on production of sophorose lipid was studied. Sophorose lipid production increased with increasing initial ammonium sulphate concentration. Both growth and product formation were strongly reduced at 73.6mm ammonium. With 58.9mm ammonium a microcrystalline sophorose lipid was formed. The ratio of the two isomers of the sophorose lipid, harbouring either ω- or ω-1 hydroxy fatty acid, was influenced by the initial concentration of ammonium. Both production kinetics, yields and profiles of the total cellular fatty acids express alterations with enlarged ammonium concentrations. These results suggest regulatory effects of ammonium onC. apicola and its sophorose lipid synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desai JD, Desai AJ (1993) Production of biosurfactants. In: Kosaric N (ed) Biosurfactants. Production—properties—applications. Dekker, New York, pp 65–97
Giusti G (1970) Adenosin Desaminase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, vol 2. Akademie Verlag, Berlin, pp 1048–1056
Guerra-Santos LH, Käppeli O, Fiechter A (1984)Pseudomonas aeruginosa biosurfactant production in continuous culture with glucose as carbon source. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:301–305
Haferburg D, Hommel R, Claus R, Kleber H-P (1986) Extracellular microbial lipids as biosurfactants. Adv Biochem Eng/Biotechnol 33:53–93
Hommel R, Stüwer O, Stuber W, Haferburg D, Kleber H-P (1987) Production of water-soluble surface-active exolipids byTorulopsis apicola. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:199–205
Hommel R, Stegner S, Ziebolz C, Weber L, Kleber H-P (1990) Effect of cerulenin on growth and glycolipid production ofCandida apicola. Microbios Lett 45:41–47
Hommel R, Stegner S, Huse K, Kleber H-P (1994a) Cytochrome P-450 inCandida (Torulopsis)apicola and its involvement in sophorose lipid biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:724–728
Hommel R, Lassner D, Weiss J, Kleber H-P (1994b) The microsomal fatty alcohol oxidase of the sophorose lipid producing yeastCandida (Torulopsis)apicola. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:729–734
Hommel R, Weber L, Weiss A, Himmelreich U, Rilke O, Kleber H-P (1994c) Production of sophorose lipid byCandida (Torulopsis)apicola grown on glucose. J Biotechnol 33:147–155
Kosaric N, Cairns WL, Gray NCC, Stechey D, Wood J (1984) The role of nitrogen in multiorganism strategies for biosurfactant production. J Am Oil Chem Soc 61:1735–1743
Lebrihi A, Lamsaif D, Lefebvre G, Germain P (1992) Effect of ammonium ions on spiramycin biosynthesis inStreptomyces ambofaciens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37:382–387
Novotny C, Beran K, Behalova B, Dolezalova L, Zajicek J (1987) Effect of ammonium ions on Δ5,7-sterol synthesis inSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Folia Microbiol 322:206–210
Ratledge C (1989) Biotechnology of oil and fats. In: Ratledge C, Wilkinson SG (eds) Microbial lipids, vol 2. Academic Press, London, pp 567–668
Stüwer O (1988) Gewinnung von extrazellulären Glykolipiden mitTorulopsis apicola. PhD thesis, Karl Marx University, Leipzig
Stüwer O, Hommel R, Haferburg D, Kleber H-P (1987) Production of crystalline surface-active glycolipids by a strain ofTorulopsis apicola. J Biotechnol 6:259–269
Suzuki T, Yamane T, Shimizu S (1988) Effect of ammonium feeding on production of thiostrepton by fed-batch culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:188–192
Viljoen BC, Kock JLF, Thoupou K (1989) The significance of cellular long-chain fatty acid compositions and other criteria in the study of the relationship between sporogenous ascomycete species and asporogenousCandida species. Syst Appl Microbiol 12:80–90
Weber L, Stach J, Haufe G, Hommel R, Kleber H-P (1990) Elucidation of the structure of an unusual cyclic glycolipid fromTorulopsis apicola. Carbohydr Res 206:13–19
Weber L, Döge C, Hanle G, Hommel R, Kleber H-P (1992) Oxygenation of hexadecane in the biosynthesis of cyclic glycolipids inTorulopsis apicola. Biocatalysis 5:267–272
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. Fritz Wagner on the occasion of his 65th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hommel, R.K., Stegner, S., Kleber, H.P. et al. Effect of ammonium ions on glycolipid production byCandida (Torulopsis)apicola . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42, 192–197 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00902716
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00902716