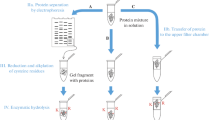
Summary
Conditions are described for the reduction and alkylation of cysteines in peptides and proteins with volatile reagents by use of triethylphosphine as reductant, bromopropane as alkylating reagent and triethylamine as base. Alkylated samples need only be vacuum dried prior to subsequent analysis steps. Alkylated samples have been acid hydrolyzed and analyzed on an amino acid analyzer with recoveries of cysteine within 10% of the expected value. Alkylated samples have been directly applied to a sequencer membrane, dried on the surface and cysteines identified by sequence analysis without additional wash steps. In addition proteins blotted onto PVDF have been alkylatedin situ and sequenced with identification of cysteines. On the analyzer and sequencer the S-propylcysteine derivative elutes at a unique position allowing for the unambiguous identification of cysteine. Cysteine residues are quantitativly alkylated under the conditions developed. The ease of this procedure allows the routine analysis of cysteine in peptides and proteins without additional, time consuming repurification or dialysis steps.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- dptu:
-
diphenylthiourea
- dmptu:
-
dimethylphenylthiourea
- prop-cys:
-
S-propylcysteine
References
Andrews PC, Dixon JE (1987) A procedure for in situ alkylation of cysteine residues on glass fiber prior to protein microsequence analysis. Anal Biochem 209: 109–116
Brune DC (1992) Alkylation of cysteine with acrylamide for protein sequence analysis. Anal Biochem 207: 285–290
Chang JY (1978) A novel Edman-type degradation: direct formation of the thiohydantoin ring in alkaline solution by reaction of Edman-type reagents with N-monomethyl amino acids. FEBS Letters 91: 63–68
Hale JE, Beidler DE, Jue RA (1994) Quantitation of cysteine residues alkylated with 3-bromopropylamine by amino acid analysis. Anal Biochem 161: 524–528
Hawke D, Yuan P (1987) S-pyridylethylation of cysteine residues. ABI User Bull 28: 470A/477A-120A
Henschen A (1986) Analysis of cyst(e)ine residues, disulfide bridges, and sulfhydryl groups in proteins. In: Wittmann-Liebold B, Salnikow J, Erdmann VA (eds) Advance methods in microsequence analysis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 244–255
Jue RA, Hale JE (1993) Identification of cysteine residues alkylated with 3-bromopropylamine by sequence analysis. Anal Biochem 210: 39–44
Jue RA, Hale JE (1994) On-line procedures for alkylation of cysteine rewidues with 3-bromopropylamine prior to protein sequence analysis. Anal Biochem 221: 374–378
Krutzsch HC, Inman JK (1993) N-isopropyliodoacetamide in the reduction and alkylation of proteins: use in microsequence analysis. Anal Biochem 209: 109–116
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Matsudaira PT (1987) Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidine difluoride membranes J Biol Chem 262: 10035–10038
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hale, J.E., Butler, J.P. & Pourmand, R.R. Analysis of cysteine residues in peptides and proteins alkylated with volatile reagents. Amino Acids 10, 243–252 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00807326
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00807326