Summary
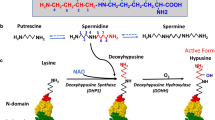
The unusual amino acid hypusine [Nε-(4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)lysine] is a unique component of one cellular protein, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF-5A, old terminology, eIF-4D). It is formed posttranslationally and exclusively in this protein in two consecutive enzymatic reactions, (i) modification of a single lysine residue of the eIF-5A precursor protein by the transfer of the 4-aminobutyl moiety of the polyamine spermidine to itsε-amino group to form the intermediate, deoxyhypusine [Nε-(4-aminobutyl)lysine] and (ii) subsequent hydroxylation of this intermediate to form hypusine. The amino acid sequences surrounding the hypusine residue are strictly conserved in all eukaryotic species examined, suggesting the fundamental importance of this amino acid throughout evolution. Hypusine is required for the activity of eIF-5Ain vitro. There is strong evidence that hypusine and eIF-5A are vital for eukaryotic cell proliferation. Inactivation of both of the eIF-5A genes is lethal in yeast and the hypusine modification appears to be a requirement for yeast survival (Schnier et al., 1991 [Mol Cell Biol 11: 3105–3114]; Wöhl et al., 1993 [Mol Gen Genet 241: 305–311]). Furthermore, inhibitors of either of the hypusine biosynthetic enzymes, deoxyhypusine synthase or deoxyhypusine hydroxylase, exert strong anti-proliferative effects in mammalian cells, including many human cancer cell lines. These inhibitors hold potential as a new class of anticancer agents, targeting one specific eukaryotic cellular reaction, hypusine biosynthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbruzzese A, Park MH, Folk JE (1986) Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase from rat testis. Partial purification and characterization. J Biol Chem 261: 3085–3089
Abbruzzese A, Hanauske-Abel HM, Park MH, Henke S, Folk JE (1991) The active site of deoxyhypusyl hydroxylase: use of catechol peptides and their component chelator and peptide moieties as molecular probes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1077: 159–166
Bevec D, Klier H, Holter W, Tschachler E, Valent P, Lottspeich F, Baumruker T, Hauber J (1994) Induced gene expression of the hypusine-containing protein eukaryotic initiation factor 5A in activated human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 10829–10833
Byers TL, Ganem B, Pegg AE (1992) Cytostasis induced in L1210 murine leukemia cells by the S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase inhibitor, Biochem J 287: 717–724
Chen, K-Y, Dou Q-P (1988) NAD+ stimulated the spermidine-dependent hypusine formation on the 18-kDa protein in cytosolic lysates derived from NB-15 mouse neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Letters 229: 325–328
Cooper HL, Park MH, Folk JE (1982) Post-translational formation of hypusine in a single major protein occurs generally in growing cells and is associated with activation of lymphocyte growth. Cell 29: 791–797
Cooper HL, Park MH, Folk JE, Safer B, Braverman R (1983) Identification of the hypusine-containing protein Hy+ as translation initiation factor eIF-4D. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 1854–1857
Duncan RF, Hershey JWB (1986) Changes in eIF-4D hypusine modification or abundance are not correlated with translational repression in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem 261: 12903–12906
Hanauske-Abel HM, Park MH, Hanauske A-R, Popowicz AM, Lalande M, Folk JE (1994) Inhibition of the G1/S of the cell cycle by inhibitors of deoxyhypusine hydroxylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1221: 115–124
Hölttä E, Pohjanpelto P, Jänne J (1979) Dissociation of the early antiproliferative action of methylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone) from polyamine depletion. A comparison of the effects of DL-alpha-difluoromethyl ornithinine and methylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone) on the growth of human fibroblasts. FEBS Lett 97: 9–14
Imaoka N, Nakaijima T (1973) Hypusine, N6-(4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid, in tissue proteins of mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta 320: 97–103
Jakus J, Wolff EC, Park MH, Folk JE (1993) Features of the spermidine-binding site of deoxyhypusine synthase as derived from inhibition studies: effective inhibition by bis- and mono-guanylated diamines and polyamines. J Biol Chem 268: 13151–13159
Joe YA, Park MH (1994) Structural features of the eIF-5A precursor required for posttranslational synthesis of deoxyhypusine. J Biol Chem 269: 25916–25921
Joe YA, Wolff EC, Park MH (1995) Cloning and expresssion of human deoxyhypusine synthase cDNA: structure-function studies with the recombinant enzyme and mutant proteins. J Biol Chem 270: 22386–22392
Kang HA, Hershey JWB (1994) Effect of initiation factor eIF-5A depletion on protein synthesis and proliferation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 269: 3934–3940
Kang KR, Wolff EC, Park MH, Folk JE, Chung SI (1995) Identification of YHR068w in Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome VIII as a gene for deoxyhypusine synthase: expression and characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 270: 18408–18412
Kemper WM, Berry KW, Merrick WC (1976) Purification and properties of rabbit reticulocyte protein synthesis initiation factors M2Bα and M2Bβ. J Biol Chem 251: 5551–5557
Klier H, Csonga R, Steinkasser A, Wöhl T, Lottspeich F, Eder J (1995) Purification and characterization of human deoxyhypusine synthase from HeLa cells. FEBS Lett 364: 207–210
Lee YB, Park MH, Folk JE (1995) Diamine and triamine analogs and derivatives as inhibitors of deoxyhypusine synthase: synthesis and biological activity. J Med Chem 38: 3053–3061
Lee YB, Joe YA, Park MH (1996) Inhibitors of hypusine biosynthesis: potential anticancer agents. J Biomedical Res (in press)
Murphey RJ, Gerner EW (1987) Hypusine formation in protein by a two-step process in cell lysates. J Biol Chem 262: 15033–15036
Nakajima T, Matsubayashi T, Kakimoto Y, Sano I (1971) Distribution of hypusine, N6-(4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid, in mammalian organs. Biochim Biophys Acta 252: 92–97
NC-IUB [Nomenclature Committee, IUB], Safer B (1989) Nomenclature of initiation, elongation and termination factors for translation in eukaryotes. Recommendations 1988. Eur J Biochem 186: 1–3
Park MH (1987) Regulation of biosynthesis of hypusine in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Evidence for eIF-4D precursor polypeptides. J Biol Chem 262: 12730–12734
Park MH (1989) The essential role of hypusine in eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4D (eIF-4D). Purification of eIF-4D and its precursors and comparison of their activities. J Biol Chem 264: 18531–18535
Park MH, Folk JE (1986) Biosynthetic labeling of hypusine in mammalian cells. Carbonhydrogen bond fissions revealed by dual labeling. J Biol Chem 261: 14108–14111
Park MH, Cooper HL, Folk JE (1981) Identification of hypusine, an unusual amino acid, in a protein from human lymphocytes and of spermidine as its biosynthetic precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78: 2869–2873
Park MH, Cooper HL, Folk JE (1982) The biosynthesis of protein-bound hypusine [Nε-(4-anmino-2-hydroxybutyl)-lysine]. lysine as the amino acid precursor and the intermediate role of deoxyhypusine [Nε-(4-aminobutyl)lysine]. J Biol Chem 257: 7217–7222
Park MH, Chung SI, Cooper HL, Folk JE (1984a) The mammalian hypusine-containing protein, eukaryotic initiation factor 4D. Stuctural homology of this protein from several species. J Biol Chem 259: 4563–4565
Park MH, Liberato DJ, Yergey AL, Folk JE (1984b) The biosynthesis of hypusine [Nε-(4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)lysine]. Alignment of the butylamine segment and source of the secondary amino nitrogen. J Biol Chem 259: 12123–12127
Park MH, Wolff EC, Smit-McBride Z, Hershey JWB, Folk JE (1991) Comparison of the activities of variant forms of eIF-4D. The requirement for hypusine or deoxyhypusine. J Biol Chem 266: 7988–7994
Park MH, Wolff EC, Folk JE (1993a) Hypusine: its post-translational formation in eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and its potential role in cellular regulation. BioFactors 4: 95–104
Park MH, Wolff EC, Folk JE (1993b) Is hypusine essential for eukaryotic cell proliferation? Trends Biochem Sci 18: 475–479
Park MH, Wolff EC, Lee YB, Folk JE (1994) Antiproliferative effects of inhibitors of deoxyhypusine synthase: inhibition of growth of CHO cells by guanyl diaminess. J Biol Chem 269: 27827–27832
Paz MA, Torrelio BM, Gallop PM (1984) Hydralazine inhibition of the posttranslational hydroxylation of deoxyhypusine, a polyamine-derived amino acid. Biochem Pharmacol 33: 779–785
Pegg AE (1988) Polyamine metabolism and its importance in neoplastic growth and a target for chemotherapy. Cancer Res 48: 759–774
Ruhl M, Himmelspach M, Bahr GM, Hammerschmid F, Jaksche H, Wolff B, Aschauer H, Farrington GK, Probst H, Bevec D, Hauber J (1993) Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A is a cellular target of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev activation domain mediating trans-activation. J Cell Biol 123: 1309–1320
Sano A, Kotani K, Kakimoto Y (1986) Isolation and identification of 2-(γ-aminobutyryl) hypusine. J Neurochem 46: 1046–1049
Schnier J, Schwelberger H, Smit-McBride Z, Kang HA, Hershey JWB (1991) Translation initiation factor 5A and its hypusine modification are essential for cell viability in yeast. Mol Cell Biol 11: 3105–3114
Schreier MH, Erni B, Staehelin T (1977) Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. Purification and characterization of seven initiation factors. J Mol Biol 116: 727–753
Schümann H, Klink F (1989) Archaebacterial protein contains hypusine, a unique amino acid characteristic for eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4D. System Appl Microbiol 11: 103–107
Shiba T, Mizote H, Kaneko T, Nakajima T, Kakimoto Y, Sano I (1971) Hypusine, a new amino acid occuring in bovine brain. Isolation and structural determination. Biochim Biophys Acta 244: 523–531
Shiba T, Akiyama H, Umeda I, Okada S, Wakamiya T (1982) Synthesis and stereochemistry of hypusine, a new amino acid. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 55: 899–903
Smit-McBride Z, Dever TE, Hershey JWB, Merrick WC (1989) Sequence determination and cDNA cloning of eukaryotic initiation factor 4D, the hypusine-containing protein. J Biol Chem 264: 1578–1583
Smit-McBride Z, Schnier J, Kaufman RJ, Hershey JWB (1989) Protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4D. Functional comparison of native and unhypusinated forms of the protein. J Biol Chem 264: 18527–18530
Tabor CW, Tabor H (1984) Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem 53: 749–790
Tao Y, Chen KY (1995) Purification of deoxyhypusine synthase from Neurospora crassa to homogeneity by substrate elution affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem 270: 383–386
Ueno S, Kotani K, Sano A, Kakimoto Y (1991) Isolation and identification of 2-(β-alanyl)hypusine from bovine brain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1073: 233–235
Wöhl T, Klier H, Ammer H, Lottspeich F, Magdolen V (1993) The HYP2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is essential for aerobic growth: characterization of different isoforms of the hypusine-containing protein Hyp2p and analysis of gene disruption mutants. Mol Gen Genet 241: 305–311
Wolff EC, Park MH, Folk JE (1990) Cleavage of spermidine as the first step in deoxyhypusine synthesis. The role of NAD+. J Biol Chem 265: 4793–4799
Wolff EC, Lee YB, Chung SI, Folk JE, Park MH (1995) Deoxyhypusine synthase from rat testis: purification and characterization. J Biol Chem 270: 8660–8666
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, M.H., Joe, Y.A., Kang, K.R. et al. The polyamine-derived amino acid hypusine: its post-translational formation in eIF-5A and its role in cell proliferation. Amino Acids 10, 109–121 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00806584
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00806584