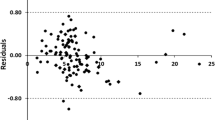
Because the properties are a consequence of the structure (Kier and Hall, 1986)
Summary
The linear combinations of connectivity indices method (LCCI) is here employed to model the water solubility and activity of 19 natural amino acids. Starting with the molecular connectivity indices, reciprocal and supra molecular connectivity indices are designed to model the solubility and activity spaces of the natural amino acids. The reciprocal and supra molecular reciprocal connectivity indices have been obtained following the variability of the connectivity indices along solubility space of the natural amino acids. A linear combination of the reciprocals of the connectivity indices (LCRCI) showed a satisfactory modelling of the solubility and activity space while a model based on the LCRCI together with the introduction of supra reciprocal molecular connectivity indices for Pro, Ser and Arg achieved an optimal modelling of the solubility and activity space of the natural amino acids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (1991–1992) 72nd edn. Boca Raton, pp: 7–1
Christensen U (1994) Kinetic characterization of carboxypeptidase-Y-catalyzed peptide semisynthesis prediction of yields. Amino Acids 6: 177–187
Kier LB, Hall LH (1986) Molecular connectivity in structure-activity analysis. Wiley, New York (and references therein)
Mihalić Z, Nikolić S, Trinajstić N (1992) Comparative study of molecular descriptors derived from distance matrix. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 32: 28–37
Pogliani L (1992) Molecular connectivity model for determination of isoelectric point of amino acids. J Pharm Sci 81: 334–336
Pogliani L (1993a) Molecular connectivity model for determination of T1 relaxation times of α-carbons of amino acids and cyclic dipeptides. Comput Chem 17: 283–286
Pogliani L (1993b) Molecular connectivity model for determination of physicochemical properties of α-amino acids. J Phys Chem 97: 6731–6736
Pogliani L (1994a) Structure property relationships of some amino acids and dipeptides. Amino Acids 6: 141–153
Pogliani L (1994b) Molecular connectivity descriptors of the physicochemical properties of the α-amino acids. J Phys Chem 98: 1494–1499
Pogliani L (1994c) On a graph theoretical characterization of cis/trans isomers. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 34: 801–804
Pogliani L (1995a) Molecular modeling with linear combination of connectivity indices. J Phys Chem 99: 925–937
Pogliani L (1995b) The molecular connectivity method: a powerful tool in the study of biological relevant molecules. Curr Top Pept Prot Res (in press)
Pogliani L (1995c) Modeling hydration processes of biochemical and inorganic compounds. (submitted)
Randić M (1975) On characterization of molecular branching. J Am Chem Soc 97: 6609–6615
Randić M (1991a) Orthogonal molecular descriptors. N J Chem 15: 517–525
Randić M (1991b) Resolution of ambiguities in structure-property studies by use of orthogonal descriptors. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 31: 311–320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pogliani, L. Modeling the solubility and activity of amino acids with the LCCI method. Amino Acids 9, 217–228 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00805953
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00805953