Abstract
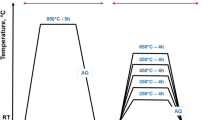
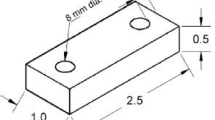
The zinc-aluminium alloys containing 8, 12, and 27% aluminium are finding increasing applications in the casting industry. These alloys are stronger than most aluminium alloys. In addition, they possess high wear resistance and bearing properties. However, surface sinks and shrinkage defects are observed on the bottom faces of such castings, contrary to general foundry practice. In the present investigation, this problem observed in the Zn-8%Al, Zn-12%Al, Zn-27%Al alloys was tackled by controlling various casting parameters and also by additions of the master alloys of strontium and lithium into the molten alloys. It was found that the underside shrinkage problem was influenced by the aluminium content of the alloy, melt superheat, casting size and cooling conditions. The strontium and lithium additions were found to be beneficial in reducing the underside shrinkage problem. The ultimate tensile strength, fracture elongation and Vickers hardness were all increased with aluminium concentration and lithium addition. It was found also that the most problematical Zn-27%Al alloy, which provided the highest mechanical properties, was very suitable for the squeeze-casting technique. The mechanical properties were increased sharply in these squeeze-cast bars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Gervais,CIM Bull. 90 (1987) 67.
E. J. Kubel Jr,Adv. Mater. Processes 132 (1987) 51.
T. Calayage andD. Ferres,Automotive Engng 90(9) (1982) 40.
R. J. Barnhurst, E. Gervais andF. D. Boyles,AFS Trans. 72 (1983) 569.
R. J. Barnhurst andE. Gervais,ibid. 91 (1985) 591.
N. Tunca andR. W. Smith,J. Mater. Sci. 23 (1988) 111.
M. Sahoo, L. V. Whiting, V. Chartrand andG. Weatherall,AFS Trans. 44 (1986) 225.
S. Sonek andB. Senturk, “Improvement of the Quality of Metal-Matrix Composites via Squeeze Casting Method”, 4th Year Engineering Project (Mechanical Engineering Department Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey, 1989).
S. K. Verma andJ. L. Dorcic,Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 9 (1988) 579.
M. A. Dellis, J. P. Keustermans andF. Delanney,Mater. Sci. Engng A135 (1991) 253.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savas, M.A., Altintas, S. The microstructural control of cast and mechanical properties of zinc-aluminium alloys. J Mater Sci 28, 1775–1780 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595744
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595744