Summary
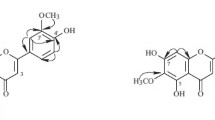
FromFerula tenuisecta Eug. Kor. a new substance with the composition C19H24O4 (mp 121–122°C) has been isolated, and it has been named ferutinin. On the basis of UV, IR, mass, and NMR spectra and the products of alkaline hydrolysis it has been established that ferutinin is an ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and ferutinol.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. Sh. Kadyrov and G. K. Nikonov, Khim. Prirodn. Soedin., 59 (1972).
A. I. Saidkhodzhaev and G. K. Nikonov, Khim. Prirodn. Soedin., 559 (1972).
Kh. M. Kamilov and G. K. Nikonov, Khim. Prirodn. Soedin., 114 (1972).
Kh. M. Kamilov and G. K. Nikonov, Khim. Prirodn. Soedin., 718 (1972).
Additional information
Institute of the Chemistry of Plant Substances, Academy of Sciences of the Uzbek SSR. Translated from Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 1, pp. 28–30, January–February, 1973.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saidkhodzhaev, A.I., Nikonov, G.K. The structure of ferutinin. Chem Nat Compd 9, 25–26 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580882
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580882