Abstract
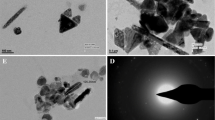
The structural features and mechanism of crystallization of CuO ultrafine particles (200–450 nm) were, studied by transmission electron microscopy, as well as by thermal analyses (differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetric analysis, etc). The CuO ultrafine particles were not single crystals, but built up of subunits of much smaller size; between two of these subunits low-angle crystal boundaries exist. In the heating procedure, as the temperature increased, CuO ultrafine particles lost their absorbed and inclusive water gradually, the crystalline completeness was improved, and the temperature of crystallization was about 320 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. B. Scott andE. Matijevic,J. Colloid Interface Sci. 66, (1978) 447.
E. Matijevic andP. Scheiher,ibid. 63 (1978) 509.
“Analytic Chemistry” (TsingHua University, Beijing) p. 196, in Chinese.
E. Matijevic,J. Colloid Interface Sci. 36 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hai -Yan, D., Yu -Ling, Z., Jing -Kui, L. et al. Structural features and mechanism of crystallization of CuO ultrafine particles. J Mater Sci 28, 5176–5178 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00570059
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00570059