Abstract
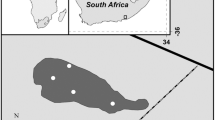
Coordinated environmental, ecological and biochemical studies have been applied to assess the impact of sewage disposal in a fjordic system near Bergen, Norway. The ecological and biochemical effects were studied in 1983 at four sampling locations situated along a spatial gradient of effects of the sewage on conditions in the sediments. Two of the locations, near Dolviken, were found to be considerably affected by the sewage. Relatively few species of macrobenthic invertebrate fauna were present at these locations, and analysis of the distribution of individuals among species indicated distortion of the benthic community structure. On the basis of its distribution along spatial gradients of organic enrichment and various criteria relating to its suitability for biochemical analysis, the polychaete Glycera alba (Müller) was selected as the most suitable pollution-sensitive indicator species for use in the biochemical studies. In individuals from the two affected locations near Dolviken, maximal activities of the regulatory glycolytic enzyme, phosphofructokinase, and the pyruvate oxidoreductase, alanopine dehydrogenase, were very low. Activities of several other enzymes associated with carbohydrate catabolism were also lower in these groups than in the reference group collected from Raunefjorden. The ecological and biochemical measures both corresponded closely with the changes in environmental conditions along the gradient of sewage effects. The results are discussed with reference to earlier coordinated ecological and biochemical investigations carried out in Scotland and Norway and to experimental studies of the effects of pollutants and hypoxia on energy-yielding metabolism of polychaetes. It is suggested that the enzymatic changes in G. alba may be a sensitive component of an integrated metabolic response, which may involve a decrease in glycolytic energy production for the fuelling of muscular activity. Further development of this coordinated ecological and biochemical approach is discussed, with emphasis on its potential utility in the assessment of biological effects of the disposal of organically rich waste materials in coastal waters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bayne, B. L.: Aspects of physiological condition in Mytilus edulis L., with special reference to the effects of oxygen tension and salinity. Proc. 9th Eur. mar. Biol. Symp. 213–238 (1975). (Ed. by H. Barnes. Aberdeen: Aberdeen University Press)
Bayne, B. L.: Responses to environmental stress: tolerance, resistance and adaptation. Proc. 18th Eur. mar. Biol. Symp. 331–349 (1985). (Ed. by J. S. Gray and M. E. Christiansen. Chichester, England: Wiley)
Blackstock, J.: A biochemical approach to assessment of effects of organic pollution on the metabolism of the non-opportunistic polychaete, Glycera alba. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 33, 546–555 (1980a)
Blackstock, J.: Estimation of activities of some enzymes associated with energy yielding metabolism in the polychaete, Glycera alba (Müller) and application of the methods to the study of effects of organic pollution. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 46, 197–217 (1980b)
Blackstock, J.: Biochemical metabolic regulatory responses of marine invertebrates to natural environmental change and marine pollution. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 22, 263–313 (1984a)
Blackstock, J.: Enzymatic responses of sublittoral polychaetes to hypoxia. In: First Congress of Comparative Physiology and Biochemistry Section of International Union of Biological Sciences, Liège, 1984, p. A116. Liège: European Society for Comparative Physiology and Biochemistry 1984b
Blackstock, J. and C. Filion-Myklebust: Environmental and biochemical investigation of some effects of organic pollution in Inner Oslofjord, Norway. Mar. Biol. 73, 155–163 (1983)
Blackstock, J. and T. H. Pearson: The sub-lethal effects of solid waste disposal on selected marine invertebrates. Report to the Commission of European Communities on research conducted under Contract No. ENV 456-80 UK, 58 pp. Oban: Scottish Marine Biological Association 1981. (SMBA Internal Report No. 54)
Brett, J. R.: Implications and assessment of environmental stress. In: Investigation of fish-power problems, pp 69–83. Ed. by P. A. Larkin. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press 1958
Carr, R. S. and J. M. Neff: Biochemical indices of stress in the sandworm Neanthes viresn (Sars). II. Sublethal responses to cadmium. Aquat. Toxic. 2, 319–333 (1982)
Dando, P. R.: Strombine [N-(carboxymethyl)-D-alanine] dehydrogenase and alanopine [meso-N-(1-carboxyethyl)-alanine] dehydrogenase from the mussel Mytilus edulis L. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 9, 297–298 (1981)
Dando, P. R., K. B. Storey, P. W. Hochachka and J. M. Storey: Multiple dehydrogenases in marine molluscs: electrophoretic analysis of alanopine dehydrogenase, strombine dehydrogenase, octopine dehydrogenase and lactate dehydrogenase. Mar. Biol. Lett 2, 249–257 (1981)
Dillon, T. M. and M. P. Lynch: Physiological responses as determinants of stress in marine and estuarine organisms. In: Stress effects on natural ecosystems, pp 227–241. Ed. by G. W. Barrett and R. Rosenberg. Chichester: Wiley 1981
Ebberink, R. H. M. and A. de Zwaan: Control of glycolysis in the posterior adductor muscle of the sea mussel Mytilus edulis. J. comp Physiol. (Sect. B) 137, 165–171 (1980)
Gray, J. S.: Pollution induced changes in populations. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 286, 545–561 (1979)
Gray, J. S. and F. B. Mirza: A possible method for the detection of pollution-induced disturbance on marine benthic communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 10, 142–146 (1979)
Gray, J. S. and T. H. Pearson: Objective selection of sensitive species indicative of pollution-induced change in benthic communities. 1. Comparative methodology. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 9, 111–119 (1982)
Ivanovici, A. M. and W. J. Wiebe: Towards a working ‘definition’ of ‘stress’: a review and critique. In: Stress effects on natural ecosystems, pp 13–27. Ed. by G. W. Barret and R. Rosenberg. Chichester: Wiley 1981
Johannessen, P. J.: Byfjordundersøkelsen. Resipientundersøkelse av fjordence rundt Bergen 1979–1980, 108 pp Bergen: Statlig Program for Forurensningsovervåking, Bergen Kommune 1981. (Rapp. Nr. 1, Tidsrommet fra oktober 1979 til og med desember 1980)
Johannessen, P. J.: Byfjordundersøkelsen. Resipientundersøkelse av fjordene rundt Bergen 1983, 88 pp. Bergen: Statlig Program for Forurensningsovervåking, Bergen Kommune 1984. (Rapp. Nr. 4)
Livingstone, D. R., A. de Zwaan, M. Leopold and E. Marteijn: Studies on phylogenetic distribution of pyruvate oxidoreductases. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 11, 415–425 (1983)
Lowry, O. H., N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr and R. J. Randall: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Mangum, C.: Respiratory physiology in annelids. Am. Scient. 58, 641–647 (1970)
Olla, B. L., A. J. Bejda, A. L. Studholme and W. H. Pearson: Sublethal effects of oiled sediment on the sand worm Nereis (Neanthes) virens: induced changes in burrowing and emergence. Mar. envirl Res. 13, 121–139 (1984)
Pearson, T. H. and J. Blackstock: Selection of indicator species: a coordinated ecological and biochemical approach to the assessment of pollution. Proc. 17th Eur. mar. Biol. Symp. 147–151 (1983). (Oceanol. Acta Vol. spéc.)
Pearson, T. H. and E. Eleftheriou: The benthic ecology of Sullom Voe, Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. (Sect. B), 241–269 (1981)
Pearson, T. H., J. S. Gray and P. J. Johannessen: Objective selection of sensitive species indicative of pollution induced changes in benthic communities. 2. Data analyses. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 12, 237–255 (1983)
Pearson, T. H. and R. Rosenberg: Macrobenthic succession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 16, 229–311 (1978)
Pearson, T. H. and S. O. Stanley: Comparative measurement of the redox potential of marine sediments as a rapid means of assessing the effect of organic pollution. Mar. Biol. 53, 371–379 (1979)
Pörtner, H.-O., U. Kreutzer, B. Siegmund, N. Heisler and M. K. Grieshaber: Metabolic adaptations of the intertidal worm Sipunculus nudus to functional and environmental hypoxia. Mar. Biol. 79, 237–247 (1984)
Reish, D. J.: The sublethal effects of pollutants on polychaetous annelids. Inn: Proceedings of a Conference on Marine Biology in Environmental Protection (San Clemente Island, 1973), pp 89–101. Springfields: U.S. Department of Commerce 1974
Reish, D. J.: Bristle worms (Annelida: Polychaeta). In: Pollution ecology of estuarine invertebrates, pp 77–125. Ed. by C. W. Hart and S. H. Fuller. New York: Academic Press 1979
Reish, D. J. and R. S. Carr: The effect of heavy metals on the survival, reproduction, development and life cycles for two species of polychaetous annelids. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 9, 24–27 (1978)
Siegel, S.: Nonparametric statistics for the behaviorla sciences, 312 pp. New York: McGraw-Hill 1956
Siegmund, B. and M. K. Grieshaber: Opine metabolism of Arenicola marina L. In: First Congress of Comparative Physiology and Biochemistry Sectionof International Union of Biological sciences, Liège, 1984, p. A134. Liège: European Society for Comparative Physiology and Biochemistry 1984
Ugland, K. I. and J. S. Gray: Log-normal distributions and the concept of community equilibrium. Oikos 39, 171–178 (1982)
Watt, W. B.: Bioenergetics and evolutionary genetics: opportunities for new synthesis. Am. Nat. 125, 118–143 (1985)
Zammit, V. A. and E. A. Newsholme: The maximum activities of hexokinase, phosphorylase, phosphofructokinase, glycerolphosphate dehydrogenases, lactate dehydrogenase, octopine dehydrogenase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, nucleoside diphosphate kinase, glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase and arginine kinase in relation to carbohydrate utilisation in muscles from marine invertebrates. Biochem. J. 160, 447–462 (1976)
Zwaan, A. de and V. Putzer: Metabolic adaptations of intertidal invertebrates to environmental hypoxia (a comparison of environmental anoxia to exercise anoxia). Symp. Soc. exp. Biol. 39, 33–62 (1985)
Zwaan, A. de and W. Zurburg: The formation of strombine in the adductor muscle of the sea mussel Mytilus edulis L. Mar. Biol. Lett 2, 179–192 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mauchline, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blackstock, J., Johannessen, P.J. & Pearson, T.H. Use of a sensitive indicator species in the assessment of biological effects of sewage disposal in fjords near Bergen, Norway. Mar. Biol. 93, 315–322 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508270
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508270