Abstract
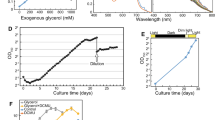
Sodium cyanide (NaCN) was used to partially uncouple respiration and photosynthesis in the symbiotic sea anemone Condylactis gigantea. NaCN significantly increased the ratio of gross photosynthesis to respiration in both intact tentacles and isolated zooxanthellae (Symbiodinium microadriaticum), increased carbon translocation from 17.7±3.5% of total fixed in controls to 43.5±5.8%, and doubled the amount of photosynthetically fixed carbon accumulating in the coelenterate host over that in controls. Only 2% of the non-particulate radioactivity recovered in the host tissue was 14C-glycerol when uninhibited symbiotic tentacles were incubated in 14C-bicarbonate for 1 h. At 10-5 M NaCN, approximately 25% of the host nonparticulate radioactivity was recovered as 14C-glycerol, the absolute concentration of glycerol in the host tissue was three times higher than in controls, and 14C-glycerol was found in the medium. While glycerol has been proposed to play a major role in the translocation of photosynthetically fixed carbon from zooxanthellae to their coelenterate hosts, its concentration has never been measured in the animal and algal components of the symbiosis. The isolated zooxanthellae contained 3.62±0.33 mM glycerol, 26x the 0.141±0.02 mM found in the anemone. Aposymbiotic anemone tissue contained 0.169±0.06 mM glycerol. The rate of glycerol mineralization was not saturated even when exogenous glycerol levels were 70x internal concentrations. These data show that respiration and photosynthesis in symbiotic associations may be partially uncoupled by NaCN, and that this uncoupling allows the verification of the translocation and rapid catabolism of glycerol within the host.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Battey, J. F. and J. S. Patton: A reevaluation of the role of glycerol in carbon translocation in zooxanthellae-coelenterate symbiosis. Mar. Biol. 79, 27–38 (1984)
Bell, J. D., I. L. O. Buxton and L. L. Brunton: A kinetic isotope dilution assay for glycerol. Analyt. Biochem. 139, 305–308 (1984)
Bevington, P. R.: Data reduction and error analysis for the physical sciences, 336 pp. New York: McGraw Hill Book Co. 1969
Blank, R. J. and R. K. Trench: Speciation and symbiotic dinoflagellates. Science, N.Y. 229, 656–658 (1985)
Blanquet, R. S., J. C. Nevenzel and A. A. Benson. Acetate incorporation into the lipids of the sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima and its associated zooxanthellae. Mar. Biol. 54, 185–194 (1979)
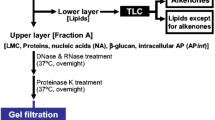
Bligh, E. G. and W. J. Dyer: A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37, 911–917 (1959)
Cook, C.: Metabolic interchanges in algae-invertebrate symbiosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 14, 177–210 (1983)
Crossland, C. J., D. J. Barnes and M. A. Borowitzka: Diurnal lipid and mucus production in the staghorn coral Acropora acuminata. Mar. Biol. 60, 81–90 (1980)
Crumeyrolles-Duclaux, G.: Premières observations ultrastructurales sur les zooxanthelles de Viguieriotes edwardsii. Protistologica 5, 471–479 (1969)
D'agnolo, G. D., I. S. Rosenfeld, J. Anaya, S. Omura and P. R. Vagelos: Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis by the antibiotic cerulenin, specific inactivation of β-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase. Biochim. biophys. Acta 326, 155–166 (1973)
Davies, P. S.: The role of zooxanthellae in the nutritional energy requirements of Pocillopora evdouxi. Coral Reefs 2, 181–186 (1984)
Hartree, E. F.: Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Analyt. Biochem. 48, 422–427 (1972)
Hellebust, J. A.: Excretion of some organic compounds by marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 10, 192–206 (1965)
Goreau, T. J.: Coral skeletal chemistry: physiological and environmental regulation of stable isotopes and trace metals in Montastrea annularis. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 196, 291–315 (1977)
Hotta, S. S.: Oxidative metabolism of isolated brain mitochondria: changes caused by aminooxyacetic acid. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 127, 132–139 (1968)
Kellogg, R. B. and J. S. Patton: Lipid droplets, medium of energy exchange in the symbiotic anemone Condylactis gigantea: a model coral polyp. Mar. Biol. 75, 137–149 (1983)
Lewis, D. H., and D. C. Smith: The autotrophic nutrition of symbiotic marine coelenterates with special reference to hermatypic corals. I. Movement of photosynthetic products between the symbionts. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 178, 111–129 (1971)
Muscatine, L.: Glycerol excretion by symbiotic algae from corals and Tridacna and its control by the host. Science, N.Y. 156, 516–519 (1967)
Muscatine, L.: Nutrition of corals. In: Coelenterate biology: reviews and new perspectives, pp 359–395. Ed. by L. Muscatine and H. M. Lenhoff. New York: Academic Press 1974
Muscatine, L. and E. Cernichiari: Assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by a reef coral. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 137, 506–523 (1969)
Muscatine, L., P. G. Falkowski, J. W. Porter and Z. Dubinsky: Fate of photosynthetic fixed carbon in light and shadeadapted colonies of the symbiotic coral Stylophora pistillata. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 222, 181–202 (1984)
Muscatine, L., R. R. Pool and E. Cernichiari: Some factors influencing selective release of soluble organic material by zooxanthellae from reef corals. Mar. Biol. 13, 298–308 (1972)
Packter, N. M. and P. K. Stumpf: Fat metabolism in higher plants. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 167, 655–667 (1975)
Patton, J. S., S. Abraham and A. A. Benson: Lipogenesis in the intact coral Pocillopora capitata and its isolated zooxanthellae: evidence for a light-driven carbon cycle between symbiont and host. Mar. Biol. 44, 235–247 (1977)
Patton, J. S., J. F. Battey, M. W. Rigler, J. W. Porter, C. C. Black and J. E. Burris: A comparison of the metabolism of bicarbonate 14C and acetate 1-14C and the variability of the species lipid compositions in reef corals. Mar. Biol. 75, 121–130 (1983)
Patton, J. S., and J. E. Burris: Lipid synthesis and extrusion by freshly isolated zooxanthellae (symbiotic algae). Mar. Biol. 75, 131–136 (1983)
Schlichter, D., B. P. Kremer and A. Svoboda: Zooxanthellae providing assimilatory power for the incorporation of exogenous acetate in Heteroxenia fuscescens (Cnidaria: Alcyonaria). Mar. Biol. 83, 277–286 (1984)
Schlichter, D., A. Svoboda and B. P. Kremer: Functional autotrophy of Heteroxenia fuscescens (Anthozoa: Alcyonaria): carbon assimilation and translocation of photosynthates from symbionts to host. Mar. Biol. 78, 29–38 (1983)
Schmitz, K. and B. P. Kremer: Carbon fixation and analysis of assimilates in a coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Mar. Biol. 42, 305–313 (1977)
Sharp, H. H.: Excretion of organic matter by marine phytoplankton: do healthy cells do it? Limnol. Oceanogr. 22, 381–399 (1977)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates: I. the assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 177, 225–235 (1971a)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates: II. Liberation of fixed 14C by zooxanthellae in vitro. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 177, 237–250 (1971b)
Trench, R. K.: The cell biology of plant-animal symbiosis. A. Rev. Pl. Physiol. 30, 485–532 (1979)
Wishnick, M. and M. D. Lane: Inhibition of ribulose disphosphate carboxylase by cyanide. J. biol. Chem. 244, 55–59 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Lawrence, Tampa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Battey, J.F., Patton, J.S. Glycerol translocation in Condylactis gigantea . Mar. Biol. 95, 37–46 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00447483
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00447483