Abstract
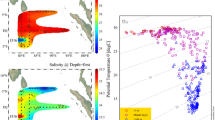
Coccolithophores, together with other phytoplankton, were sampled at ten stations along a transect following the general orientation of the Cape Peninsula upwelling plume in March, 1983. Thirteen coccolithophore species were identified with Emiliania huxleyi dominating the assemblages. Coccolithophores and other microflagellates were more abundant than diatoms along the transect except at one station in mature upwelled water. Very high populations (2 340×103 cells l-1) of coccolithophores were found in mature upwelled water adjacent to the oceanic front. This count is one of the highest counts ever recorded in an upwelling area. The anomalous warm event prior to sampling may have had a residual effect on seeding, contributing towards the predominance of small-celled phytoplankton over chain-forming diatoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Andrews, W. R. H. and L. Hutchings: Upwelling in the southern Benguela Current. Prog. Oceanogr. 9, 1–81 (1980)
Austin, N. E. H.: Plankton of the Benguela Current. A preliminary survey, 127 pp. M. Sc. thesis, University of Natal (Pietermaritzburg), South Africa 1980
Bang, N. D. and W. R. H. Andrews: Direct current measurements of a shelf-edge frontal jet in the southern Benguela system. J. mar. Res. 32, 405–417 (1974)
Barber, R. T. and R. L. Smith: Coastal upwelling ecosystems. In: Analysis of marine ecosystems, pp 31–68. Ed. by A. R. Longhurst. London: Academic Press 1981
Berge, G.: Discoloration of the sea due to Coccolithus huxleyi “bloom”. Sarsia 6, 27–40 (1962)
Boyd, A. J., J. D. Hewitson, I. Kruger and F. Le Clus: Temperature and salinity trends off Namibia from August 1982 to August 1984, and their relation to plankton abundance and the reproductive success of pelagic fish. Colln scient. Pap. int. Commn SE Atl. Fish. 12, 53–58 (1985)
Chavez, F. P.: Ocean variability and phytoplankton community structure: onset of the 1982–83 El Nino in the Peruvian upwelling region. In: Preprints of the symposium on vertical motion in the equatorial upper ocean and its effects upon living resources and the atmosphere. Paris: SCOR-UNESCO 1985
Grindley, J. R. and F. J. R. Taylor: Factors affecting plankton blooms in False Bay. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 39, 201–210 (1970)
Hutchings, L., D. A. Armstrong and B. A. Mitchell-Innes: The frontal zone in the southern Benguela Current. In: Marine interfaces ecohydrodynamics, Elsevier Oceanography Series 42, pp 67–94. Ed. by J. C. J. Nihoul. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1986
Hutchings, L., C. Holden and B. Mitchell-Innes: Hydrological and biological shipboard monitoring of upwelling off the Cape Peninsula. S. Afr. J. Sci. 80, 83–89 (1984)
Kollmer, W. E.: The pilchard of South West Africa (Sardinops ocellata Pappé). The annual cycle of phytoplankton in the waters off Walvis Bay 1958. Invest. Rep. mar. Res. Lab. S.W. Afr. 4, 1–44 (1962)
McIntyre, A. and A. W. H. Bé: Modern Coccolithophoridae of the Atlantic Ocean — I. Placoliths and cyrtoliths. Deep-Sea Res. 14, 561–597 (1967)
Mitchell-Innes, B. A. and M. J. Jury: Phytoplankton assemblages, community structure and biomass along a transect of the Benguela Upwelling System. (In press)
Nelson, G.: Notes on the physical oceanography of the Cape Peninsula upwelling system. In: South African Ocean Colour and upwelling experiment, pp 63–69. Ed. by L. V. Shannon. Cape Town: Sea Fisheries Research Institute 1985
Nelson, G. and L. Hutchings: The Benguela upwelling area. Prog. Oceanogr. 12, 333–356 (1983)
Nelson, G. and N. Walker: Comparison of summer winds on the west coast of South Africa between 1979 and 1983 and the response of coastal upwelling. S. Afr. J. Sci. 80, 90–93 (1984)
Okada, H. and S. Honjo: The distribution of oceanic coccolithophorids in the Pacific. Deep-Sea Res. 20, 355–374 (1973)
Okada, H. and S. Honjo: Distribution of coccolithophores in marginal seas along the Western Pacific Ocean and in the Red Sea. Mar. Biol. 31, 271–285 (1975)
Okada, H. and A. McIntyre: Modern coccolithophores of the Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans. Micropaleontol. 23, 1–55 (1977)
Olivieri, E. T.: Colonization, adaptations and temporal changes in diversity and biomass of a phytoplankton community in upwelled water off the Cape Peninsula, South Africa, in December 1979. S. Afr. J. mar. Sci. 1, 77–109 (1983)
Parsons, T. R. and M. Takahashi: Environmental control of phytoplankton cell size. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 511–515 (1973)
Raymont, J. E. G.: Plankton and productivity in the oceans, Vol. 1. Phytoplankton, 489 pp, New York: Pergamon Press 1980
Semina, H. J.: The size of phytoplankton cells in the Pacific Ocean. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 57, 177–205 (1972)
Shannon, L. V.: The Benguela ecosystem. 1. Evolution of the Benguela, physical features and processes. In: Oceanography and marine biology. An annual review 23, pp 105–182. Ed. by M. Barnes. Aberdeen: University Press 1985
Shannon, L. V. and S. C. Pillar: The Benguela ecosystem. 3. Plankton. In: Oceanography and marine biology. An annual review 24, pp 65–170. Ed. by M. Barnes. Aberdeen: University Press 1986
Smayda, T. J.: A quantitative analysis of the phytoplankton of the Gulf of Panama. III. General ecological conditions, and the phytoplankton dynamics at 8°45′N, 79°23′W from November 1954 to May 1957. Bull. inter-Am. trop. Tuna Commn 11, 355–612 (1966)
Walker N., J. Taunton-Clark and J. Pugh: Sea temperatures off the South African west coast as indicators of Benguela warm events. S. Afr. J. Sci. 80, 72–77 (1984)
Winter, A.: Paleoenvironmental interpretation of Quaternary coccolith assemblages from the Gulf of Aquaba (Elat), Red Sea. Rev. Esp. Micropaleontol. 14, 291–314 (1982)
Winter, A.: Distribution of living coccolithophores in the California Current System, southern California Borderland. Mar. Micropaleontol. 9, 385–393 (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell-Innes, B.A., Winter, A. Coccolithophores: a major phytoplankton component in mature upwelled waters off the Cape Peninsula, South Africa in March, 1983. Mar. Biol. 95, 25–30 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00447481
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00447481