Abstract
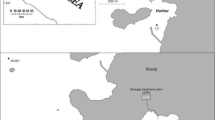
Coordinated environmental monitoring and biochemical studies of the polychaete Glycera alba (Müller) have been applied to the assessment of the impact of inputs of organically rich waste material into Inner Oslofjord. Six sampling stations at intervals of 5 km on a transect extending from Lysakerfjord, 5 km from Oslo harbour, to Vollengropen, a few kilometres from the Drobak sill were used in the investigation. Samples of water, sediment and biological material were collected from these sampling stations on one occasion, in September 1980. On the basis of dissolved oxygen content of the water column near the sediment surface, carbon and nitrogen contents and redox potential (Eh) in the sediments, the greatest impact of organic enrichment was found at Lysakerfjord. Localised variations in sediment condition were, however, pronounced in the transect. Maximal activities of 4 enzymes associated with energy-yielding metabolism were estimated in 7 to 11 individual G. alba from each sampling station. Relatively low activities of the glycolytic enzyme phosphofructokinase in the group of G. alba from Lysakerfjord may constitute a biochemical response to the effects of organic enrichment in this area. In G. alba from the sampling station at Slemmestad, it is suggested that low phosphofructokinase and malate dehydrogenase activities may reflect a biochemical response to effects of prelominantly inorganic waste material from a nearby cement factory. In groups of G. alba from 5 sampling stations, i.e., excluding Slemmestad, mean phosphofructokinase activity is correlated with redox potential at 4 to 5 cm depth in the sediments. The results are discussed with reference to earlier biological studies and it is shown that low phosphofructokinase activities are found in the groups of G. alba from those areas where low diversity of macrobenthic fauna have been reported. It is concluded that the changes in phosphofructokinase activity may consistently reflect effects of environmental changes that are characteristically associated with inputs of waste material.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Beyer, F.: Zooplankton, zoobenthos and bottom sediments as related to pollution and water exchange in the Oslofjord. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 17, 496–509 (1968)
Blackstock, J.: Activities of some enzymes associated with energy yielding metabolism in Glycera alba (Müller) from three areas of Loch Eil. In: Physiology and behaviour of marine organisms, pp 11–20. Ed. by D. S. McLusky and A. J. Berry, Oxford, U.K.: Pergamon Press 1978
Blackstock, J.: A biochemical approach to assessment of effects of organic pollution on the metabolism of the non-opportunistic polychaete, Glycera alba. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 33, 546–555 (1980a)
Blackstock, J.: Estimation of activities of some enzymes associated with energy yielding metabolism in the polychaete, Glycera alba (Müller) and application of the methods to the study of the effects of organic pollution. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 46, 197–217 (1980b)
Blackstock, J. and C. Filion-Myklebust: Maximal enzyme activities in the polychaete Glycera alba (Müller) in relation to detection of effects of organic pollution. In: Indices biochimiques et milieux marins. Publs. Cent. natn. Exploit. Océans (Sér. Act. Colloques), 14, 369–384 (1982)
Føyn, E.: Removal of sewage nutrients by electrolytic treatment. Verh. int. Verein. theor. angew. Limnol. 15, 569–579 (1964)
Gade, H. G.: Horizontal and vertical exchanges and diffusion in the water masses of the Oslo Fjord. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 17, 462–475 (1968)
Gray, J. S.: Pollution induced changes in populations. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 286, 545–561 (1979)
Lowry, O. H., N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr and R. J. Randall: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Mirza, F. B.: The fauna of marine benthic sediments from the organically enriched Oslofjord, Norway, 130 pp. Cand. Sci. thesis, University of Oslo 1980
Mirza, F. B. and J. S. Gray: The fauna of benthic sediments from the organically enriched Oslofjord, Norway. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 54, 181–207 (1981)
NIVA: Indre Oslofjord. Forurensningstilførsler 1920–1980 tilførsel av fosfor. Rep. Norw. Inst. Wat. Res. (NIVA), Oslo 0-78084-03, 1–124 (1981a)
NIVA: Forurensningstilførsler til Indre Oslofjord 1979–80. Rep. Norw. Inst. Wat. Res. (NIVA), Oslo O-78084-04, 1–59 (1981b)
Pearson, T. H.: The benthic biology of Loch Linnhe and Loch Eil, a sea loch system on the west coast of Scotland. Changes in the benthic fauna attributable to organic enrichment. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 20, 1–41 (1975)
Pearson, T. H.: Stress and catastrophe in marine benthic ecosystems. In: Stress effects on natural ecosystems, pp 201–214. Ed. by G. W. Barrett and R. Rosenberg, Chichester, England: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. 1981
Pearson, T. H. and R. Rosenberg: Macrobenthic succession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 16, 229–311 (1978)
Pearson, T. H. and S. O. Stanley: The benthic ecology of some Shetland voes. In: Biology of benthic organisms, pp 503–512. Ed. by B. F. Keegan, P. O. Ceidigh and P. J. S. Boaden. Oxford & New York: Pergamon Press 1977
Pearson, T. H. and S. O. Stanley: Comparative measurement of the redox potential of marine sediments as a rapid means of assessing the effect of organic pollution. Mar. Biol. 53, 371–379 (1979)
Siegel, S.: Non-parametric statistics for the beavioural sciences, 312 pp. New York: McGraw-Hill 1956
Stanley, S. O., J. W. Leftley, A. Lightfoot, N. Robertson, L. M. Stanley and I. Vance: The loch Eil project: sediment chemistry, sedimentation and the chemistry of the overlying water in Loch Eil. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 55, 299–313 (1981)
Stanley, S. O., J. Leftley, D. Miller and T. H. Pearson: Chemical changes in the sediments of Loch Eil arising from the input of cellulose fibre. In: Analytical techniques in environmental chemistry, pp 409–418. Ed. by J. Albaiges. Oxford and New York: Pergamon Press 1980
Whitfield, M.: Eh as an operational parameter in estuarine studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 547–558 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mauchline, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blackstock, J., Filion-Myklebust, C. Environmental and biochemical investigation of some effects of organic pollution in Inner Oslofjord, Norway. Mar. Biol. 73, 155–163 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406883
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406883