Abstract
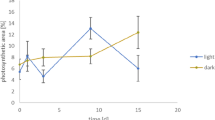
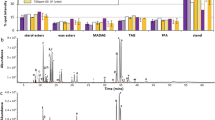
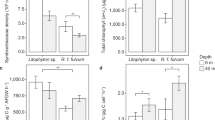
Freshly collected pieces of the hermatypic coral Acropora cf. scandens containing dinoflagellate endosymbionts (presumably Gymnodinium microadriaticum) were allowed to assimilated 14C from H14CO -3 in the light and in the dark. Time-dependent carbon uptake resulted in intense 14C-labelling of ethanol-soluble as well as of insoluble assimilates. About forty 14C-labelled assimilates have been identified. Polymeric (ethanol-insoluble) compounds achieve about 30% of total radiocarbon incorporation after 60 min incubation. Kinetics of 14C-labelling of single assimilates are analyzed. Percentages of typical photosynthates in the soluble fraction undergo characteristic time-dependent changes. Lipids proved to be the main accumulation products of carbon assimilation by incorporating more than 50% of 14C after 60 min photosynthesis. The data indicate that low-molecular weight photosynthates such as 14C-glycerol and 14C-glucose are rapidly converted to constituents of the polymeric fraction(s) of the coral. Besides peptides, polysaccharides, and lipophilic substances, considerable amounts of 14C are confined to skeletal CaCO3 of the coral. The results are discussed with respect to trophic and metabolic interrelationships between the autotrophic dinoflagellates and the A. cf. scandens tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Balderston, W.L. and G. Claus: A study of the symbiotic relationship between Symbiodinium microadriaticum Freudenthal, a zooxanthella and the upside down jellyfish, Cassiopea spec. Nova Hedwigia 17, 373–382 (1969)
Buchsbaum Pearse, V. and L. Muscatine: Rate of symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) in coral calcification. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 141, 350–363 (1971)
Drew, E.: The biology and physiology of algainvertebrate symbioses. I. Carbon fixation in Cassiopea sp. at Aldabra atoll. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 9, 65–69 (1972)
Feige, B., H. Gimmler, W. D. Jeschke and W. Simonis: Eine Methode zur dünnschichtchromatographischen Auftrennung von 14C- und 32p-markierten Stoffwechselprodukten. J. Chromat. 41, 80–90 (1969)
Glasl, H. und H. Pohl: Fettsäuren und Lipide in farblosen Algen. Z. Naturf. (Sect. C) 29, 399–406 (1974)
Hansen, S.A.: Thin-layer chromatographic method for the identification of mono-, di- and trisaccharides. J. Chromat. 107, 224–226 (1975)
Kremer, B.P.: Separation of isomeric pentitols and hexitols by paper and thin-layer chromatography. J. Chromat. 110, 171–173 (1975a)
—: Mannitmetabolismus in der marinen Braunalge Fucus serratus. Z. PflPhysiol. 74, 255–263 (1975b)
—: Rotalgen-Chloroplasten als funktionelle Endosymbionten. Naturwissenschaften 64, 147–148 (1977)
Lewis, D.H. and D.C. Smith: The autotrophic nutrition of symbiotic marine coelenterates with special reference to hermatypic corals. I. Movement of photosynthetic products between the symbionts. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (Ser. B) 178, 111–129 (1971)
Lobban, C.S.: A simple, rapid method of solubilizing algal tissue for scintillation counting. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19, 356–359 (1974)
McLaughlin, J.J.A. and P.A. Zahl: Endozoic algae. In: Symbiosis, Vol. 1 pp 257–297. Ed. by S. M. Henry, New York: Academic Press 1966
Mergner, H. and H. Schuhmacher: Morphologie, Ökologie und Zonierung von Korallenriffen bei Aqaba (Golf von Aqaba, Rotes Meer). Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 26, 238–358 (1974)
Muscatine, L.: Glycerol excretion by symbiotic algae from corals and Tridacna and its control by the host. Science, N.Y. 156, 516–519 (1967)
—: Endosymbiosis of cnidarians and algae. In: Coelenterate biology, pp 359–396. Ed. by L. Muscatine and H.M. Lenhoff, New York: Academic Press 1974
— and E. Cernichiari: Assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by a reef coral. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 137, 506–523 (1969)
—, R.R. Pool and E. Cernichiari: Some factors affecting selective release of soluble organic material by zooxanthellae from reef corals. Mar. Biol. 13, 298–308 (1972)
Splittstoesser, W.E.: Arginine metabolism by pumpkin seedlings. Separation of plant extracts by ion exchange resins. Pl. Cell Physiol., Tokyo 10, 87–94 (1969)
Taylor, D.L.: Symbiotic pathway of carbon in a coral reef ecosystem. Present status and future prospects. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 24, 276–283 (1973)
—: Symbiotic marine algae: taxonomy and biological fitness. In: Symbiosis in the sea. pp 245–262. Ed. by W.B. Vernberg, Columbia: University of South Carolina Press 1974
Trench, R.K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. I. The assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (Ser. B) 177, 225–235 (1971a)
—: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. II. Liberation of fixed 14C by zooxanthellae in vitro. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (Ser. B) 177, 237–250 (1971 b)
—: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. III. The effect of homogenates of host tissues on the excretion of photosynthetic products in vitro by zooxanthellae from two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (Ser. B) 177, 251–264 (1971 c)
—: Nutritional potentials in the sea anemone Zoanthus sociatus. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 26, 174–216 (1974)
Von Holt, C. and M. Von Holt: Transfer of photosynthetic products from zooxanthellae to coelenterate hosts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 24, 83–92 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Hamburg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitz, K., Kremer, B.P. Carbon fixation and analysis of assimilates in a coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Mar. Biol. 42, 305–313 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00402192
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00402192