Abstract
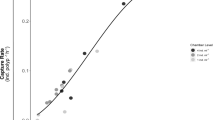
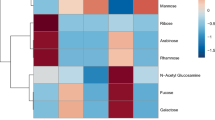
The copepod Acartia tonsa and the reef mysid Mysidium integrum ingest stained coral mucus. Ingestion rates determined with radioisotope-labeled mucus ranged from 4 to 81% body carbon · 24 h-1 for the copepods and I to 70% body carbon · 24 h-1 for the mysids. Incorporation was measured by comparing the organic composition of fecal material and by the incorporation of isotope-labeled mucus. A. tonsa incorporated 47% of ingested ash-free material, 68% of carbon and 36% of nitrogen. M. integrum incorporated 44% of ingested ash-free matter, 57% of carbon and 55% of nitrogen. Incorporation estimates using 14C-labeled mucus were 65% and 39% for incorporation by A. tonsa and M. integrum respectively. A. tonsa and M. integrum incorporated both the mucus substrate and the epiphytic bacteria of the mucus-detritus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Adams, J. A. and J. H. Steele: Shipboard experiments on the feeding of Calanus finmarchicus (Gunnerus). In: Some contemporary studies in marine science, pp 19–35. Ed. by H. Barnes. New York: Hafner Publ. Co. 1966
Alldredge, A.: The chemical composition of macroscopic aggregates in two neritic seas. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24, 855–866 (1979)
Alldredge, A., and J. M. King: Distribution, abundance and substrate preferences of demersal reef zooplankton at Lizard Island Lagoon, Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Biol. 41, 317–333 (1977)
Baker, J. H. and L. A. Bradnam The role of bacteria in the nutrition of aquatic detritivores. Oecologia 24, 95–104 (1976)
Beers, J. R.: Studies on the chemical composition of the major zooplankton groups in the Sargasso Sea off Bermuda. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11, 520–528 (1966)
Benson, A. and L. Muscatine: Wax in coral mucus: energy transfer from corals to reef fish. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19, 810–814 (1974)
Brown, J. W., G. R. Harvey and P. Betzer: Particulate lipid flux in tropical east Pacific Ocean. (In preparation)
Caperon, J., W. Harvey and F. Steinhilper: Particulate organic carbon, nitrogen and chlorophyll as measures of phytoplankton and detritus standing crops in Kaneohe Bay, Oahu, Hawaiian Is. Pac. Sci. 30, 317–327 (1976)
Chervin, M. B.: Assimilation of particulate organic carbon by estuarine and coastal copepods. Mar. Biol. 49, 265–275 (1978)
Clutter, R. and G. Theilacker. Ecological efficiency of a pelagic mysid shrimp: estimates from growth, energy budget and mortality studies. Fish. Bull, U.S. 69, 93–115 (1969)
Coles, S. L. and R. Strathmann. Observations on coral mucus ‘flocs’ and their potential trophic significance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 673–678 (1973)
Conover, R.: Assimilation of organic matter by zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11, 338–345 (1966)
Conover, R. and V. Francis: The use of radioactive isotopes to measure the transfer of materials in aquatic food chains. Mar. Biol. 18, 272–283 (1973)
Conover, R. and M. E. Huntley: General rules of grazing in pelagic ecosystems. In: Primary productivity in the sea, pp 461–486. Ed. by P. G. Falkowski. New York, Plenum Press 1980
Cosper, T. C. and M. R. Reeve: Digestive efficiency of the chaetognath Sagitta hispida Conant. J. exp mar. Biol. Ecol. 17, 33–38 (1975)
Crossland, C. J., D. J. Barnes, T. Cox and M. Devereux: Compartmentation and turnover of organic carbon in the staghorn coral Acropora formosa. Mar. Biol. 59, 181–187 (1980 a)
Crossland, C. J., D. J. Barnes and M. A. Borowitzka: Diurnal lipid and mucus production in the staghorn coral Acropora acuminata. Mar. Biol. 60, 81–90 (1980 b)
Dagg, M. and D. W. Grill: Natural feeding rates of Centropages typicus females in the New York bight. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25, 597–609 (1980)
Daumas, R. and B. A. Thomassin: Protein fractions in coral and zoantharian mucus: possible evolution in coral reef environments. Proc. 3rd int Symp. coral reefs, pp 517–523. Ed. by D. L. Taylor. Miami: School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences, University of Miami 1977
Ducklow, H. and R. Mitchell: Composition of mucus releases by coral reef coelenterates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24, 706–714 (1979 a)
Ducklow, H. and R. Mitchell. Bacterial populations and adaptations in the mucus layers on living corals. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24, 715–725 (1979 b)
Emery, A. R.: Preliminary observation on coral reef plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 13, 293–303 (1968)
Feaguson, R. and P. Rublee. Contribution of bacteria to standing crop of coastal plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 21, 141–145 (1976)
Fleming, J. M. and J. Coughlan: Preservation of vitally stained zooplankton for live dead sorting. Estuaries 1, 135–137 (1978)
Foulds, J. B. and K. H. Mann. Cellulose digestion in Mysis stenolepis and its ecological imlications. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 760–766 (1978)
Gerber, R. and M. Gerber: Ingestion of natural particulate organic matter and subsequent assimilation, respiration and growth by tropical lagoon zooplankton. Mar. Biol. 52, 33–43 (1979)
Gerber, R. and N., Marshall: Ingestion of detritus by the lagoon pelagic community at Eniwetok Atoll. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19, 815–824 (1974)
Glynn, P.: Ecology of a Caribbean coral reef, the Porites reef flat biotope: Part II, Plankton community with evidence for depletion. Mar. Biol. 22, 1–21 (1973)
Hiatt, R. and D. Strasburg. Ecological relationships of the fish fauna on coral reefs of the Marshall Islands. Ecol. Monogr. 30, 65–127 (1960)
Hickel, W.: Seston composition of the bottom waters of Great Lameshur Bay, St. John, U.S.V.I. Mar. Biol. 24, 125–130 (1974)
Hobbie, J. E., R. I. Daley and S. Jasper: Use of nucleopore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl. environ. Microbiol. 33, 1225–1228 (1977)
Hobson, E.: Feeding relationships of teleostean fishes on coral reefs in Kona Hawaii. Fish. Bull. U.S. 72, 915–1031 (1974)
Hollibaugh, J. T., J. A. Fuhrman and F. Azam. Radioactively labeling of natural assemblages of bacterioplankton for use in trophic studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25, 172–181 (1980)
Johannes, R. E.: Ecology of organic aggregates in the vicinity of a coral reef. Limnol. Oceanogr. 12, 189–195 (1967)
Johannes, R. E.: Sources of nutritional energy for reef corals. Proc. 2nd int. symp. coral reefs, pp 133–137. Ed. by Great Barrier Reef Committee Brisbane, Australia 1974
Knudsen, J. W.: Trapezia and Tetralia (Decapods, Brachyura, Xanthidae) as obligate ectoparasites of pocilloporid and acroporid corals. Pac. Sci. 21, 51–57 (1967)
Lampert, W.: A tracer study on the carbon tunover of Daphnia pulex. Verh. internat. Verein. Limnol. 19, 2913–2921 (1975)
Lampert, W.: Studies on the carbon balance of Daphnia pulex as related to environmental conditions I. Methodological problems of the use of 14C for the measurement of carbon assimilation. Arch. Hydrobiol. 48 (supp.), 287–309 (1977)
Landry, M. R.: Predatory feeding behavior of a marine copepod, Labidocera trispinosa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 1103–1113 (1978)
Lasenby, D. and R. Langford: Feeding and assimilation of Mysis relicta. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 280–285 (1973)
Lasker, H. R.: Intraspecific variability of zooplankton feeding in the hermatypic coral Montastrea cavernosa. In: Coelenterate ecology and behavior, pp 101–116. Ed. by G. O. Mackie, New York: Plenum Press 1976
Lee, R. F. J. C. Nevenzel and G. A. Pafenhöfer: Importance of wax esters and other lipids in the marine food chain: phytoplankton and copepods. Mar. Biol. 9, 99–108 (1971)
Lewis, J. B.: Experimental tests of suspension feeding in Atlantic reef corals. Mar. Biol. 36, 147–150 (1976)
Lewis, J. B.: Suspension feeding in Atlantic reef corals and the importance of suspended particulate matter as a food source. Proc. 3rd int. Symp. coral reefs, pp 406–408. Ed. by D. L. Taylor Miami: School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences, University of Miami 1977
Marshall, N.: Observations on organic aggregates in the vicinity of coral reefs. Mar. Biol. 2, 50–53 (1968)
Marshall, N.: Notes on mucus and zooxanthellae discharged from reef corals. Proc. symp. corals and coral reefs, pp 59–65. Ed. by C. Mukundan and C. S. Gopinadha-Pillai. Mar. Biol Assoc. India, Cochin 1972
Marshall, N., A. G. Durbin, R. Gerber, and G. Telek: Observations on particulate and dissolved organic matter in coral reef areas. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 60, 335–345 (1975)
Oláh, J.: Leaching, colonization and stabilization during detritus formation. Mem. Ist. Ital. Idrobiol. Dott Marco de Marchi Pallanza Italy 29 (supp.), 105–128 (1972)
Patton, J., S. Abraham and A. A. Benson: Lipogenesis in the intact coral Pocillopora capitata and its isolated zooxanthellae: evidence for a light driven carbon cycle between symbiont and host. Mar. Biol. 44, 235–247 (1977)
Qasim, S. Z. and V. N. Sankaranarayanan: Production of particulate matter by the reef on Kavaratti Atoll. Limnol. Oceanogr. 15, 574–578 (1970)
Richman, S., Y. Loya and L. B. Slobodkin: The rate of mucus production by corals and its assimilation by the coral reef cepepod Acartia negligens. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20, 918–923 (1975)
Roman, M. R.: Feeding of the copepod Acartia tonsa on the diatom Nitzschia closterium and brown algae (Fucus vesiculosis) detritus. Mar. Biol. 42, 149–155 (1977)
Rublee, P. A.: Bacteria in a North Carolina salt marsh: standing crop and importance in the decomposition of Spartina alterniflora, 80 pp. Ph.D. thesis, North Carolina State University 1978
Rublee, P. A., H. Lasker, M. Gottfried and M. R. Roman: Production and bacterial colonization of mucus from the soft coral Briarium asbestinum. Bull. mar. Sci., 30, 888–893 (1980)
Russell, M. A. C.: The ingestion and assimilation of coral mucus particles by gorgonian soft corals, 45 pp. M.S. thesis, University of Miami 1981
Scott, B. D. and H. R. Jitts: Photosynthesis of phytoplankton and zooxanthellae on a coral reef. Mar. Biol. 41, 307–315 (1977)
Shanks, A. and J. Trent: Marine snow: microscale nutrient patches. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24, 850–854 (1979)
Silver, M. W., A. Shanks and J. Trent: Marine snow: microplankton habitat and source of small scale patchiness in pelagic populations. Science, N.Y. 201, 371–373 (1978)
Simmons, G.: Abundance and size distribution of particulate matter fractions near a Caribbean bank barrier reef. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1, 7–11 (1979)
Steedman, H. F.: Alcian blue 8GS: a new stain for mucin. Q. J. Microsc. Sci. 91, 477–479 (1950)
Tenore, T.: Utilization of aged detritus derived from different sources by the polychaete Capitella capitata. Mar. Biol. 44, 51–55 (1977)
Trent, J. D., A. L., Shanks and M. Silver: In situ and laboratory measurements on macroscopic aggregates in Monterey Bay, California. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 626–635 (1978)
Westrum, B. and P. Meyers. Organic carbon content of seawater from over three Caribbean reefs. Bull. mar. Sci. 28, 153–158, (1978)
Yentsch, C. and D. W. Menzel: A method for the determination of phytoplankton chlorophyll and phaeophytin by fluorescence. Deep Sea Res 10, 221–231 (1963)
Yingst, J. Y.: The utilization of organic matter in shallow marine sediments by an epibenthic deposit feeding holothurian. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 23, 55–69 (1976)
Youngbluth, M. J.: Daily, seasonal and annual fluctuations among zooplankton populations in an unpolluted, tropical embayment. Est. coast. mar. Sci. 10, 265–287 (1980)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Lawrence, Tampa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gottfried, M., Roman, M.R. Ingestion and incorporation of coral-mucus detritus by reef zooplankton. Marine Biology 72, 211–218 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396825
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396825