Abstract
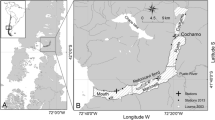
The condition of the green-lipped mussel Perna canaliculus (Gmelin) from 7 sites around the northern half of New Zealand was determined monthly between December 1973 and February 1975. Seven separate estimates of condition were calculated for each sample; 4 condition indices, 2 percentage glycogen analyses and 1 estimate of percentage solids. All showed a similar annual cycle, with minimum values in winter (June/ August) rising to peak levels in spring (October/ December). The 7 sites were divided into 3 groups, (i) a central New Zealand group, characterised by high levels of condition index (CI) throughout most of the year >10 CIweight for 8 to 11 months, average to high percentage glycogen (annualmeans 25 to 35% dry weight), and high percentage solids (annual means > 20% dry weight); (ii) an intertidal group, having low levels of CI (<10 CIweight for 10 to 11 months), low percentage glycogen(mean <20%), and low percentage solids (mean <18%); and (iii) a northern group, showing intermediate values for each of the estimates of condition. Difficulties in defining the causes of changes in the condition cycle are discussed. There is an inverse relationship between CI and mussel size, resulting from changes in body proportions. An inverse relationship is also suggested between CI and water temperature. A precise index,
is recommended for biological studies on mussels and a rapid simple index,
for use in the field and in mussel farming practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Andreu, B.: Fishery and culture of mussels and oysters in Spain. Symp. Ser., mar. biol. Ass., India 3, 835–846 (1970)
Baird, R. H.: Measurement of condition in mussels and oysters. J. Cons. perm. int. Explor. Mer. 23, 249–257 (1958)
Baird, R. H.: Factors affecting the growth and condition of mussels (Mytilus edulis L.). Fish Invest., Lond. (Ser. 2) 25(2), 1–33 (1966)
Benitez, A. J. y T. Okuda: Variación estacional en la composición química del mejillón Perna perna (L) natural. Boln Inst. oceanogr. Univ. Oriente (Cumaná Venezuela) 10(1), 3–8 (1971)
Booth, J. D.: Common bivalve larvae from New Zealand: Mytilacea. N.Z. Jl mar. Freshwat. Res. 11, 407–440 (1977)
Daniel, R. J.: Seasonal changes in the chemical composition of the mussel (Mytilus edulis) (continued), Proc. Trans. Lpool biol. Soc. 36, 269–285 (1922)
Dare, P. J. and G. Davies: Experimental suspended culture of mussels (Mytilus edulis L.) in Wales using spat transplanted from a distant settlement ground. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 6, 257–274 (1975)
Dare, P. J. and D. B. Edwards: Seasonal changes in flesh weight and biochemical composition of mussels (Mytilus edulis L.) in the Conwy Estuary, North Wales. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 18, 89–97 (1975)
Davies, G.: Observations on the growth of Mytilus edulis L. in the Menai Straits in the period 1962–68. Int. Counc. Explor. Sea Comm. Meet. (Shellfish and Benthos Committee) 1969/ K: 39, 1–5 (1969)
Drzycimski, I.: Nutrition, chemical composition and possibilities for utilization of the sea mussel, Mytilus edulis L., from the southern Baltic. Annls biol., Copenh. 18, 209–210 (1961)
Flaws, D. E.: Observations on mussel biology, Cook Strait area. In: Report on mussel cultivation seminar, October 1971. Tech. Rep. N.Z. Fish. Ind. Bd 5, 14–20 (1972)
Flaws, D. E.: Aspects of the biology of mussels in the Cook Strait area, 219 pp. Unpublished PhD thesis, Zoology Department, Victoria University of Wellington, New Zealand 1975
Fraga, F.: Variacion estacional de la composicion quimica del mejillon (Mytilus edulis) I. Investigación pesq. 4, 109–125 (1956)
Fraser, J. R. and D. C. Holmes: The determination of glycogen in oysters. Analyst, Lond. 86, 131–132 (1961)
Gabbott, P. A.: Energy metabolism. In: Marine mussels: their ecology and physiology, pp 293–355. Ed. by B. L. Bayne. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1976
Gabbott, P. A. and B. L. Bayne: Biochemical effects of temperature and nutritive stress on Mytilus edulis L. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 53, 269–286 (1973)
Giese, A. C.: A new approach to the biochemical composition of the mollusc body. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 7, 175–229 (1969)
Greenway, J. P. C.: Development of a colony of green mussels, Perna canaliculus in Coromandel Harbour 1971–72. Fish. tech. Rep. N.Z. Minist. Agric. Fish. 141, 1–15 (1975)
Hickman, R. W.: Potential for the use of stranded seed mussels in mussel farming. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 9, 287–293 (1976)
Hickman, R. W.: Incidence of a pea crab and a trematode in cultivated and natural green-lipped mussels. N.Z. Jl mar. Freshwat. Res 12, 211–215 (1978)
Hickman, R. W.: Allometry and growth of the green-lipped mussel Perna canaliculus in New Zealand. Mar. Biol 51, 311–327 (1979)
Jørgensen, C. B.: Growth efficiencies and factors controlling size in some mytilid bivalves, especially Mytilus edulis L.: Review and interpretation. Ophelia 15, 175–192 (1976)
Korringa, P.: Qualitatsbestimmungen an Miesmuscheln und Austern. Arch. FischWiss 6, 189–193 (1955)
MacLean, J. L.: Mussel culture: methods and prospects. Aust. Fish. Pap. 20, 1–13 (1972). (Fish. Div., Dep. prim. Ind., Canberra)
Mason, J.: Mussel raft trials succeed in Scotland. Wld Fishg April 1969 (18) 22–24 (1969)
Mason, J.: Mussel cultivation. Underwat. J. 3(2), 52–59 (1971)
Medcof, J. C. and A. W. H. Needler: The influence of temperature and salinity on the condition of oysters (Ostrea virginica). J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 5, 253–257 (1941)
Padilla, M.: Observaciones biologicas relacionadas con el cultivo de Mytilus edulis chilensis en Aysen. Publnes Inst. Fomento pesq. (Santiago) 54, 1–21 (1973)
Seed, R.: Factors influencing shell shape in the mussel Mytilus edulis. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 48, 561–584 (1968)
Seed, R.: Ecology. In: Marine mussels: their ecology and physiology, pp 13–65. Ed. by B. L. Bayne. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1976
Shaw, W. N., H. S. Tubiash and A. M. Barker: Freeze-drying for determining total solids in shellfish. J. Fish Res. Bd Can. 24, 1413–1417 (1967)
Vande Velde, A. J. J.: De chemische Samenstelling von de Zeemossel (Mytilus edulis). Natuurw. Tijdschr. 21, 32–46 (1939)
Vélez, A. R.: Fluctuación mensual del indice de engorde del mejillon Perna perna natural y cultivado. Boln Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. Oriente (Cumaná, Venezuela) 10(2), 3–8 (1971)
Williams, C. S.: The effect of Mytilicola intestinalis on the biochemical composition of mussels. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 49, 161–173 (1969)
Winer, B. J.: Statistical principles in experimental design, 672 pp. New York: McGraw Hill 1962
Zwaan, A., de, W. J. A. Marrewijk and D. A. Holwerda: Anaerobic carbohydrate metabolism in the sea mussel Mytilus edulis L. Neth. J. Zool. 23, 225–228 (1973)
Zwaan, A., de and D. I. Zandee: Body distribution and seasonal changes in the glycogen content of the common sea mussel Mytilus edulis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 43A, 53–58 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hickman, R.W., Illingworth, J. Condition cycle of the green-lipped mussel Perna canaliculus in New Zealand. Mar. Biol. 60, 27–38 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395603
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395603