Abstract
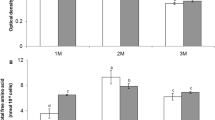
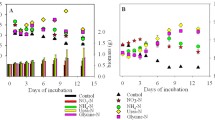
The role of organic solutes in the osmotic adjustment processes of the marine macroalga Enteromorpha intestinalis (L.) Link was investigated in 1986, using fresh samples collected from mid-shore rock pools at Tayport, Fife, Scotland. Natural-abundance 13C nuclear magnetic-resonance spectroscopy revealed β-dimethylsulphoniopropionate (DMSP) to be the only major low molecular weight organic osmolyte present. However, on transfer to a hypersaline medium (300% sea water; 100%=35 S‰), tissue sucrose and proline levels increased markedly, while DMSP remained constant. Recovery of optimal photosynthetic activity and increases in inorganic ion levels occurred over a similar time scale to the changes in sucrose and proline (within 48 h), indicating that these two organic solutes are involved in hyperosmotic adjustment in E. intestinalis while DMSP is not. Freshly-collected plants transferred to 300% sea water medium in the dark showed no significant increases in organic osmolytes. In contrast, starch-enrichment (16 d continuous illumination) led to enhanced synthesis of sucrose and proline in the light and in darkness, but tissue DMSP levels showed no variation throughout. These observations suggest that DMSP is not involved in short-term osmoacclimation in E. intestinalis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Ackman, R. C., C. S. Tocher and J. McLachlan: Dimethyl-β-propiothetin: determination by reactor gas-liquid chromatography, occurrence in algae and implications in fisheries. Proc. int. Seaweed Symp. 5, 235–242 (1966). (Ed. by E. G. Young and J. L. McLachlan. Oxford: Pergamon Press)
Ahmad, I and J. A. Hellebust: Osmoregulation in the extremely euryhaline marine micro-alga Chlorella autotrophica. Pl. Physiol. 74, 1010–1015 (1984)
Andreae, M. O.: Dimethyl sulphoxide in marine and freshwaters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25, 1054–1063 (1980)
Bates, L. S., R. P. Waldren and I. D. Teare: Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Pl. Soil 39, 205–207 (1973)
Ben-Amotz, A. and M. Avron: Accumulation of metabolites by halotolerant algae and its industrial potential. A. Rev. Microbiol. 17, 95–119 (1983)
Black, D. R. and D. C. Weeks: Ionic relationships of Enteromorpha intestinalis. New Phytol. 71, 119–127 (1972)
Borowitzka, L. J.: Solute accumulation and regulation of cell water activity. In: The physiology and biochemistry of drought resistance in plants, pp 97–130. Ed. by L. G. Paleg and D. Aspinall. London: Academic Press 1981
Borowitzka, L. J. and A. D. Brown: The salt relations of marine and halophilic species of the unicellular green alga Dunaliella. The role of glycerol as a compatible solute. Archs Microbiol. 96, 37–52 (1974)
Borowitzka, L. J., S. Demmerle, M. A. Mackay and R. S. Norton: Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic study of osmoregulation in a blue-green alga. Science, N.Y. 210, 650–651 (1980)
Brady, C. J., T. S. Gibson, E. W. R. Barlow, J. Spiers and R. G. Wyn Jones: Salt tolerance in plants. I. Ions, compatible organic solutes and the stability of plant ribosomes. Pl. Cell Envir. 7, 571–578 (1984)
Brown, A. D.: Physiological problems of water stress. In: Strategies of microbial life in extreme environments, pp 65–81. Ed by M. Shilo. Berlin: Dahlem Konferenzen 1979
Brown, A. D. and J. R. Simpson: Water relations of sugartolerant yeasts: the role of intracellular polyols. J. gen. Microbiol. 72, 589–591 (1972)
Brown, L. M. and J. A. Hellebust: Sorbitol and proline as intracellular osmotic solutes in the green alga Stichococcus bacillaris. Can. J. Bot. 56, 676–679 (1980)
Challenger, F.: Aspects of the organic chemistry of sulphur, 71 pp. Butterworths: London 1959
Clark, M. E.: The osmotic role of amino acids: discovery and function In: Transport processes: iono- and osmoregulation, pp 412–423. Ed. by R. Gilles and M. Gilles-Ballier. Berlin: Springer-Verlag 1985
Craigie, J. S. and J. McLachlan: Glycerol as a photosynthetic product in Dunaliella tertiolecta Butcher. Can. J. Bot. 42, 777–778 (1964)
Cram, W. J.: Negative feedback regulation of transport in cells. The maintenance of turgor, volume and nutrient supply. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, Vol. 2A pp 284–326. Ed. by U. Luttge and M. G. Pitman. Berlin: Springer-Verlag 1976
Dickson, D. M. J. and G. O. Kirst: The role of β-dimethylsulphoniopropionate, glycine betaine and homarine in the osmoacclimation of Platymonas subcordiformis. Planta 167, 536–543 (1986)
Dickson, D. M. J., R. G. Wyn Jones and J. Davenport: Steady state osmotic adaptation in Ulva lactuca. Planta 150, 158–166 (1980)
Dickson, D. M. J., R. G. Wyn Jones and J. Davenport: Osmotic adaptation in Ulva lactuca under fluctuating salinity regimes. Planta 155, 409–415 (1982)
Diggelen, J. von, J. Rozema, D. M. J. Dickson and R. Broekman: β-3-dimethylsulphoniopropionate, proline and quaternary ammonium compounds in Spartina anglica in relation to sodium chloride, nitrogen and sulphur. New Phytol. 103, 573–586 (1986)
Flowers, T. J., P. F. Troke and A. R. Yeo: The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. A. Rev. Pl. Physiol. 28, 89–121 (1977)
Galinski, E. A. and H. G. Trüper: Betaine, a compatible solute in the extremely halophilic phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halochloris. Fedn eur. microbiol. Soc. (FEMS) Lett 13, 357–360 (1982)
Gilles, R.: Mechanisms of osmoregulation in animals: maintenance of cell volume, 274 pp. Chichester: Wiley 1979
Greenway, H. and T. L. Setter: Na+, K+ and Cl- concentrations in Chlorella emersonii exposed to 100 and 335 mM NaCl. Aust. J. Pl. Physiol. 6, 61–67 (1979)
Gutknecht, J. and J. Dainty: Ionic relations of marine algae. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev 6, 163–260 (1968)
Hanisak, M. P.: The nitrogen relationships of marine macroalgae. In: Nitrogen in the marine environment, pp 699–730. Ed by E. J. Carpenter and D. G. Capone. New York: Academic Press 1983
Heber, U., L. Tyanova and K. A. Santarius: Stabilisation and inactivation of biological membranes during freezing in the presence of amino acids. Biochem. biophys. Acta 241, 578–592 (1971)
Hellebust, J. A. and S. M. L. Le Gresley: Growth characteristics of the marine rock pool flagellate Chlamydomonas pulsatilla Wallenweber (Chlorophyta). Phycologia 24, 225–229 (1985)
Jennings, D. H.: Some aspects of the physiology and biochemistry of marine fungi. Biol. Rev. 58, 423–459 (1983)
Kirst, G. O.: The cell volume of the unicellular alga Platymonas subcordiformis Hazen. Effect of the salinity of the culture medium and of osmotic stresses. Z. Pfl Physiol. 81, 386–394 (1977)
Larher, F., J. Hamelin et G. R. Stewart: L'acide dimethyl sulphonium-3-propionique de Spartina anglica. Phytochem. 16, 2019–2020 (1977)
Lutz, P. L. and J. D. Robertson: Osmotic constituents of the coelocanth Latimeria cholumeae Smith. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab, Woods Hole 141, 553–560 (1971)
Mackay, M. A., R. S. Norton and L. J. Borowitzka: Organic osmoregulatory solutes in cyanobacteria. J. gen. Microbiol. 130, 2177–2191 (1984)
Reed, R. H.: The influence of salinity upon cellular mannitol concentration of the euryhaline marine alga Pilayella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. (Phaeophyta, Ectocarpales). Preliminary observations. Botanica mar. 23, 603–605 (1980)
Reed, R. H.: Measurement and osmotic significance of β-dimethylsulphoniopropionate in marine macroalgae. Mar. Biol. Lett. 4, 173–181 (1983a)
Reed, R. H.: The osmotic responses of Polysiphonia lanosa (L.) Tandy from marine and estuarine sites: evidence for incomplete recovery of turgor. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 68, 169–173 (1983b)
Reed, R. H., L. J. Borowitzka, M. A. Mackay, J. A. Chudek, R. Foster, S. R. C. Warr, D. J. Moore and W. D. P. Stewart: Organic solute accumulation in osmotically-stressed cyanobacteria. Fedn. eur. microbiol. Soc. (FEMS) Microbiol. Rev. 39, 51–56 (1986)
Reed, R. H., J. A. Chudek, R. Foster, and W. D. P. Stewart: Osmotic adjustment in cyanobacteria from hypersaline environments. Archs Microbiol. 138, 333–337 (1984)
Reed, R. H., J. C. Collins and G. Russell: The influence of varying salinity upon photosynthesis in the marine alga Porphyra purpurea Z. PflPhysiol. 98, 183–187 (1979)
Reed, R. H., J. C. Collins and G. Russell: The effects of salinity upon cellular volume of the marine red alga Porphyra purpurea (Roth) C. Ag. J. exp. Bot. 31, 1521–1537 (1980)
Reed, R. H., J. C. Collins and G. Russell: The effects of salinity upon ion content and ion transport in the marine red alga Porphyra purpurea (Roth) C. Ag. J. exp. Bot. 32, 347–362 (1981)
Reed, R. H. and I. R. Davison: Gas-liquid chromatography of low molecular weight carbohydrates from marine macroalgae: a rapid direct extraction procedure using dimethyl sulphoxide. Br. phycol. J. 19, 381–383 (1984)
Reed, R. H., I. R. Davison, J. A. Chudek and R. Foster: The osmotic role of mannitol in the Phaeophyta: an appraisal. Phycologia 24, 35–47 (1985a)
Reed, R. H. and G. Russell: Adaptation to salinity stress in populations of Enteromorpha intestinalis (L.) Link. Estuar. cstl. mar. Sci. 8, 251–258 (1979)
Reed, R. H., S. R. C. Warr, D. L. Richardson, D. J. Moore and W. D. P. Stewart: Multiphasic osmotic adjustment in a euryhaline cyanobacterium. Fedn eur. microbiol. Soc. (FEMS) Lett. 28, 225–229 (1985b)
Ritchie, R. J. and A. W. D. Larkum: Potassium transport in Enteromorpha intestinalis (L.) Link. I. Measurement of intracellular K+, exchange fluxes and thermodynamic analysis. J. exp. Bot. 36, 63–78 (1985a)
Ritchie, R. J. and A. W. D. Larkum: Potassium transport in Enteromorpha intestinalis (L.) Link. II. Effects of medium composition and metabolic inhibitors. J. exp. Bot. 36, 394–412 (1985b)
Salt, R. W.: Role of glycerol in cold hardness of Bracon cephi (Gohon). Can. J. Zool. 37, 59–69 (1959)
Santarius, K. A.: The protective effect of sugars on chloroplast membranes during temperature and water stress and its relationship to frost, desiccation and heat resistance. Planta 113, 105–114 (1973)
Setter, T. L. and H. Greenway: Changes in the proportion of endogenous osmotic solutes accumulated by Chlorella emersonii in the light and dark. Plant Cell Envir. 6, 227–234 (1983)
Stewart, G. R. and J. A. Lee: The role of proline accumulation in halophytes. Planta 120, 279–289 (1974)
Storey, R and R. G. Wyn Jones: Betaine and choline levels in plants and their relationship to NaCl stress. Pl. Sci. Lett. 4 161–168 (1975)
Vairavamurthy, A., M. O. Andreae and R. L. Iverson: Biosynthesis of dimethylsulphide and dimethylpropiothetin by Hymenomonas carterae in relation to sulphur source and salinity variation. J. Oceanogr., Kobe 30, 59–75 (1985)
Warr, S. R. C., R. H. Reed and W. D. P. Stewart: Osmotic adjustment of cyanobacteria: the effects of NaCl, KCl, sucrose and glycine betaine on glutamine synthetase activity in a marine and a halotolerant strain. J. gen. Microbiol. 130 2169–2171 (1984)
Wetherall, D. F.: Osmotic equilibrium and growth of Scenedesmus obliquus in saline medium. Physiologia Pl. 16, 82–91 (1963)
White, R. H.: Analysis of dimethyl sulphonium compounds in marine algae. J. mar. Res. 40, 529–535 (1982)
Wyn Jones, R. G., R. Storey and H. Pollard: Ionic and osmotic regulation in plants, particularly halophytes. In: Transmembrane ionic exchanges in plants, pp 537–544. Ed. by M. Thellier, A. Monnier, M. Demarty and J. Dainty. Paris: CNRS 1977
Yancey, P. H.: Organic osmotic effectors in cartilagenous fishes. In: Transport processes: iono- and osmoregulation, pp 424–436. Ed. by R. Gilles and M. Gilles-Bailien. Berlin: Springer-Verlag 1985
Yancey, P. H., M. E. Clark, S. C. Hand, R. D. Bowlus and G. N. Somero: Living with water stress: evolution of osmolyte systems. Science, N.Y. 217, 1214–1222 (1982)
Young, A. J.: Responses to salinity in the genus Enteromorpha, 147 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of Liverpool 1984
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mauchline, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edwards, D.M., Reed, R.H., Chudek, J.A. et al. Organic solute accumulation in osmotically-stressed Enteromorpha intestinalis . Mar. Biol. 95, 583–592 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393102
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393102