Abstract
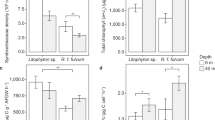
Capnella gaboensis Verseveldt, 1977 (Coelenterata: Octocorallia: Alcyonacea: Nephtheidae) is an abundant soft coral in the temperate waters of south-eastern Australia. From 1981 to 1984, using material collected from Sydney Harbour (33°50′S; 151°15′E), we investigated certain aspects of its apparently obligate association with its symbiotic zooxanthellae, Symbiodinium sp. Numbers of zooxanthellae and chlorophyll content were recorded throughout the first year, then net photosynthesis and respiratory rates of the coral as a function of photo-flux densities, temperature and season were measured in later years. The fractions into which photosynthetically fixed carbon was incorporated were also determined. The zooxanthellae contained a mean of 4.1 μg chlorophyll a 10-6 zooxanthellae. Neither the numbers of zooxanthellae in C. gaboensis nor the chlorophyll a content varied on a seasonal basis. Photon-flux densities in the field ranged from 5 to 120 μE m-2 s-1 over the year. The maximum net oxygen-exchange rate recorded for C. gaboensis was 9.4 μmol O2 mg-1 chlorophyll a h-1 at 871 μE m-2 s-1. The maximum carbon fixation rate obtained was 65.6 μmol C mg-1 chlorophyll a h-1 at 100 μE m-2 s-1. Photosynthesis of C. gaboensis was not light-saturated at 871 μE m-2 s-1; the light compensation point was in the range 50 to 90 μE m-2 s-1 and the optimum temperature was 25°C. Photosynthetic rates were highest in populations sampled in summer. Labelling with 14C showed that photosynthetically fixed carbon was initially incorporated into the aqueous-methanol (low molecular weight) fraction of the coral tissues. From 20 to 100 min after the introduction of the 14C label the rate of incorporation was fairly evenly divided between the aqueous methanol-soluble, the chloroform-soluble (lipid) and the insoluble fractions. In the light, little 14C was released as particulate and/or dissolved organic carbon. Translocation of products of photosynthesis represented up to approximately 10% of the total fixation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Battey, J. F. and J. S. Patton: A reevaluation of the role of glycerol in carbon translocation in zooxanthellae-coelenterate symbiosis. Mar. Biol. 79, 27–38 (1984)
Blank, R. J. and R. K. Trench: Symbiodinium microadriaticum: a single species? Proc. 5th int. coral Reef Congr. 6, 113–117 (1985). (Ed. by C. Gabrie et al. Moorea, French Polynesia: Antenne Museum-EPHE)
Burris, J. E., J. W. Porter and W. A. Laing: Effects of carbon dioxide concentration on coral photosynthesis. Mar. Biol. 75, 113–116 (1983)
Chalker, B. E.: Simulating light-saturation curves for photosynthesis and calcification by reef-building corals. Mar. Biol. 63, 135–141 (1981)
Clark, K. B. and K. R. Jensen: Effects of temperature on carbon fixation and carbon budget partitioning in the zooxanthellal symbiosis of Aiptasia pallida (Verrill). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 64, 215–230 (1982)
Crossland, C. J.: Release of photosynthetically-derived organic carbon from a hermatypic coral, Acropora cf. acuminata. In: Endocytobiology. Endosymbiosis and cell biology: a synthesis of recent research, pp 163–172. Ed. by W. Schwemmler and H. E. A. Schenk. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter 1980. [Proceedings of an International Colloquium on Endosymbiosis and Cell Research]
Crossland, C. J., D. J. Barnes and M. A. Borowitzka; Diurnal lipid and mucus production in the staghorn coral Acropora acuminata. Mar. Biol. 60, 81–90 (1980)
Farrant, P. A.: Reproduction in the temperate Australian soft coral Capnella gaboensis. Proc. 5th int. coral Reef Congr. 4, 319–324 (1985). (Ed. by C. Gabrie et al. Moorea, French Polynesia: Antenne Museum-EPHE)
Farrant, P. A.: Gonad development and the planulae of the temperate Australian soft coral Capnella gaboensis. Mar. Biol. 92, 381–392 (1986)
Feige, B., H. Gimmler, W. D. Jeschke und W. Simonis: Eine Methode zur Dünnschichtchromatographischen Auftrennung von 14C- und 32P-markierten Stoffwechselprodukten. J. Chromat. 41, 80–90 (1969)
Grant, B. R. and M. A. Borowitzka: Changes in isolated chloroplasts of Codium fragile and Caulerpa filiformis in response to osmotic shock and detergent treatments. Protoplasma 120, 155–164 (1984)
Jeffrey, S. W. and G. F. Humphrey: New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c 1 , and c 2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pfl. 167, 191–194 (1975)
Kellogg, R. B. and J. S. Patton: Lipid droplets, medium of energy exchange in the symbiotic anemone Condylactis gigantea: a model coral polyp. Mar. Biol. 75, 137–149 (1983)
Mews, L. K.: Transfer of photosynthate in green hydra. In: Endocytobiology. Endosymbiosis and cell biology: a synthesis of recent research, pp 259–267. Ed. by W. Schwemmler and H. E. A. Schenk. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter 1980. [Proceedings of International Colloquium on Endosymbiosis and Cell Research]
Muscatine, L.: Productivity of zooxanthellae. In: Primary productivity in the sea, pp 381–402. Ed. P. G. Falkowski. New York: Plenum 1980
Muscatine, L. and E. Cernichiari: Assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by a reef coral. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 137, 506–523 (1969)
Patton, J. S., J. F. Battey, M. W. Rigler, J. W. Porter, C. C. Black and J. E. Burris: A comparison of the metabolism of bicarbonate 14C and acetate 1-14C and the variability of species lipid compositions in reef corals. Mar. Biol. 75, 121–130 (1983)
Redgwell, R. J.: Fractionation of plant extracts using ion-exchange Sephadex. Analyt. Biochem. 107, 44–50 (1980)
Schlichter, D., A. Svoboda and B. P. Kremer: Functional autotrophy of Heteroxenia fuscescens (Anthozoa: Alcyonaria): carbon assimilation and translocation of photosynthates from symbionts to host. Mar. Biol. 78, 29–38 (1983)
Schmitz, K. and B. P. Kremer: Carbon fixation and analysis of assimilates in a coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Mar. Biol. 42, 305–313 (1977)
Scott, B. D. and H. R. Jitts: Photosynthesis of phytoplankton and zooxanthellae on a coral reef. Mar. Biol. 41, 307–315 (1977)
Skirrow, G.: The dissolved gases-carbon dioxide. In: Chemical oceanography, pp 1–112. Ed. by J. P. Riley and G. Skirrow. New York and London: Academic Press 1975
Smith, I. (ed.) Chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques. Vol. 1. Chromatography, 3 edn. pp 1–1080. Bath, England, Pitman Press 1969
Szmant-Froelich, A.: Coral nutrition: comparison of the fate of 14C from ingested labeled brine shrimp and from the uptake of NaH14CO3 by its zooxanthellae. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 55, 133–144 (1981)
Taylor, D. L.: Identity of zooxanthellae isolated from some Pacific Tridacnidae. J. Phycol. 5, 336–340 (1969)
Titlyanov, E. A., V. I. Zvalinskii, M. G. Shaposhnikova and V. A. Leletkin: Some adaptation mechanisms of coral-reef formations of Australia to light intensity. Soviet J. mar. Biol. 7, 93–102 (1982)
Trevelyan W. E., D. P. Procter and J. S. Harrison: Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature, Lond. 166, 444–445 (1950)
Verseveldt, J.: Australian Octocorallia (Coelenterata). Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 28, 171–240 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farrant, P.A., Borowitzka, M.A., Hinde, R. et al. Nutrition of the temperate Australian soft coral Capnella gaboensis . Mar. Biol. 95, 565–574 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393100
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393100