Abstract
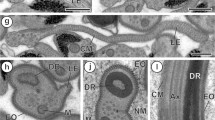
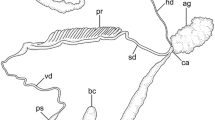
In the spiny lobster Panulirus homarus (Linnaeus) the spermatophoric mass consists of a highly convoluted tube, containing the sperm mass and a gelatinous matrix. The spermatophoric components have their origin in the proximal vas deferens and the completed spermatophoric mass is stored within the distal dilated part of the vas deferens. In the proximal vas deferens the inner glandular epithelial cells give rise to leaf-like typhlosoles which gradually diminish in size and finally disappear in the distal vas deferens. The secretions originating from the typhlosole form the outer gelatinous matrix of the spermatophoric mass. Histochemical observations reveal that the wall of the spermatophore tube consists of neutral mucopolysaccharide, whereas the sperm mass and the gelatinous matrix are rich in acidic mucopolysaccharides. Both polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and agarose gel electrophoresis were used to separate the acidic mucopolysaccharide (AMPS) complexed with the proteins and the simple proteins. In addition, AMPS have been isolated following the method of Rahemtulla and Lovtrup (1974) and used for electrophoresis. In both the polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and agarose gel electrophoresis, the extracted acid mucopolysaccharides give only a single fraction which, in comparison with the standard acid mucopolysaccharides, corresponds to chondroitin sulphate. The functional significance of the chondroitin sulphate and neutral mucopolysaccharides in the spermatophoric components of P. homarus is discussed in relation to their functional role in spermatophore hardening and protection of the delicate spermatozoa during their prolonged storage on the sternum of the female.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Aminoff, D., W. W. Binkley, R. Schaffer and R. W. Mowry: Analytical methods for carbohydrates. In: The carbohydrates, Vol. 2, pp 748–809. Ed by W. Pigman and D. Horton. New York: Academic Press 1978
Berry, P. F. and A. E. F. Heydorn: A comparison of the spermatophoric masses and mechanisms of fertilization in southern African spiny lobsters (Palinuridae). Oceanogr. Res. Inst. (Durban), Invest. Rep. 25, 1–18 (1970)
Chayen, J., I. Bitensky and R. G. Butcher: Practical histochemistry, pp 1–271. New York: John Wiley and Sons 1973
Davis B. J.: Disc electrophoresis. ii. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 121, 404–427 (1964)
Deecaraman, M. and T. Subramoniam: Male reproductive tract and accessory glands of a stomatopod, Squilla holoschista. Int. J. Invertebr. Repod. 2, 175–188 (1980)
Dudenhausen, E. E. and P. Talbot: An ultrastructural comparison of soft and hardened spermatophores from the crayfish, Pacifastacus leniusculus Data. Can. J. Zool. 61, 182–194 (1983)
Jaques, L. B., T. K. Sue, N. M. Mc Duffie and S. Wice: Optical densitometry on electrophoretic agarose slides. Methods Biochem. Anal. 24, 203–312 (1977)
Kent, P. W. and M. W. Whitehouse: Biochemistry of the aminosugars, pp 1–311. London: Butterworths Scientific Publication, 1955
King, J. E.: A study on the reproductive organs of the common marine shrimp, Penaeus setiferaus (Linnaeus) Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 94, 244–262 (1948)
Malek, S. R. A. and F. M. Bawab: The formation of the spermatophore in Penaeus kerathurus (Forskal, 1975) (Decapoda, Penaeidae). 1. The initial formation of sperm mass. Crustaceana (Leiden) 26, 273–285 (1974)
Matthews, D. C.: The origin, development and nature of the spermatophoric mass of the spiny lobster, Panulirus penicillatus (Oliver) Pac. Sci. 5, 359–371 (1951)
Pearse, A. G. E.: Histochemistry. Theoretical and applied. Vol. 1, pp 1–759. London: Churchill Livingstone 1968
Pigman, W. and D. Horton: The carbohydrates, Vol. 2 B, pp 592–604. New York: Academic Press 1970
Rahemtulla, F. and S. Lovtrup: The comparative biochemistry of invertebrate mucopolysaccharides — I. Methods: Platyhelminthes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 49 B, 631–637 (1974)
Smith, I.: Chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques, Vol. 2, pp 365–389. London: William Heinemann Medical Books Ltd. 1968
Smith, J. V. and A. N. Ratchiffe: Host defence reactions of the shore crab, Carcinus maenus (L) in vitro. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 58, 367–379 (1978)
Spalding, J. F.: The nature and formation of the spermatophore and sperm plug in Carcinus maenas. Q. J. microsc. Sci. 83, 299–422 (1942)
Subramoniam, T.: Spermatophore formation in two intertidal crabs Albunea symnista and Emerita asiatica (Decapoda, Anomura). Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 166, 78–95 (1984)
Uma, K. and T. Subramoniam: Histochemical characteristics of spermatophore layers of Scylla serrata (Forskal) (Decapoda, Portunidae) Int. J. Invertebr. Reprod. 1, 31–41 (1979)
White, A., P. Handler, E. L. Smith, R. L. Hill and R. Lehman: Principles of biochemistry, pp 1155. London: Academic Press 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by D. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radha, T., Subramoniam, T. Origin and nature of spermatophoric mass of the spiny lobster Panulirus homarus . Marine Biology 86, 13–19 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392575
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392575