Abstract
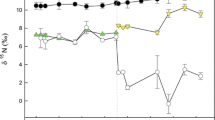
Seasonal variations in the balance between physiological mechanisms of feeding and digestion are considered among 45 to 57 mm shell length Mytilus edulis L. from southwest England. Mussels had been acclimated to standardised conditions of food availability in March, June and October, 1981. Results indicate that despite showing a negative relationship (P<0.001) with the efficiency of 15N absorption, coincident alterations of both ingestion rate (0.17 to 0.54 mg total Phaeodactylum tricornutum h-1) and organic gut content (1.00 to 1.80 mg) represent significant mechanisms effecting the seasonal regulation of nutrient acquisition. Concurrent changes in absorption efficiency alone clearly exerted a relatively minor influence upon seasonal rates of absorption. Associated gut residence times of 15N-labelled material varied between 4 and 10 h. Furthermore, despite the ensuing deleterious effects, together with increased gut contents, absorption efficiencies among mussels that had been starved throughout acclimation were consistently maintained equivalent to those among individuals feeding normally. Such constancy was at least partially achieved by an increased residence time of material within diverticulae, relative to the digestive system as a whole. Finally, comparison of isotopic absorption efficiencies with those recorded for total organics and organic nitrogen has demonstrated differences of as much as 30% between “gross” and “net” uptake due, we suggest, to excretion of metabolically derived material within the alimentary canal.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Allen, J. A.: Preliminary experiments on the feeding and excretion of bivalves using Phaeodactylum labelled with 32P. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 42, 609–623 (1962)
Almada-Villela, P. C., P. C. Davenport and L. D. Gruffydd: The effects of temperature on the shell growth of young Mytilus edulis L. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 59, 275–288 (1982)
Bayne, B. L.: Physiological changes in Mytilus edulis L. induced by temperature and nutritive stress. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 53, 39–58 (1973)
Bayne, B. L., D. W. Klumpp and K. R. Clarke: Rates of feeding, including estimates of gut residence time, in three mytilid species (Mollusca, Bivalvia) at two contrasting sites on the Cape Peninsular, South Africa. Oecologia (In press) (1984)
Bayne, B. L. and R. C. Newell: Physiological energetics of marine molluscs. In: The Mollusca, Vol. IV. pp 407–515. Ed. by K. M. Wilbur. New York: Academic Press 1983
Bayne, B. L. and C. Scullard: Rates of nitrogen excretion by species of Mytilus (Bivalvia: Mollusca). J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 57, 355–369 (1977)
Bayne, B. L. and J. Widdows: The physiological ecology of two populations of Mytilus edulis L. Oecologia 37, 137–162 (1978)
Bremner, J. M.: Total nitrogen. In: Methods of soil analysis, pp 1149–1178. Ed. by C. A. Black. Madison: American Society of Agronomy (1965a)
Bremner, J. M.: Isotope-ratio analysis of nitrogen in nitrogen-15 tracer investigations. In: Methods of soil analysis, pp 1256–1286. Ed. by C. A. Black. Madison: American Society of Agronomy (1965b)
Bremner, J. M. and A. P. Edwards: Determination and isotoperatio analysis of different forms of nitrogen in soils: 1. Apparatus and procedure for distillation and determination of ammonium. Proc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 29, 504–507 (1965)
Bricelj, V. M., A. E. Bass and G. R. Lopez. Absorption and gut passage time of microalgae in a suspension feeder: an evaluation of the 51C:14C twin tracer technique. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 17, 57–63 (1984)
Calow, P.: The feeding strategies of two freshwater gastropods, Ancylus fluviatilis Müll. and Planorbis contortus Linn. (Pulmonata), in terms of ingestion rates and absorption efficiencies. Oecologia 20, 33–49 (1975a)
Calow, P.: Defecation strategies of two freshwater gastropods, Ancylus fluviatilis Müll. and Planorbis contortus Linn. (Pulmonata) with a comparison of field and laboratory estimates of food absorption rate. Oecologia 20, 51–63 (1975b)
Calow, P.: Ecology, evolution and energetics: a study in metabolic adaptation. Adv. ecol. Res. 10, 1–62 (1977)
Calow, P. and C. R. Fletcher: A new radiotracer technique involving 14C and 51Cr, for estimating the assimilation efficiencies of aquatic primary producers. Oecologia 9, 155–170 (1972)
Cammen, L. M.: Ingestion rate: an empirical model for aquatic deposit feeders and detritivores. Oecologia 44, 303–310 (1980)
Cassie, R. M.: Some uses of probability paper in the analysis of size frequency distributions. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 5, 513–522 (1954)
Conover, R. J.: Assimilation of organic matter by zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11, 338–345 (1966)
Conover, R. J.: Transformation of organic matter. In: Marine ecology. Vol. IV. Dynamics, pp 221–500. Ed. by O. Kinne. New York: Wiley Interscience 1978
Crisp, D. J.: Energy flow measurements. In: Methods for the study of marine benthos, pp 197–279. Ed. by N. A. Holme and A. D. McIntyre. Oxford: Blackwell 1971
Dole, M., G. A. Lane, D. P. Rudd and D. A. Zaukelies: Isotopic composition of atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 6, 65–78 (1954)
Doyle, R. W.: Ingestion rate of a selective deposit feeder in a complex mixture of particles: testing the energy-optimization hypothesis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24, 867–874 (1979)
Famme, P. and L. H. Kofoed: Rates of carbon release and oxygen uptake by the mussel, Mytilus edulis L., in response to starvation and oxygen. Mar. Biol. Lett. 3, 241–256 (1982)
Forster, J. R. M. and P. A. Gabbott: The assimilation of nutrients from compounded diets by the prawns Palaemon serratus and Pandalus platyceros. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 51, 943–961 (1971)
Foster-Smith, R. L.: The effect of concentration of suspension and inert material on the assimilation of algae by three bivalves. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 55, 411–418 (1975a)
Foster-Smith, R. L.: The effect of concentration of suspension on the filtration rates and pseudofaecal production for Mytilus edulis L., Cerastoderma edule (L.) and Venerupis pullastra (Montagu). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 17, 1–22 (1975b)
Gabbott, P. and B. L. Bayne: Biochemical effects of temperature and nutritive stress on Mytilus edulis L. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 53, 269–286 (1973)
Galkina, V. N.: Metabolites of mussels (Mytilus edulis) in the organic matter dissolved in seawater. Oceanology, Wash. 22, 90–93 (1982)
Gerdes, D.: The Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Part I. Feeding behaviour of larvae and adults. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 31, 195–219 (1983)
Griffiths, R. J.: Filtration, respiration and assimilation in the black mussel Choromytilus meridionalis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 3, 63–70 (1980)
Guillard, R. R. L. and J. H. Ryther: Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve). Can. J. Microbiol. 8, 229–239 (1962)
Hauck, R. D. and J. M. Bremner: Use of tracers for soil and fertilizer nitrogen research. Adv. Agron. 28, 219–266 (1976)
Hawkins, A. J. S., B. L. Bayne and K. R. Clarke: Co-ordinated rhythms of digestion, absorption and excretion in Mytilus edulis (Bivalvia: Mollusca). Mar. Biol. 74, 41–48 (1983)
Hawkins, A. J. S., P. N. Salkeld, B. L. Bayne, E. Gnaiger and D. M. Lowe: Feeding and resource allocation in Mytilus edulis: evidence for time-averaged optimisation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. (In press) (1984)
Holling, C. S.: The functional response of invertebrate predators to prey density. Mem. ent. Soc. Can. 48, 1–86 (1966)
Hughes, R. N.: A study of feeding in Scrobicularia plana (Da Costa). J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 49, 805–823 (1969)
Hylleberg, J. and V. F. Gallucci: Selectivity in feeding by the deposit-feeding bivalve Macoma nasuta. Mar. Biol. 32, 167–178 (1975)
Jordan, T. E. and I. Valiela: A nitrogen budget of the ribbed mussel, Geukensia demissa, and its significance in nitrogen flow in a New England salt marsh. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27, 75–90 (1982)
Junk, G. A. and H. J. Svec: Nitrogen isotope abundance measurements, 37 pp. U.S. Atomic Energy Commission: Office of Technical Information ISC-1138 (1958)
Kuenzler, E. J.: Structure and energy flow of a mussel population in a Georgia salt marsh. Limnol. Oceanogr. 6, 191–204 (1961a)
Kuenzler, E. J.: Phosphorus budget of a mussel population. Limnol. Oceanogr. 6, 400–415 (1961b)
Lowe, D. M. and R. K. Pipe: Seasonal cycles in the digestive epithelial cells of Mytilus edulis L. (In preparation)
Nash, J. C.: Compact numerical methods for computers: linear algebra and function minimisation, 227 pp. Bristol: Adam Hilger 1979
Navarro, J. M. and J. E. Winter: Ingestion rate, assimilation efficiency and energy balance in Mytilus chilensis in relation to body size and different algal concentrations. Mar. Biol. 67, 255–266 (1982)
Newell, R. I. E.: The eco-physiology of Cardium edule (Linné), 215 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of London 1977
Nose, T.: On the metabolic fecal nitrogen in young rainbow trout. Bull. Freshwat. Fish. Res. Lab., Tokyo 17, 97–105 (1967)
Palmer, R. E. and L. G. Williams: Effect of particle concentration on filtration efficiency of the bay scallop Argopecten irradians and the oyster Crassostrea virginica. Ophelia 19, 163–174 (1980)
Platt, A. M.: Studies on the digestive diverticula of Mytilus edulis L., 86 pp. Ph.D. thesis, Queens University, Belfast 1971
Preston, T. and N. J. P. Owens: Interfacing an automatic elemental analyser with an isotope ratio mass spectrometer: the potential for fully automated total nitrogen and nitrogen-15 analysis. Analyst, Lond. 108, 971–977 (1983)
San Pietro, A.: The measurement of stable isotopes. Meth. Enzym. 4, 473–488 (1957)
Sokal, R. R. and F. J. Rohlf: Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research, 776 pp. San Francisco: Freeman & Co. 1969
Taghon, G. L.: Beyond selection: optimal ingestion rate as a function of food value. Am. Nat. 118, 202–214 (1981)
Taghon, G. L.: Optimal foraging by deposit-feeding invertebrates: roles of particle size and organic coating. Oecologia 52, 295–304 (1982)
Taghon, G. L., R. F. L. Self and P. A. Jumars: Predicting particle selection by deposit feeders: a model and its implications. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 752–759 (1978)
Thompson, R. J.: The reproductive cycle and physiological ecology of the mussel Mytilus edulis in a subarctic, non-estuarine environment. Mar. Biol. 79, 277–288 (1984)
Thompson, R. J. and B. L. Bayne: Active metabolism associated with feeding in the mussel Mytilus edulis L. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 9, 111–124 (1972)
Thompson, R. J. and B. L. Bayne: Some relationships between growth, metabolism and food in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 27, 317–326 (1974)
Thompson, R. J., N. A. Ratcliffe and B. L. Bayne: Effects of starvation on structure and function in the digestive gland of the mussel (Mytilus edulis L.). J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 54, 699–712 (1974)
Tsuchiya, M.: Biodeposit production by the mussel Mytilus edulis L. on rocky shores. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 47, 203–222 (1980)
Van Weel, P. B.: The comparative physiology of digestion in molluscs. Am. Zool. 1, 245–252 (1961)
Widdows, J.: Combined effects of body size, food concentration and season on the physiology of Mytilus edulis. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 58, 109–124 (1978a)
Widdows, J.: Physiological indices of stress in Mytilus edulis. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 58, 125–142 (1978b)
Widdows, J., P. Fieth and C. M. Worrall: Relationships between seston, available food and feeding activity in the common mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 50, 195–207 (1979)
Wikander, P. B.: Quantitative aspects of deposit feeding in Abra nitida (Müller) and A. longicallus (Sacchi) (Bivalvia, Tellinacea). Sarsia 66, 35–48 (1980)
Winter, J. E.: The filtration rate of Mytilus edulis and its dependence on algal concentration, measured by a continuous automatic recording apparatus. Mar. Biol. 22, 317–328 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mauchline, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hawkins, A.J.S., Bayne, B.L. Seasonal variation in the balance between physiological mechanisms of feeding and digestion in Mytilus edulis (Bivalvia: Mollusca). Marine Biology 82, 233–240 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392404
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392404