Abstract
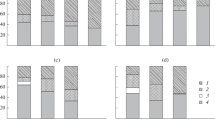
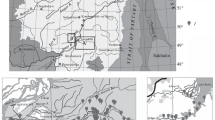
In November 1973 the benthic macrofauna of two shallow-water areas in the lower Sheepscot River estuary (New England, USA) was quantitatively sampled. Numerical classification of the data, in both the normal and inverse modes, produced 4 site-groups and 7 species-groups. Each site-group was characterized by at least one of the species-groups. The fauna of the site-groups differed in several community parameters, particularly the patterns of dominance, but it was not possible to correlate these differences with any of the several extrinsic factors measured. A factor, or factors, related to water-column stability is the probable overriding ecological determinant of the observed community patterns. Comparisons with an earlier investigation in 1955 demonstrate dramatic changes in density, dominance and species composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Barnes, R.S.K., D.B. Sattelle, I.J. Everton, W. Nicholas, and D.H. Scott: Intertidal sands and interstitial fauna associated with different stages of salt-marsh development. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 4, 497–511 (1976)
Bilyard, G.R.: The feeding habits and ecology of Dentalium entale stimpsoni, Henderson (Mollusca: Scaphopoda). Veliger 17, 126–138 (1974)
Boesch, D.F.: Application of numerical classification in ecological investigations of water pollution, 114 pp. Corvallis, Oregon: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency 1977. (Ecol. Res. Ser. EPA-600/3-77-033)
Bousfield, E.L.: Shallow-water gammaridean Amphipoda of New England, 312 pp. Ithaca, N.Y. and London: Cornell University Press 1973
Clifford, H.T. and W. Stephenson: An introduction to numerical classification. 229 pp. New York: Academic Press 1975
Dexter, R.W.: The bottom community of Ipswich Bay, Massachusetts. Ecology 25, 352–359 (1944)
—: The marine communities of a tidal inlet at Cape Ann, Massachusetts: a study in bio-ecology. Ecol. Monogr. 17, 262–294 (1947)
Dow, R.L. and D.E. Wallace: The distribution of the green crab (Carcinides maenas L.) in the northwestern Atlantic. II. Observations on green crabs (C. maenas) in Maine. Fish. Circ. Me 8, 11–15 (1952)
Gage, J.: Shallow-water zonation of sea-loch benthos and its relation to hydrographic and other physical features. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 54, 223–249 (1974)
Hanks, R.W.: A study of the macroscopic benthic fauna of an estuary on the coast of Maine, 99 pp. M.S. thesis, University of New Hampshire, Durham 1961
—: A benthic community in the Sheepscot River estuary, Maine. Fishery Bull. Fish Wildl. Serv. U.S. 63, 343–353 (1964)
Hughes, R.N. and M.L.H. Thomas: The classification and ordination of shallow-water benthic samples from Prince Edward Island, Canada. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 7, 1–39 (1971)
Kingsley, J.S.: Preliminary catalogue of marine invertebrates of Casco Bay, Maine. Proc. Portland Soc. nat. Hist. 2, 159–183 (1901)
Margalef, R.: Information theory in ecology. Gen. Syst. 3, 36–71 (1958)
Pettibone, M.H.: Marine polychaete worms of the New England region. Bull. U.S. natn. Mus. 227, 1–356 (1963)
Pielou, E.C.: An introduction to mathematical ecology, 286 pp. New York: Wiley-Interscience 1970
Procter, W.: Biological survey of the Mt. Desert region. Part 5. Marine fauna, 402 pp. Philadelphia: Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology 1933
Shepard, F.P.: Nomenclature based on sand-silt clay-ratios. J. sedim. Petrol. 24, 151–158 (1954)
Shorey, W.K.: Macrobenthic ecology of a sawdust-bearing substrate in the Penobscot River estuary (Maine). J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 30, 493–497 (1973)
Stickney, A.P.: Ecology of the Sheepscot River estuary. 21 pp. Spec. scient. Rep. U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. 309, 1–21 (1959)
Taylor, C.C., H.B. Bigelow and H.W. Graham: Climatic trends and the distribution of marine animals in New England. Fishery Bull. Fish Wildl. Serv. U.S. 57, 293–345 (1957)
Verrill, A.E.: Marine fauna of Eastport, Maine. Bull. Essex Inst. (Mass.) 3, 2–6 (1872)
—: Explorations of Casco Bay in 1873. Proc. Am. Ass. Advmt Sci. (Portland Mtg) 22, 340–395 (1874)
Warwick, R.M. and J.D. Gage: Nearshore zonation of benthic fauna, especially Nematoda, in Loch Etive. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 55, 295–311 (1975)
Watkin, E.E.: The macrofauna of intertidal sand of Kames Bay, Millport, Buteshire. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 60, 543–561 (1942)
Welch, W.R.: Changes in abundance of the green crab, Carcinus maenas (L.), in relation to recent temperature changes. Fishery Bull. Fish Wildl. Serv. U.S. 67, 337–345 (1968)
Welch, W.R.: Monthly and annual means of surface sea water temperature, Boothbay Harbor, Maine 1905 through 1978. Mimeo Rep. Maine Dept. mar. Res. 1–7 (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by I. Morris, West Boothbay Harbor
Contribution No. 78033 of the Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, P.F. The shallow-water macrobenthos of a northern New England estuary. Mar. Biol. 55, 69–78 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391719
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391719